Redux
#react
目录
- 1. 总结
- 2. 与 Flux 的关系
- 3. Redux 的核心原则
- 4. Redux 核心概念
- 5. 基本使用流程
- 6. Redux 工具链
- 7. 最佳实践
- 8. Redux 原理
- 9. 性能优化
- 10. Redux Hooks
- 11. 调试工具
- 12. 选择建议
- 13. 总结
- 14. Redux 处理异步接口有多种方案
1. 总结
- 异步方案
- redux-saga
- redux-thunk 函数
- redux-tooltik (没用过)
- Redux 是 Flux 架构的一个演进和改进版本
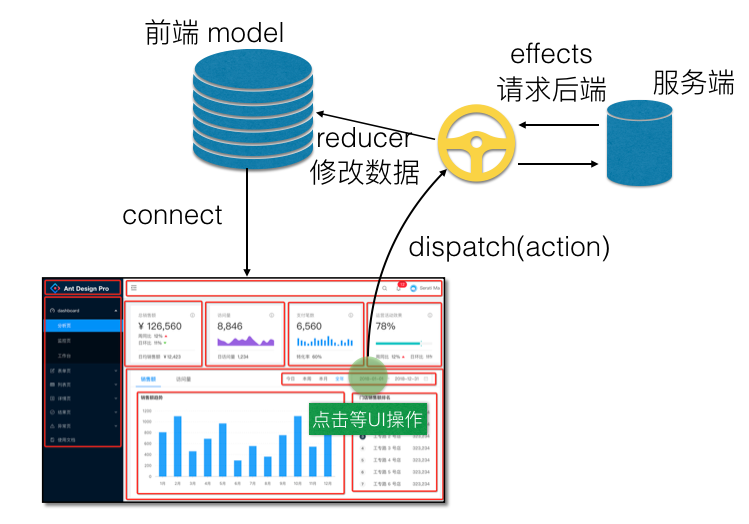
- umi 的数据流
- store 、action、state、reducer 的关系
- store 中存放了所有的状态
state,要想改变里面的状态 state,只能 dispatch 一个动作- 发出去的
action需要用reducer来处理,传入 state 和 action,返回新的state
- 发出去的
- store 中存放了所有的状态
2. 与 Flux 的关系
Flux:
- 单向数据流
- 多个 Store
- Dispatcher 是核心
- Store 之间可能存在依赖关系 Redux:
- 单向数据流
- 单一 Store:单一的 Store 存储所有状态
- Reducer 是核心
- 使用纯函数更新状态
Redux 是 Flux 架构的一个演进和改进版本。它通过引入单一数据源、纯函数更新和不可变性等概念,使得状态管理更加可预测和易于维护
3. Redux 的核心原则
- 单一数据源(Single Source of Truth)
- 整个应用的状态存储在单个 store 的对象树中
- 使状态可预测且易于调试
- 支持服务器端渲染
- 状态是只读的(State is Read-only)
唯一改变状态的方式是触发 action- 所有的状态更新都是集中化和顺序化的
- 确保视图和网络请求不能直接修改状态
- 使用纯函数进行修改(Changes are made with Pure Functions)
- Reducers 必须是纯函数
- 给定相同的输入,总是返回相同的输出
- 不产生副作用
4. Redux 核心概念
4.1. 先总结
- createStore
- 创建 store 对象,包含 getState、dispatch、subscribe、replaceReducer
- reducer
- 纯函数,接受旧的 state、action,生成新的 state
- action
- 动作,是一个对象,必须包括 type 字段,表示 view 发出通知告诉 store 要改变
- dispatch
- 派发,触发 action ,生成新的 state。是 view 发出 action 的唯一方法
- subscribe
- 订阅,只有订阅了,当派发时,会执行订阅函数
- combineReducers
- 合并 reducer 成一个 reducer
- replaceReudcer
- 代替 reducer 的函数
- middleware
- 中间件,扩展 dispatch 函数
4.2. Store
- 整个应用的状态树
- 是只读的
- 只能通过触发 action 来修改
import { createStore } from 'redux'
const store = createStore(reducer)
- 保存状态的容器
- 提供
getState()方法访问状态 - 提供
dispatch(action)方法更新状态 - 提供
subscribe(listener)方法注册监听器
4.3. Action
-
描述发生了什么的
普通对象 -
必须包含 type 属性
-
可以携带额外数据
// 普通 action const addTodo = { type: ‘ADD_TODO’, payload: { text: ‘学习 Redux’ } }
// action creator const addTodo = (text) => ({ type: ‘ADD_TODO’, payload: { text } })
### 3.4. Reducer
- 指定状态如何变化的纯函数
- 接收旧状态和 action,返回新状态
- 不应直接修改旧状态
```javascript
const todoReducer = (state = [], action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'ADD_TODO':
