Dijkstra 算法
目录
定义
- Dijkstra 算法本质上就是一个经过特殊改造的 BFS 算法
- 使用优先级列队而不是普通列队
- 添加了一个备忘录,记录起点到每个可达节点的最短路径权重和
使用第三种 BFS 写法来改造
第三种写法多维护了一个 State 类
多叉树的层序遍历
// 每个节点自行维护 State 类,记录深度等信息
class State {
constructor(node, depth) {
this.node = node;
this.depth = depth;
}
}
var levelOrderTraverse = function (root) {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
var q = [new State(root, 1)];
while (q.length !== 0) {
var state = q.shift();
var cur = state.node;
var depth = state.depth;
// 访问 cur 节点,同时知道它所在的层数
console.log("depth = " + depth + ", val = " + cur.val);
for (var i = 0; i < cur.children.length; i++) {
var child = cur.children[i];
q.push(new State(child, depth + 1));
}
}
};
图的 BFS 遍历
// 图结构的 BFS 遍历,从节点 s 开始进行 BFS,且记录路径的权重和
// 每个节点自行维护 State 类,记录从 s 走来的权重和
class State {
constructor(node, weight) {
// 当前节点 ID
this.node = node;
// 从起点 s 到当前节点的权重和
this.weight = weight;
}
}
var bfs = function (graph, s) {
var visited = new Array(graph.size()).fill(false);
var q = [new State(s, 0)];
visited[s] = true;
while (q.length !== 0) {
var state = q.shift();
var cur = state.node;
var weight = state.weight;
console.log("visit " + cur + " with path weight " + weight);
var neighbors = graph.neighbors(cur);
for (var i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) {
var e = neighbors[i];
if (!visited[e.to]) {
q.push(new State(e.to, weight + e.weight));
visited[e.to] = true;
}
}
}
};
更多请参考 5. 图的 BFS 遍历
Dijkstra 算法原理
函数签名
var dijkstra = function(start, graph) {
// 输入一幅图和一个起点 start,计算 start 到其他节点的最短距离
// code
}
// 节点 `3` 作为起点到其他节点的最小路径和数组
// 从起点 `3` 到节点 `6` 的最短路径权重和就是 `distTo[6]`
let distTo = dijkstra(3, graph);
State 类
function State(id, distFromStart) {
// 图节点的 id
this.id = id;
