JavaScript 异步编程:Promise 专题篇二
#javascript
目录
- 1. 实现 mergePromise 函数,把传进去的数组按顺序先后执行,并且把返回的数据先后放到数组 data 中
- 2. promise中 then 的返回值情况分析
- 3. Promise 相关问题
- 4. await 没报错就会往下走,别和 promise 搞混了
- 5. 如何顺序执行 10 个任务
- 6. 如何解决 promise.all 有一个任务报错了,其他任务结果都抛弃了?
- 7. promise.finally 实现
- 8. promise then 的第二个参数和 catch 的区别是什么?
- 9. 说出下面代码的执行顺序
- 10. 下面代码的执行顺序
- 11. promise的兼容性:es6
- 12. Vue 的 nextTick 如何实现的?
- 13.
async和await的串行并行问题 - 14. 假设本地机器无法做加减乘除法,需要通过远程请求让服务端来实现
- 15. 在循环中使用 async、await 的注意事项
- 16. 一个经典的循环与闭包的问题
- 17. 最后来一段代码的执行顺序
- 18. 同级的先清空,然后再到下一级
- 19. 如何中断 promise
1. 实现 mergePromise 函数,把传进去的数组按顺序先后执行,并且把返回的数据先后放到数组 data 中
关键点:
let promise = Promise.resolve();- arr.foreach
- promise = promise.then(fn).then((res) => {
- return data;
- 返回方便下面的 then 接着接受该变量处理
- return data;
- promise = promise.then(fn).then((res) => {
好像之前面试碰到过
区别于 Promise.all,Promise.all 是并行执行,而这里需要串行执行,注意下面使用 promise.resolve 包装了
// mergePromise 函数,把传进去的数组按顺序先后执行,并且把返回的数据先后放到数组 data 中
mergePromise([ajax1, ajax2, ajax3]).then((data) => {
console.log("done");
console.log(data); // data 为 [1, 2, 3]
});
function mergePromise(arr) {
// 在这里写代码
const data = [];
let promise = Promise.resolve();
// 依次执行传入的函数
// 这里的 promise.then 是为了保证顺序执行
arr.forEach((fn) => {
// 每次遍历时,promise 都是上一个 promise.then 返回的 promise
// 但是,这里 promise 不会被覆盖吗?
// 不会,因为 promise.then 返回的是一个新的 promise
promise = promise.then(fn).then((res) => {
data.push(res);
// 返回 res 保证下一个 then 中的 res 是上一个的结果
return data;
});
});
}
使用 for - of
/**
* 串行执行 Promise 任务的函数
* @param {Array<() => Promise>} tasks - Promise 任务数组
* @returns {Promise<Array>} 所有任务的结果数组
*/
async function serialPromise(tasks) {
const results = [];
for (const task of tasks) {
try {
const result = await task();
results.push(result);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Task failed:", error);
throw error;
}
}
return results;
}
const tasks = [
() => new Promise(...),
() => new Promise(...),
() => new Promise(...)
];
const results = await serialPromise(tasks);
2. promise中 then 的返回值情况分析
所以上面那题,foreach 串行执行的道理了吗?