return [...state, action.payload];
case 'REMOVE_TODO':
return state.filter(todo => todo.id !== action.payload.id);
default:
return state;
}
}
5. 基本使用流程
5.1. 创建 Store
import { createStore } from 'redux';
const store = createStore(reducer);
5.2. 订阅更新
store.subscribe(() => {
console.log('Store updated:', store.getState());
});
5.3. 触发 Action
store.dispatch(addTodo('学习 Redux'));
6. Redux 工具链
6.1. Redux Toolkit(推荐使用)
-
简化样板代码
-
内置 Immer
-
更好的开发体验
import { createSlice, configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'; const todoSlice = createSlice({ name: 'todos', initialState: [], reducers: { addTodo: (state, action) => { state.push(action.payload); }, removeTodo: (state, action) => { return state.filter(todo => todo.id !== action.payload.id); } } }); const store = configureStore({ reducer: { todos: todoSlice.reducer } });
6.2. Redux Middleware
- 处理异步操作
- 日志记录
- 错误处理
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
const store = createStore(
reducer,
applyMiddleware(thunk)
)
6.2.1. 比如日志中间件
// 日志中间件示例
const logger = store => next => action => {
console.log('dispatching', action);
let result = next(action);
console.log('next state', store.getState());
return result;
};
7. 最佳实践
7.1. State 结构设计
-
将状态扁平化
-
避免冗余数据
-
规范化复杂数据结构
-
避免冗余数据
-
合理划分 state 树
-
使用范式化数据结构
-
避免深层嵌套
const state = { entities: { todos: { byId: { 1: { id: 1, text: '学习 Redux' }, 2: { id: 2, text: '学习 React' } }, allIds: [1, 2] }, users: { // ... } }, ui: { loading: false, error: null } };
7.2. Action 设计原则
// 使用 action creator
const createUser = (user) => ({
type: 'CREATE_USER',
payload: user
})
// 使用常量定义 action types
const ActionTypes = {
CREATE_USER: 'CREATE_USER',
UPDATE_USER: 'UPDATE_USER'
}
- 使用动词+名词的命名方式
- 携带最小必要信息
- 使用标准化的结构
- 避免在一个 action 中包含多个操作
- 保持 action 的原子性
- 使用 action creator 统一创建
- 考虑使用 action 类型常量
7.3. Reducer 设计原则
- 保持纯函数特性
- 避免副作用
- 使用 combineReducers 拆分
- 使用 immer 简化不可变更新
- 保持纯函数特性
- 避免修改 state 参数
- 处理好未知的 action type
- 合理拆分 reducer
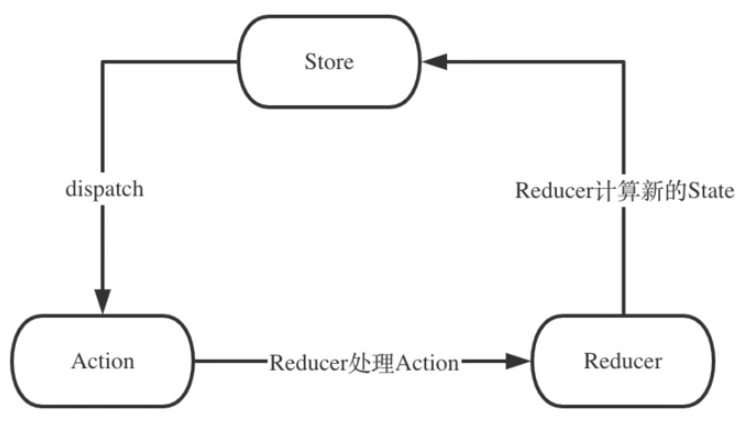
8. Redux 原理
8.1. 数据流向
- 单向数据流
- 可预测的状态变化
- 便于调试和测试