// 从 start 节点到当前节点的距离
this.distFromStart = distFromStart;
}
distTo 记录最短路径:备忘录
加权图中的 Dijkstra 算法和无权图中的普通 BFS 算法不同
- 在 Dijkstra 算法中,你第一次经过某个节点时的路径权重,不见得就是最小的
- 所以对于同一个节点,我们可能会经过多次,而且每次的
distFromStart可能都不一样,比如下图
- 所以对于同一个节点,我们可能会经过多次,而且每次的
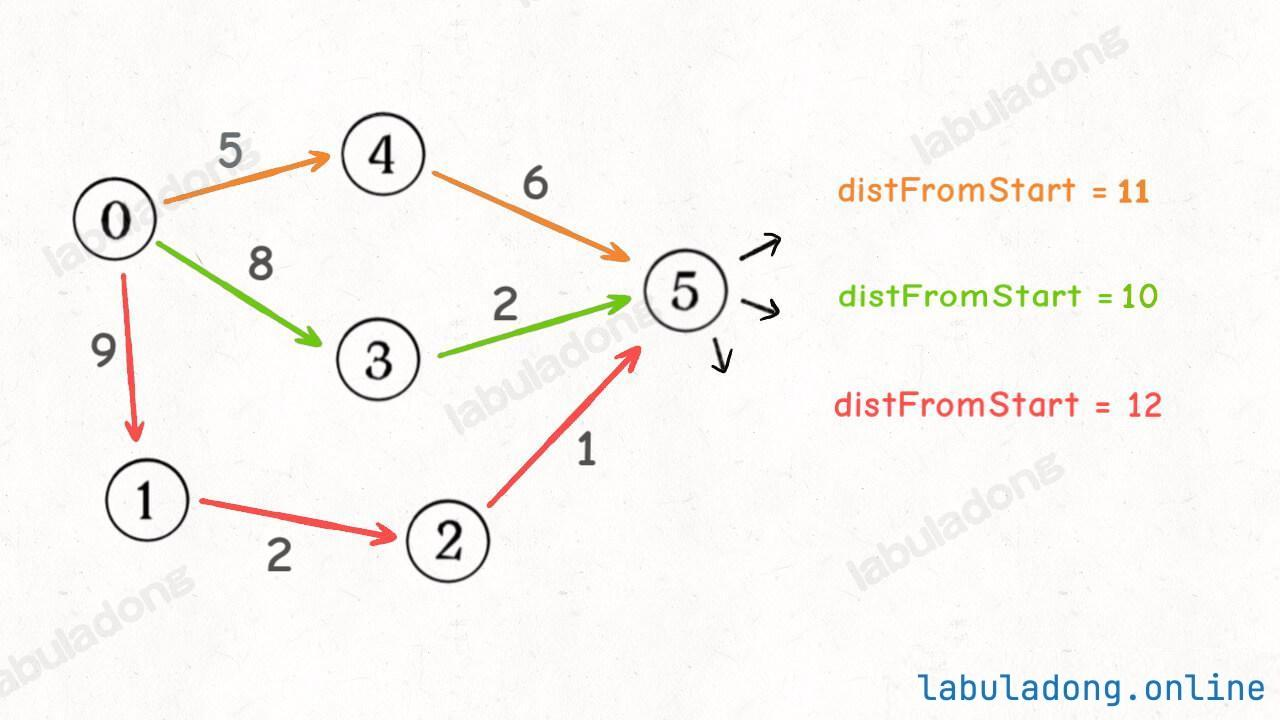
- 我会经过节点
5三次,每次的distFromStart值都不一样 - 那我取
distFromStart最小的那次,不就是从起点start到节点5的最短路径权重了么? - 所以我们需要一个
distTo数组来记录从起点start到每个节点的最短路径权重和,起到一个==备忘录==的作用。 - 当重复遍历到同一个节点时,我们可以比较一下当前的
distFromStart和distTo中的值,- 如果当前的更小,就更新
distTo, - 反之,就==不用再往后继续遍历==了
- 如果当前的更小,就更新
代码模板
/**
* Dijkstra 算法模板
* @param {number} n - 节点数量
* @param {number[][]} edges - 边的信息 [from, to, weight]
* @param {number} start - 起点
* @returns {number[]} 从起点到所有节点的最短距离
*/
function dijkstra(n, edges, start) {
// 1. 构建邻接表
const graph = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [from, to, weight] of edges) {
// 如果是无向图,需要双向添加
graph[from].push([to, weight]);
// graph[to].push([from, weight]); // 无向图时取消注释
}
// 2. start 到 0 - n 的最短路径权重
const dist = new Array(n).fill(Infinity);
// 自己到自己最短距离为 0
dist[start] = 0;
// 3. 优先队列 [distance, node]
// distance: 从 start 到 node 的最短距离
// node: 节点编号
const pq = [0, start](/post/1Wwo7hp4.html#0,-start);
while (pq.length) {
// 取出当前最短距离的节点
const [d, cur] = pq.shift();
// 如果当前距离大于已知距离,跳过
if (d > dist[cur]) continue;
// 遍历所有相邻节点
for (const [item, weight] of graph[cur]) {
const newDist = dist[cur] + weight;
// 如果找到更短的路径
if (newDist < dist[item]) {
dist[item] = newDist;
// 插入优先队列(保持队列按距离排序)
let inserted = false;
for (let i = 0; i < pq.length; i++) {
if (pq[i][0] > newDist) {
pq.splice(i, 0, [newDist, item]);
inserted = true;
break;
}
}
if (!inserted) pq.push([newDist, item]);
}
}
}
return dist;
}