// 1. 返回普通值
console.log('=== 示例1: 返回普通值 ===');
Promise.resolve(1)
.then(value => {
console.log('第一个then:', value); // 1
return 2; // 返回普通值
})
.then(value => {
console.log('第二个then:', value); // 2
});
// 2. 返回 Promise
console.log('\n=== 示例2: 返回 Promise ===');
Promise.resolve('开始')
.then(value => {
console.log('第一个then:', value); // "开始"
return Promise.resolve('Promise的结果');
})
.then(value => {
console.log('第二个then:', value); // "Promise的结果"
});
// 3. 返回 thenable 对象
console.log('\n=== 示例3: 返回 thenable 对象 ===');
Promise.resolve('开始')
.then(value => {
console.log('第一个then:', value); // "开始"
return {
then: function(resolve) {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('thenable对象的结果');
}, 1000);
}
};
})
.then(value => {
console.log('第二个then:', value); // "thenable对象的结果"
});
// 4. 抛出错误
console.log('\n=== 示例4: 抛出错误 ===');
Promise.resolve('开始')
.then(value => {
console.log('第一个then:', value); // "开始"
throw new Error('发生错误');
})
.then(
value => {
console.log('第二个then:', value); // 不会执行
},
error => {
console.log('错误处理:', error.message); // "发生错误"
}
);
// 5. 链式调用中的值传递
console.log('\n=== 示例5: 链式调用中的值传递 ===');
Promise.resolve('初始值')
.then(value => {
console.log('第一个then:', value); // "初始值"