Action -> Dispatcher -> Store -> View
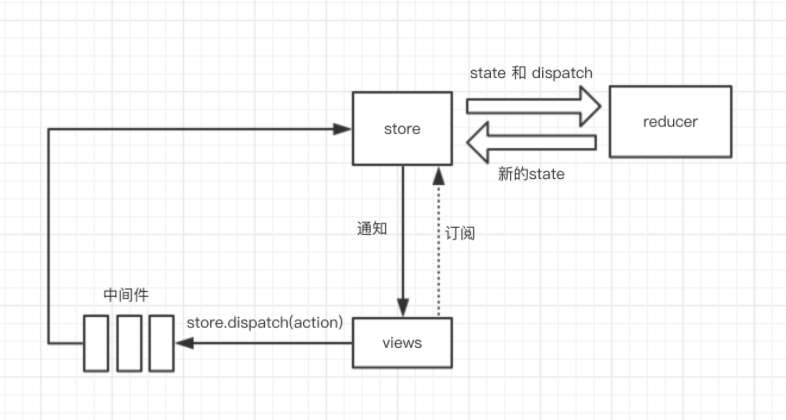
8.2. 发布订阅模式
-
通过发布订阅模式实现
-
状态更新触发监听器
-
确保状态同步更新
function createStore(reducer) { let state; let listeners = [];
const getState = () => state;
const dispatch = (action) => {
state = reducer(state, action);
listeners.forEach(listener => listener());
};
const subscribe = (listener) => {
listeners.push(listener);
return () => {
listeners = listeners.filter(l => l !== listener);
};
};
dispatch({}); // 初始化 state
return { getState, dispatch, subscribe };
}
### 8.3. 中间件实现原理
```javascript
function applyMiddleware(...middlewares) {
return (createStore) => (reducer, preloadedState) => {
const store = createStore(reducer, preloadedState);
let dispatch = store.dispatch;
const middlewareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (action) => dispatch(action)
};
const chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI));
dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch);
return {
...store,
dispatch
};
};
}
9. 性能优化
9.1. Reselect 使用
import { createSelector } from 'reselect';
const getTodos = state => state.todos;
const getFilter = state => state.filter;
const getVisibleTodos = createSelector(
[getTodos, getFilter],
(todos, filter) => {
switch (filter) {
case 'SHOW_COMPLETED':
return todos.filter(todo => todo.completed);
case 'SHOW_ACTIVE':
return todos.filter(todo => !todo.completed);
default:
return todos;
}
}
);
9.2. 避免不必要的渲染
// 使用 React.memo 或 shouldComponentUpdate
const TodoItem = React.memo(({ todo, onToggle }) => {
return (
<li onClick={() => onToggle(todo.id)}>
{todo.text}
</li>
);
});
9.3. 其他
- 避免频繁的
dispatch - 使用
reselect缓存计算结果 - 避免不必要的组件渲染
- 合理使用 connect 或 hooks
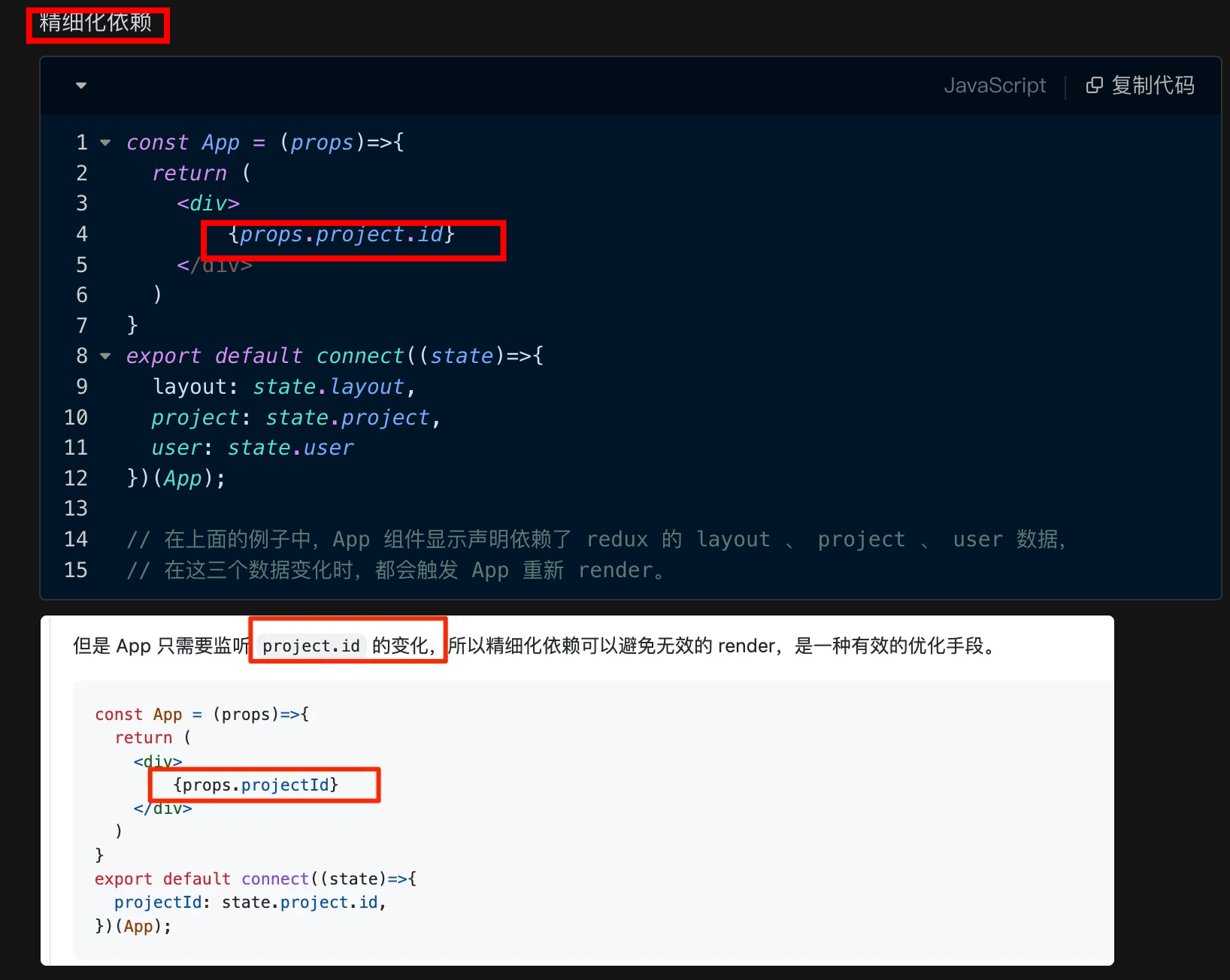
- 精细化依赖
10. Redux Hooks
10.1. useSelector
import { useSelector } from 'react-redux';
function TodoList() {
const todos = useSelector(state => state.todos);
return (
<ul>
{todos.map(todo => (
<TodoItem key={todo.id} {...todo} />
))}
</ul>
);
}
10.2. useDispatch
import { useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
