二叉堆
#数据结构/二叉堆 #堆 #二叉堆
目录
- 1. 堆、大顶堆、小顶堆的定义
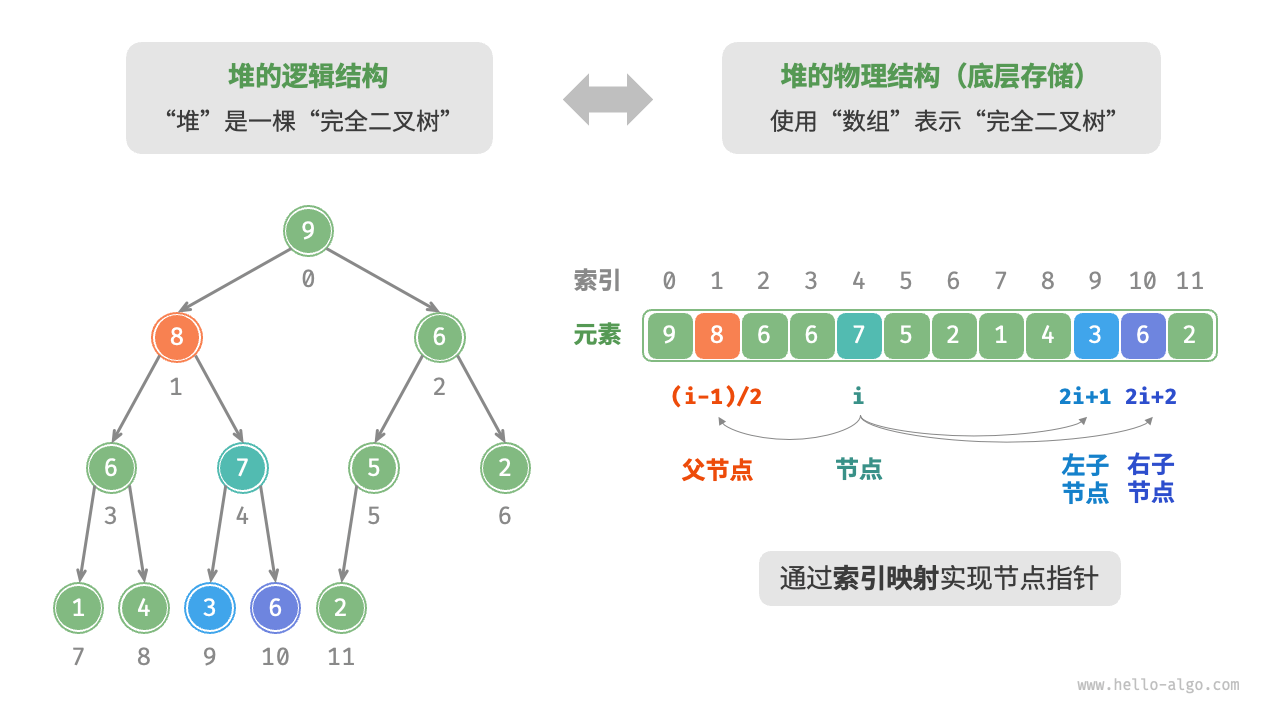
- 2. 堆的存储结构表示
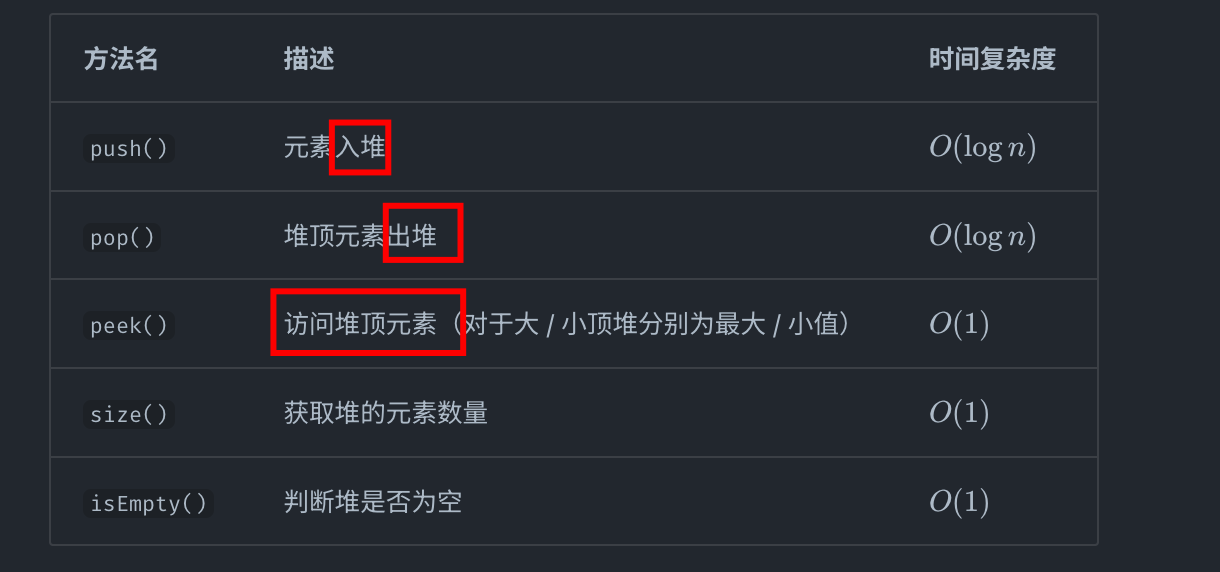
- 3. 堆的各个操作的复杂度
- 4. 堆的应用场景(或价值)
- 5. 代价
- 6. Python 中的标准库 heapq
- 7. 实现一个小顶堆:JavaScript 描述
- 堆的使用场景
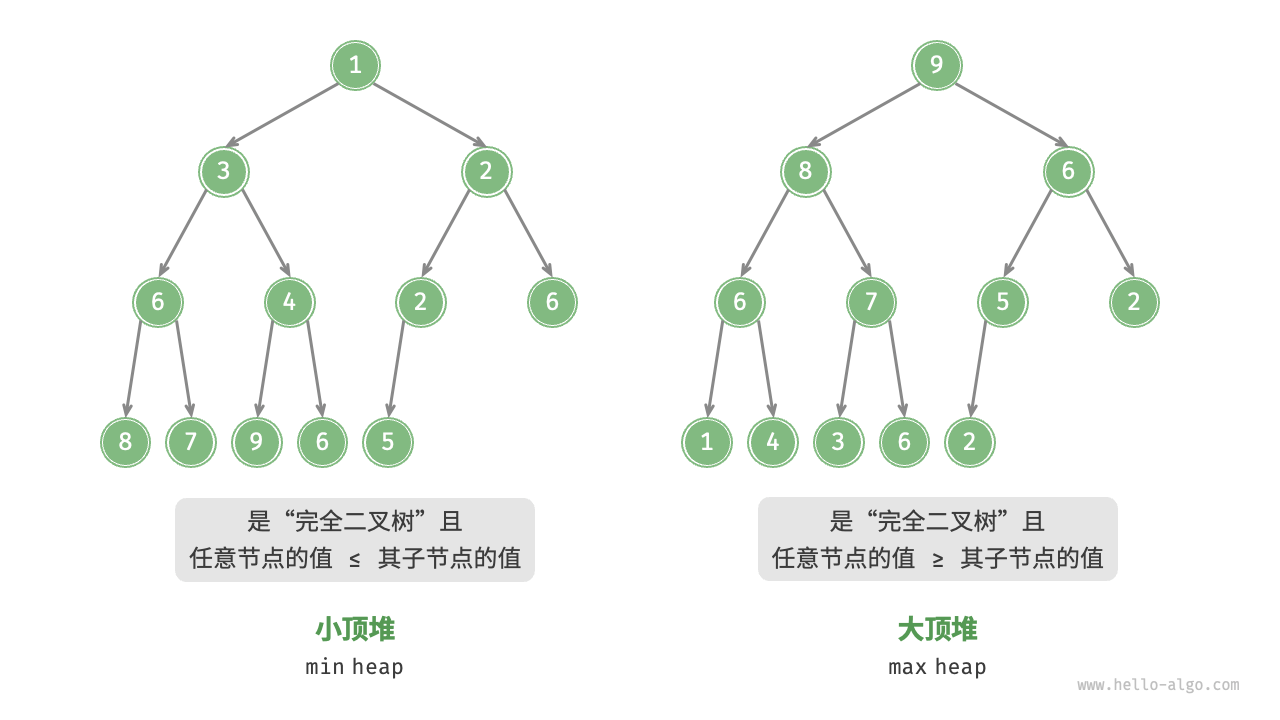
1. 堆、大顶堆、小顶堆的定义
堆是一个完全二叉树,是一种能够动态排序的数据结构
堆中每个节点的值都大于等于(或者小于等于)其左右子节点的值- 大的再上面,
大顶堆,所以堆顶肯定是最大值 - 小的再上面,
小顶堆,所以堆顶肯定是最小值
- 大的再上面,
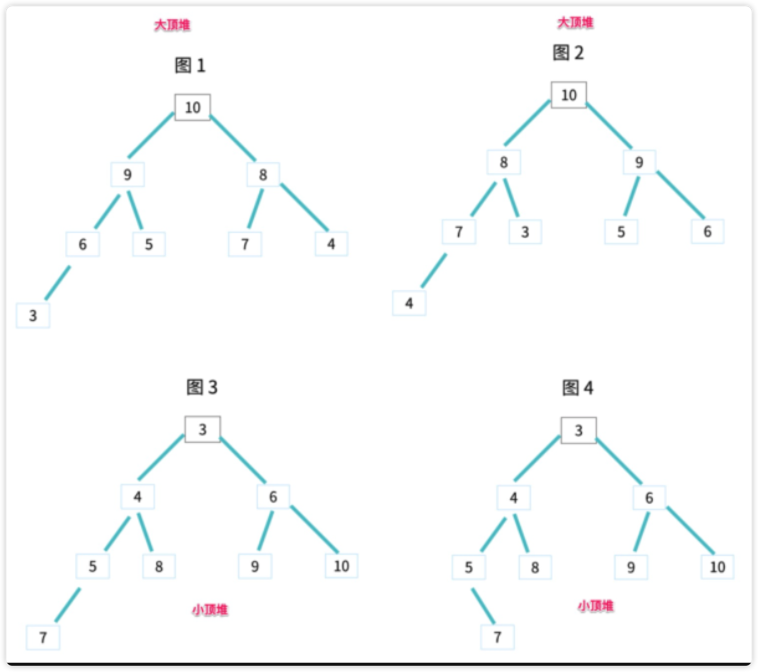
2. 堆的存储结构表示
3. 堆的各个操作的复杂度
4. 堆的应用场景(或价值)
- 堆排序
- 大顶堆的价值
- 优先队列
- 高效排序
- 高效的动态中位数
- 小顶堆的价值
- 优先队列:小顶堆也常用于实现优先队列,支持快速获取和删除最小元素。
- 图算法:在图算法中,小顶堆用于实现 Dijkstra 最短路径算法和 Prim 最小生成树算法,以快速找到权重最小的边或路径。
- 合并有序列表:小顶堆可以高效地合并多个有序列表,例如用于外部排序或归并排序
- 堆的总体价值
- 高效的插入和删除操作:堆支持
O(log n)的插入和删除操作,使其在需要频繁调整元素顺序的场景中非常高效。 - 内存利用率高:堆是一种基于数组实现的数据结构,内存利用率高,不需要额外的指针或链接。