return value + ' -> 追加1';
})
.then(value => {
console.log('第二个then:', value); // "初始值 -> 追加1"
return value + ' -> 追加2';
})
.then(value => {
console.log('第三个then:', value); // "初始值 -> 追加1 -> 追加2"
});
3. Promise 相关问题
3.1. finnaly:无论失败或者成功都会执行,且不接受结果
3.2. 注意顺序
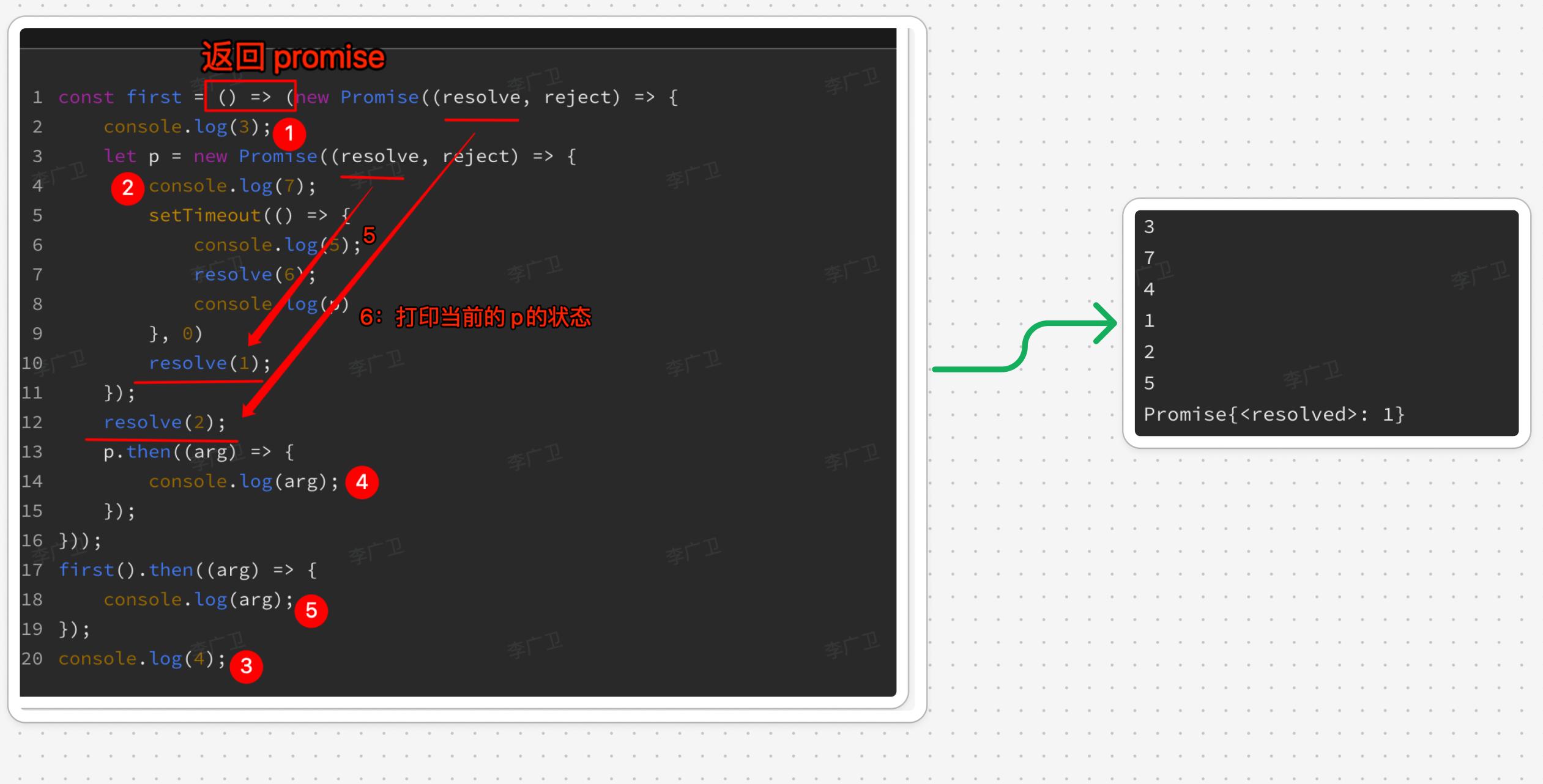
3.3. reject 包在 try 里面也会被捕获到
async function asyncl() {
try {
await Promise.reject("error!!!");
} catch (e) {
console.log(e); // 会执行到
}
}
asyncl();
3.3.1. 没有捕获会报错
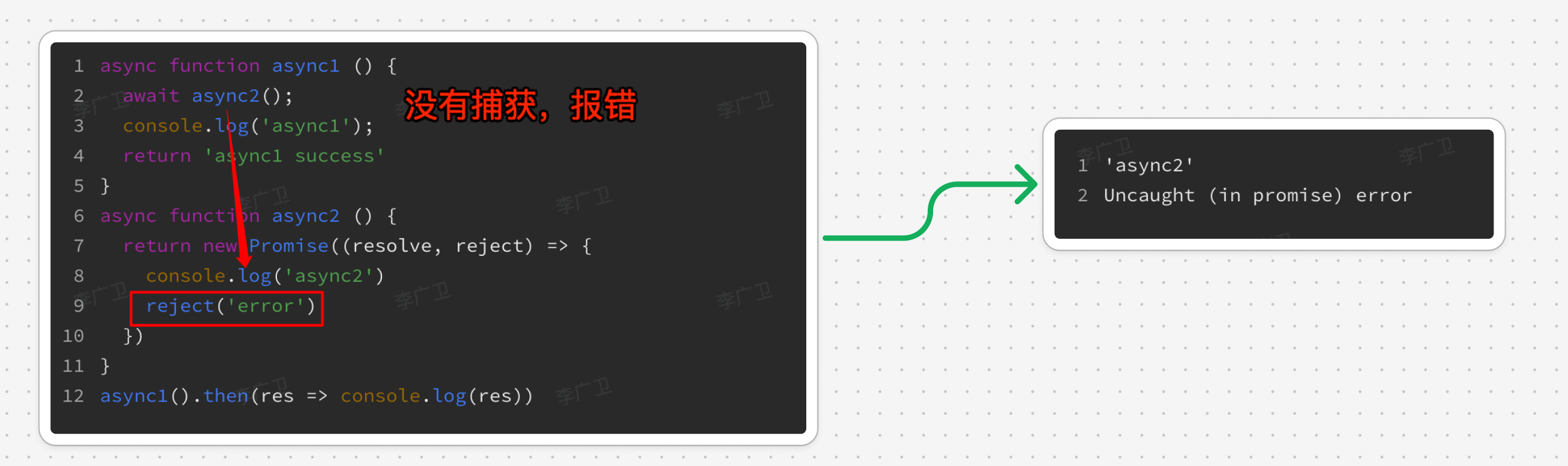
3.4. Promise 未捕获的错误并不会中断代码执行
async function a1() {
await a2();
console.log("a1");
return "a1 success!";
}