function AddTodo() {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
return (
<button onClick={() => dispatch(addTodo('新任务'))}>
添加任务
</button>
);
}
11. 调试工具
11.1. Redux DevTools
const store = createStore(
reducer,
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ &&
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
);
11.2. 日志中间件
import { createLogger } from 'redux-logger';
const store = createStore(
reducer,
applyMiddleware(createLogger())
);
12. 选择建议
对于小型项目,可能使用 React 的 Context API 或其他更轻量级的状态管理方案会更合适。
13. 总结
- Redux 是状态管理库,也是一个架构
- Redux 与 React 无关,但它是为了解决 React 组件中状态无法共享而出的一种解决方案
- 单纯的 Redux 只是一个状态机, store 中存放了所有的状态 state,要想改变里面的状态 state,只能 dispatch 一个动作
- 发出去的 action 需要用 reducer 来处理,传入 state 和 action,返回新的 state
- subscribe 方法可以注册回调方法,当 dispatch action 的时候会执行里面的回调
- Redux 其实是一个
发布订阅模式 - Redux 支持
enhancer,enhancer 其实就是一个装饰器函数,传入当前的 createStore,返回一个增强的 createStore - Redux 使用
applyMiddleware函数支持中间件,它的返回值其实就是一个 enhancer - Redux 的中间件也是一个装饰器模式,传入当前的 dispatch,返回一个增强了的 dispatch
- 单纯的 Redux 是没有 View 层的
14. Redux 处理异步接口有多种方案
14.1. Redux Thunk
最基础且使用广泛的异步处理方案。
14.1.1. 基本设置
// store.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
const store = createStore(rootReducer, applyMiddleware(thunk));
14.1.2. 使用示例
// userActions.js
const fetchUserRequest = () => ({ type: 'FETCH_USER_REQUEST' });
const fetchUserSuccess = (user) => ({ type: 'FETCH_USER_SUCCESS', payload: user });
const fetchUserFailure = (error) => ({ type: 'FETCH_USER_FAILURE', payload: error });
// Thunk action creator
export const fetchUser = (userId) => {
return async (dispatch, getState) => {
try {
dispatch(fetchUserRequest());
const response = await fetch(`/api/users/${userId}`);
const data = await response.json();
dispatch(fetchUserSuccess(data));
} catch (error) {
dispatch(fetchUserFailure(error.message));
}
};
};
// userReducer.js
const initialState = {
loading: false,
user: null,
error: null
};
const userReducer = (state = initialState, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'FETCH_USER_REQUEST':