async function a2() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log("a2");
reject("err");
});
}
a1().then((res) => {
console.log(res);
});
console.log("test..."); // 正常执行,并不会因为 Promise的错误而中断执行
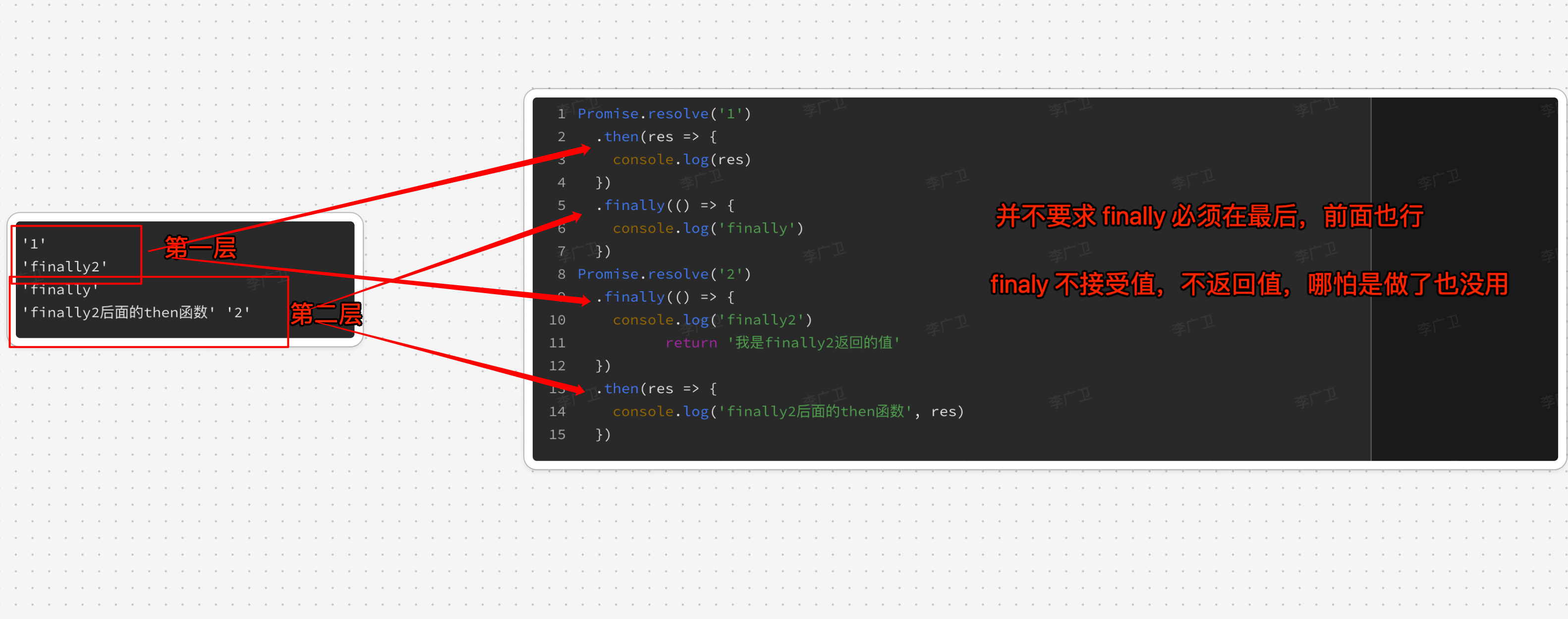
3.5. then 和 .catch 返回的值不能使 promise 对象本身,否则会死循环
4. await 没报错就会往下走,别和 promise 搞混了
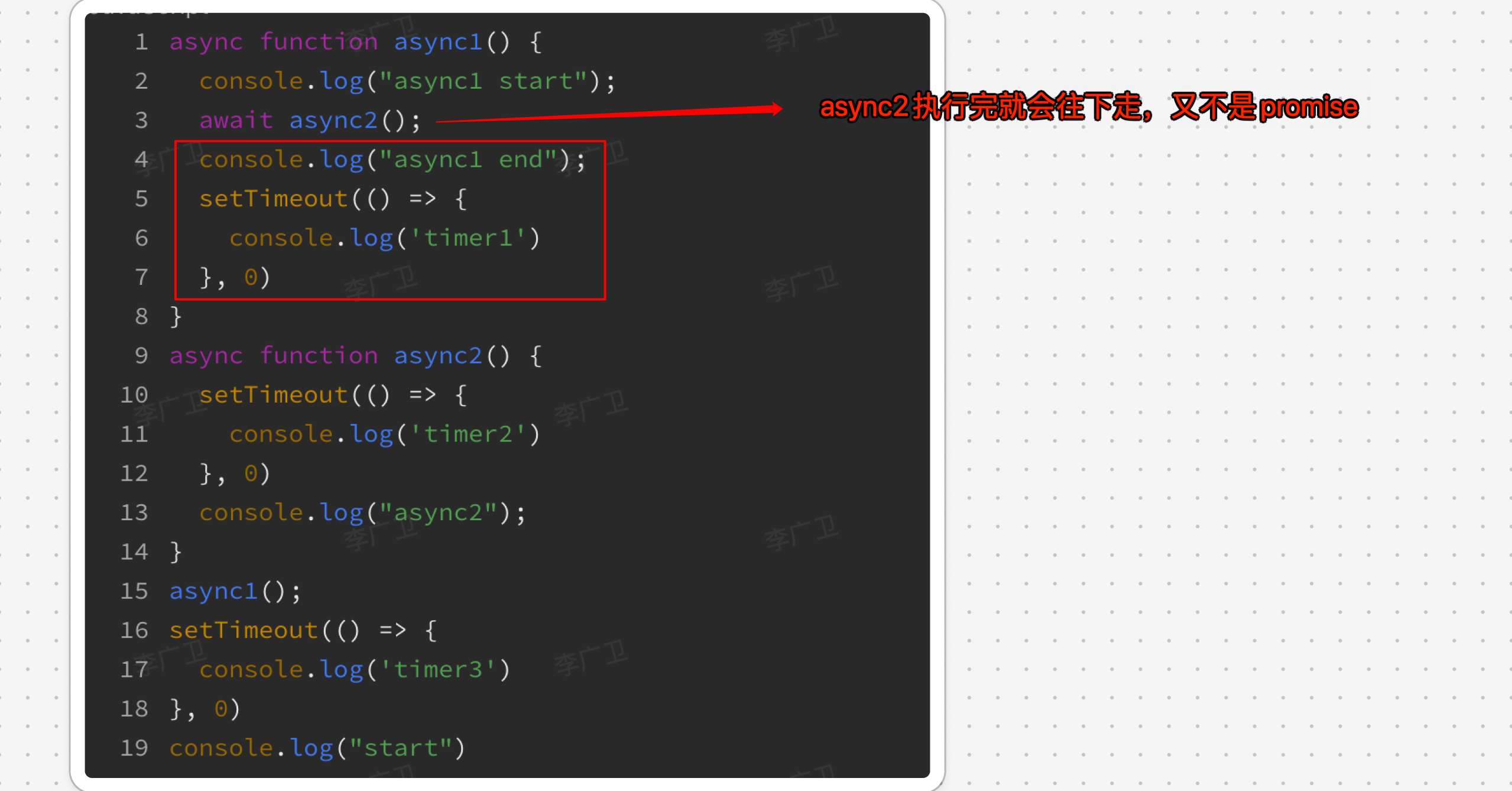
因为 如果 async 函数没有显式的返回值,它仍然会返回一个 Promise,具体行为如下:
// 没有 return 语句
async function noReturn() {
console.log("Hello");
}
// 等价于返回 Promise<undefined>
console.log(noReturn()); // Promise {<fulfilled>: undefined}
// 空 return 语句
async function emptyReturn() {
console.log("Hello");
return;
}
// 同样返回 Promise<undefined>
console.log(emptyReturn()); // Promise {<fulfilled>: undefined}
// 即使函数体为空
async function empty() {}
console.log(empty()); // Promise {<fulfilled>: undefined}
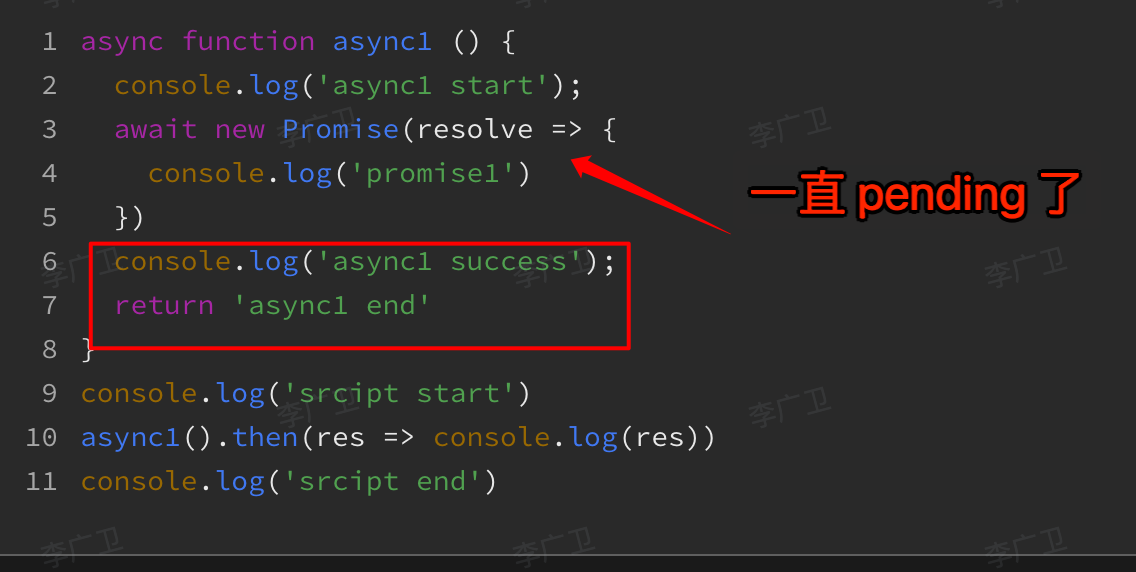
4.1. 下面的代码就一直会 pengding 住了
5. 如何顺序执行 10 个任务
- 方法一:for/for-of - await
- 方法二:reduce,两个参数
- prev task(累加值)
- current task
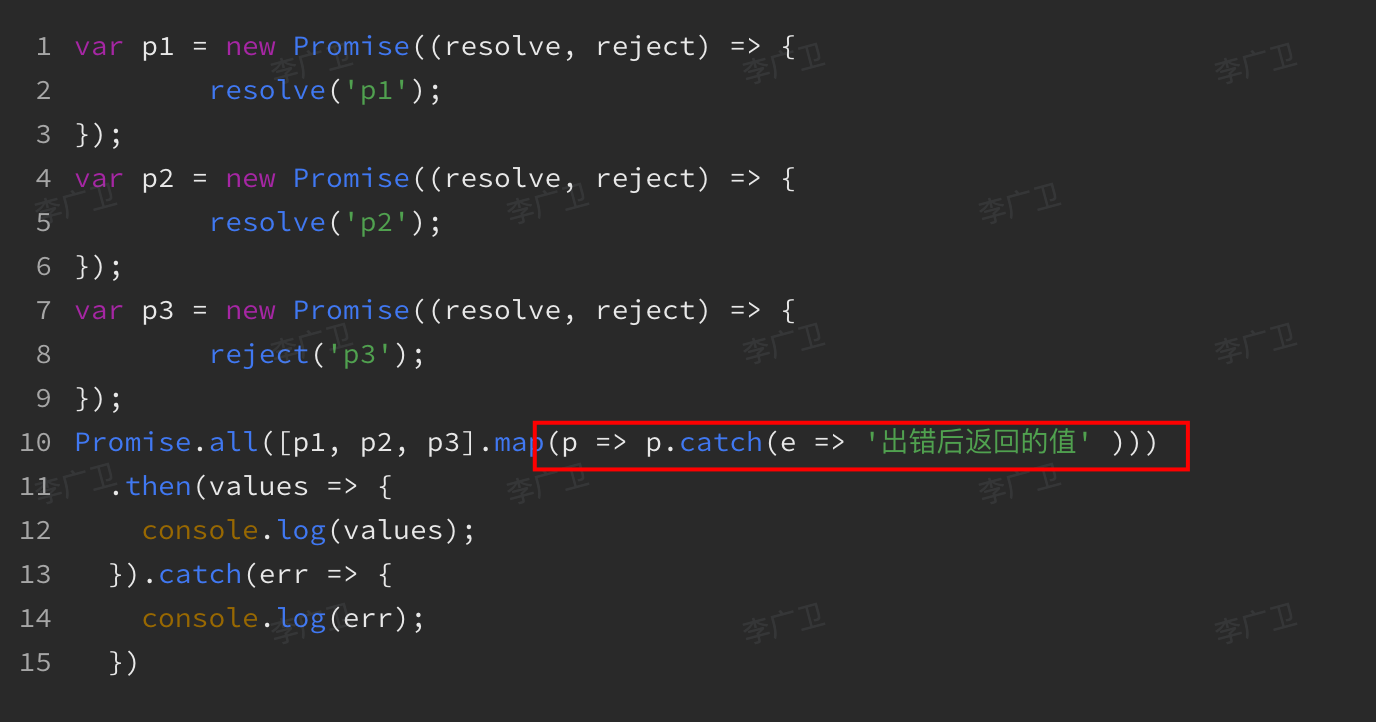
6. 如何解决 promise.all 有一个任务报错了,其他任务结果都抛弃了?
- 方案一:promise.allSetteled
- 方案二:容错下,别让
promise报错 - 方案三:
7. promise.finally 实现
- p = this.contrucotor
即再加一个
then而已

8. promise then 的第二个参数和 catch 的区别是什么?