return { ...state, loading: true };
case 'FETCH_USER_SUCCESS':
return { loading: false, user: action.payload, error: null };
case 'FETCH_USER_FAILURE':
return { loading: false, user: null, error: action.payload };
default:
return state;
}
};
14.1.3. 组件中使用
import { useEffect } from 'react';
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux';
import { fetchUser } from './userActions';
function UserProfile({ userId }) {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const { user, loading, error } = useSelector(state => state.user);
useEffect(() => {
dispatch(fetchUser(userId));
}, [dispatch, userId]);
if (loading) return <div>Loading...</div>;
if (error) return <div>Error: {error}</div>;
if (!user) return null;
return <div>{user.name}</div>;
}
14.2. Redux Saga
更强大的异步处理方案,使用 Generator 函数处理复杂的异步流程。
14.2.1. 基本设置
// store.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga';
import rootSaga from './sagas';
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware();
const store = createStore(rootReducer, applyMiddleware(sagaMiddleware));
sagaMiddleware.run(rootSaga);
14.2.2. 使用示例
// userSaga.js
import { call, put, takeLatest } from 'redux-saga/effects';
function* fetchUser(action) {
try {
yield put({ type: 'FETCH_USER_REQUEST' });
const response = yield call(fetch, `/api/users/${action.payload}`);
const data = yield call([response, 'json']);
yield put({ type: 'FETCH_USER_SUCCESS', payload: data });
} catch (error) {
yield put({ type: 'FETCH_USER_FAILURE', payload: error.message });
}
}
export function* userSaga() {
yield takeLatest('FETCH_USER', fetchUser);
}
// rootSaga.js
import { all } from 'redux-saga/effects';
import { userSaga } from './userSaga';
export default function* rootSaga() {
yield all([
userSaga(),
]);
}
14.2.3. 组件中使用
function UserProfile({ userId }) {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const { user, loading, error } = useSelector(state => state.user);
useEffect(() => {
dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_USER', payload: userId });
}, [dispatch, userId]);
// 渲染逻辑...
}
14.3. Redux Toolkit (推荐)
Redux 官方推荐的工具集,简化了 Redux 的使用,内置了 Thunk 中间件。
14.3.1. 基本设置
// store.js
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import userReducer from './userSlice';
export const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
user: userReducer,
},
});
14.3.2. 使用示例
// userSlice.js
import { createSlice, createAsyncThunk } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
export const fetchUser = createAsyncThunk(
'user/fetchUser',
async (userId, { rejectWithValue }) => {
try {
const response = await fetch(`/api/users/${userId}`);
const data = await response.json();
return data;
} catch (error) {
return rejectWithValue(error.message);
}
}
);
const userSlice = createSlice({
name: 'user',
initialState: {
loading: false,
user: null,
error: null,
},
reducers: {},
extraReducers: (builder) => {
builder
.addCase(fetchUser.pending, (state) => {
state.loading = true;
})
.addCase(fetchUser.fulfilled, (state, action) => {
state.loading = false;
state.user = action.payload;
state.error = null;
})
.addCase(fetchUser.rejected, (state, action) => {
state.loading = false;
state.user = null;
state.error = action.payload;
});
},
});
export default userSlice.reducer;
14.3.3. 组件中使用
import { useEffect } from 'react';
import { useDispatch, useSelector } from 'react-redux';
import { fetchUser } from './userSlice';
function UserProfile({ userId }) {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const { user, loading, error } = useSelector(state => state.user);
useEffect(() => {
dispatch(fetchUser(userId));
}, [dispatch, userId]);
// 渲染逻辑...
}
14.4. 最佳实践建议
-
选择合适的方案
- 简单项目:Redux Toolkit
- 复杂异步流程:Redux Saga
- 特殊需求:考虑 Redux Observable
-
错误处理
// 统一的错误处理
const handleApiError = (error) => {
if (error.response?.status === 401) {
// 处理未授权
dispatch(logout());
}
return error.message;
};
// 在异步 action 中使用
export const fetchUser = createAsyncThunk(
'user/fetchUser',
async (userId, { rejectWithValue }) => {
try {
const response = await fetch(`/api/users/${userId}`);
const data = await response.json();
return data;
} catch (error) {
return rejectWithValue(handleApiError(error));
}
}
);
- Loading 状态管理
// 创建通用的 loading selector
const createLoadingSelector = (actions) => (state) =>
actions.some(action => state.loading[action]);
// 使用
const isLoading = useSelector(createLoadingSelector(['FETCH_USER', 'FETCH_POSTS']));
- 请求缓存
// 缓存管理
const userSlice = createSlice({
name: 'user',
initialState: {
cache: {},
ttl: 5 * 60 * 1000, // 5分钟缓存
},
reducers: {
updateCache: (state, action) => {
state.cache[action.payload.id] = {
data: action.payload.data,
timestamp: Date.now(),
};
},
},
});
// 使用缓存
export const fetchUserWithCache = createAsyncThunk(
'user/fetchWithCache',
async (userId, { getState, dispatch }) => {
const state = getState();
const cached = state.user.cache[userId];
if (cached && Date.now() - cached.timestamp < state.user.ttl) {
return cached.data;
}
const response = await fetch(`/api/users/${userId}`);
const data = await response.json();
dispatch(userSlice.actions.updateCache({ id: userId, data }));
return data;
}
);
- 取消请求
// Redux Toolkit 方式
export const fetchUser = createAsyncThunk(
'user/fetchUser',
async (userId, { signal }) => {
const response = await fetch(`/api/users/${userId}`, { signal });
const data = await response.json();
return data;
}
);
// 组件中使用
useEffect(() => {
const promise = dispatch(fetchUser(userId));
return () => {
promise.abort();
};
}, [userId]);
- TypeScript 支持
// 定义类型
interface User {
id: number;
name: string;
}
interface UserState {
loading: boolean;
user: User | null;
error: string | null;
}
// 在 slice 中使用
const userSlice = createSlice({
name: 'user',
initialState: {
loading: false,
user: null,
error: null,
} as UserState,
// ...
});
这些方案各有特点,建议:
- 新项目优先使用 Redux Toolkit
- 需要处理复杂异步流程时考虑 Redux Saga
- 注意做好错误处理和加载状态管理
- 适当使用缓存优化性能
- 考虑请求取消的场景
- 使用 TypeScript 增加类型安全