8.1. 错误捕获范围
.then(onFulfilled, onRejected)的第二个参数 (onRejected):- 只能捕获在当前
Promise对象中发生的错误。 - 不能捕获 onFulfilled 函数(第一个参数)中抛出的错误。
- 只能捕获在当前
.catch(onRejected):- 可以捕获在链式调用中前面所有 Promise 产生的错误。
- 也可以捕获前面
.then()中 onFulfilled 函数里抛出的错误。
8.2. 代码示例
// 使用 .then() 的第二个参数
promise
.then(
result => {
console.log(result);
throw new Error('Error in onFulfilled'); // 这个错误 不会被捕获
},
error => {
console.error('Error caught by second argument of then:', error);
}
);
// 使用 .catch()
promise
.then(result => {
console.log(result);
throw new Error('Error in onFulfilled');
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error caught by catch:', error); // 这里可以捕获上面抛出的错误
});
8.3. 链式调用中的行为
.then()的第二个参数:- 在链式调用中,每个
.then()都可以有自己的错误处理函数。 - 如果一个
.then()的第二个参数处理了错误,错误不会继续传播。
- 在链式调用中,每个
.catch():- 通常放在 Promise 链的末尾,可以捕获整个链中的任何错误。
- 更符合“先执行所有操作,最后统一处理错误“的模式。
8.4. 代码可读性
.catch()通常提供更好的代码可读性,特别是在处理多个 Promise 的链式调用时。- 使用
.catch()可以将错误处理逻辑集中在一处- 而不是分散在每个
.then()中。
- 而不是分散在每个
8.5. 示例对比
// 使用 .then() 的第二个参数
somePromise
.then(result => processResult(result), error => handleError(error))
.then(newResult => furtherProcess(newResult), error => handleAnotherError(error));
// 使用 .catch()
somePromise
.then(result => processResult(result))
.then(newResult => furtherProcess(newResult))
.catch(error => handleAllErrors(error));
8.6. 最佳实践
- 通常推荐使用
.catch()而不是.then()的第二个参数- 除非你有特定原因需要在某个特定的 Promise 中单独处理错误。
- 在复杂的 Promise 链中,可以在关键点使用
.catch(),然后继续链式调用,这样可以进行更细粒度的错误控制。
8.7. 注意事项
.catch()本身返回一个新的 Promise,如果.catch()中没有抛出错误,后续的.then()仍会被调用。- 如果在
.catch()中抛出新的错误,可以被后续的.catch()捕获。- catch 后面还是会被新的 catch 再捕获
8.8. 总结
.then()的第二个参数适用于需要对特定Promise的错误进行精确处理的情况。.catch()更适合全局错误处理,提供了更好的链式调用错误处理能力和代码可读性。- 在实际开发中,
.catch()使用更为普遍,因为它更灵活且能处理更广泛的错误情况。

9. 说出下面代码的执行顺序
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("1");
Promise.resolve().then(function () {
console.log("2");
});
}, 0);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("3");
Promise.resolve().then(function () {
console.log("4");
});
}, 0);
// 1 2 3 4
// nodejs 12 以上 和 浏览器一样
10. 下面代码的执行顺序
setTimeout 和 setImmediate 都是宏任务
- setTimeout 通常会先于
setImmediate执行 - 但如果涉及到 I/O 操作,
setImmediate这更快执行,- 因为 setImmediate 总是在 I/O 操作之后执行
setImmediate(function () {
console.log(6);
});
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(7);
}, 0);
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("7-1s");
}, 1);
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("7-2s");
}, 2);
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("7-4s");
}, 4);
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("7-100s");
}, 100);
console.log(1);
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log(4);
});
new Promise(function (resolve, rejected) {
console.log(2);
resolve();
}).then((res) => {
console.log(5);
});
console.log(3);
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 5
// 7
// 7-1s
// 7-2s
// 7-4s
// 6
// 7-100s
下面代码就会很稳定的输出,因为代码会进入 I/O callback阶段,然后check阶段,再然后是timers阶段
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('test.js', () => {
setTimeout(() => console.log(1));
setImmediate(() => console.log(2));
});
// 2 1
11. promise的兼容性:es6
12. Vue 的 nextTick 如何实现的?
由于 Vue 的异步更新策略,如果我们在修改数据后立即操作 DOM,可能会得到更新前的旧 DOM。nextTick 提供了一种机制,确保我们的代码在 DOM 更新后执行
所以当数据发生变化时,Vue 不会立即更新 DOM,而是将更新操作推入一个队列中,这种做法可以提高性能
- 当响应式数据发生变化时,Vue 会将更新操作放入异步队列
- nextTick 会创建一个 Promise,确保回调在 DOM 更新后执行
- 多个 nextTick 会被合并到同一个 Promise 中
Vue会尝试使用原生的 Promise.then、MutationObserver 和 setImmediate,如果执行环境不支持,则会采用setTimeout(fn, 0) 代替
nextTick 的核心思想:利用 JavaScript 的事件循环,将回调推迟到 下一个"tick"执行
// 一个简单的 nextTick 实现
// 用于存储回调函数的数组
let callbacks = [];
// 代表是否正在执行回调
let pending = false;
function nextTick(cb) {
callbacks.push(cb);
if (!pending) {
pending = true;
// 使用setTimeout来调度一个刷新操作
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0);
}
}
// flushCallbacks函数负责执行所有的回调
function flushCallbacks() {
pending = false;
const copies = callbacks.slice(0);
callbacks.length = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < copies.length; i++) {
copies[i]();
}
}
// 使用示例
nextTick(() => {
console.log("这是在下一个tick执行的回调");
});
console.log("这是同步代码");
13. async和await的串行并行问题
async function main() {
// 串行
var name1 = await foo();
// 这里会等待foo执行完后在执行
var name2 = await bar();
// 并行
var [name1, name2] = await Promise.all([foo(), bar()]);
// 并行
var foo2 = foo();
var bar2 = bar();
var name1 = await foo2;
var name2 = await bar2;
}
14. 假设本地机器无法做加减乘除法,需要通过远程请求让服务端来实现
- 并行请求
- 记得缓存云端结果
// 假设本地机器无法做加减乘除法,需要通过远程请求让服务端来实现
// 本地模拟远程请求
async function addRemote(a, b) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(a + b);
}, 1000);
});
}
// 基本实现
async function add(...args) {
let res = 0;
// base case
if (args.length === 0) return res;
if (args.length === 1) return args[0];
for (const item of args) {
res = await addRemote(res, item);
}
return res;
}
// 优化 1:分组并行请求
async function add(...args) {
let res = 0;
// base case
if (args.length === 0) return res;
if (args.length === 1) return args[0];
const tasks = [];
for (const item of args) {
tasks.push(addRemote(res, item));
}
const values = await Promise.all(tasks);
values.forEach((value) => {
res += value;
});
return res;
}
// 优化 2:缓存请求,减少请求次数
async function add(...args) {
let res = 0;
// base case
if (args.length === 0) return res;
if (args.length === 1) return args[0];
const cache = new Map();
for (const item of args) {
if (cache.has(item)) {
res = cache.get(item);
} else {
res = await addRemote(res, item);
cache.set(item, res);
}
}
return res;
}
15. 在循环中使用 async、await 的注意事项
forEach不能很好地与async/await配合使用,因为它不会等待异步操作完成;- 如果一定使用,注意使用立即执行函数包装
map可以配合Promise.all使用for...of是在循环中使用 async/await 最自然和推荐的方式while循环可以很好地与 async/await 配合使用for...in主要用于遍历对象的可枚举属性,一般不用,如果使用,注意使用立即执行函数包装- 传统的
for 循环也可以与 async/await 一起使用 - 使用
filter,完全没用,因为回调返回都是promise对象,都为true
16. 一个经典的循环与闭包的问题
// 可能出现问题的代码
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
setTimeout(async () => {
await someAsyncOperation(i);
}, 1000);
}
// 修正后的代码,使用 let,不使用 var
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
setTimeout(async () => {
await someAsyncOperation(i);
}, 1000);
}
17. 最后来一段代码的执行顺序
async function async1() {
console.log("2");
await async2();
console.log("9");
}
async function async2() {
console.log("3");
}
console.log(1);
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("11");
}, 0);
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("13");
}, 300);
setImmediate(() => console.log("12"));
process.nextTick(() => console.log("7"));
async1();
process.nextTick(() => console.log("8"));
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log("4");
resolve();
console.log("5");
}).then(function () {
console.log("10");
});
console.log("6");
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
18. 同级的先清空,然后再到下一级
// 111
// 222
// 333
// 444
// 555
// 666
// 777
// :::: 同级的先清空,然后再到下一级
new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(666);
new Promise(resolve => {
resolve();
}).then(() => {
console.log(777);
})
})
resolve();
}).then(() => {
new Promise(resolve => {
resolve(); // 所以继续执行111 、 222
}).then(() => {
console.log('111');
}).then(() => {
console.log('222');
});
}).then(() => {
new Promise((resolve) => {
resolve()
}).then(() => {
// ::::又多了一层
new Promise((resolve) => {
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log(444)
})
}).then(() => {
console.log(555);
})
}).then(() => {
console.log(333);
})
19. 如何中断 promise
promise 一旦创建,是无法终止,但以下几种方式可以中断
- then 中抛错
- then 返回一个新的 Promise,且已知是 pending 状态,也算是中断了
- 总之:在合适的时候,把 pending 的状态给 reject 也就中断了