- 广泛应用:堆在各种算法和系统中有广泛应用,包括调度系统、内存管理、图算法、实时数据处理等。
- 高效的插入和删除操作:堆支持
总之,堆结构因其高效的插入、删除和查找操作,在许多需要维护动态有序集合的场景中具有重要价值。
5. 代价
自动排序是有代价的,注意优先级队列 API 的时间复杂度,增删元素的复杂度是 O(logN),其中 N 是当前二叉堆中的元素个数
6. Python 中的标准库 heapq
heapq 模块中提供。heapq 模块实现了最小堆(min heap)算法,但通过一些技巧也可以用来实现最大堆(max heap)。
以下是关于 Python 的 heapq 模块的一些关键信息:
6.1. 导入方式
import heapq
6.2. 主要函数
heapq.heapify(list): 将列表转换为堆heapq.heappush(heap, item): 将元素添加到堆中heapq.heappop(heap): 弹出并返回堆中最小的元素heapq.heappushpop(heap, item): 将 item 放入堆中,然后弹出并返回堆中最小的元素heapq.heapreplace(heap, item): 弹出并返回堆中最小的元素,然后将 item 放入堆中heapq.nlargest(n, iterable, key=None): 返回 iterable 中 n 个最大的元素heapq.nsmallest(n, iterable, key=None): 返回 iterable 中 n 个最小的元素
6.3. 使用示例
import heapq
# 创建一个堆
heap = []
heapq.heappush(heap, 4)
heapq.heappush(heap, 1)
heapq.heappush(heap, 7)
heapq.heappush(heap, 3)
print(heap) # 输出:[1, 3, 7, 4]
# 弹出最小元素
smallest = heapq.heappop(heap)
print(smallest) # 输出:1
print(heap) # 输出:[3, 4, 7]
# 将列表转换为堆
list = [4, 6, 8, 1, 2, 9]
heapq.heapify(list)
print(list) # 输出:[1, 2, 8, 4, 6, 9]
# 获取最大的3个元素
print(heapq.nlargest(3, list)) # 输出:[9, 8, 6]
# 获取最小的3个元素
print(heapq.nsmallest(3, list)) # 输出:[1, 2, 4]
6.4. 使用 heapq 实现最大堆
由于 heapq 默认实现的是最小堆,如果需要最大堆,可以通过以下方式来实现
import heapq
# 使用 heapq 实现最大堆
class MaxHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.heap = []
def push(self, val):
heapq.heappush(self.heap, -val)
def pop(self):
# heapq 默认实现的是最小堆,所以取相反数
return -heapq.heappop(self.heap)
def peek(self):
# 三元表达式,如果 heap 不为空,返回 heap[0],否则返回 None
# 格式为:value_if_true if condition else value_if_false
# 格式为:为真时的返回值 if 判定条件 else 为假时的返回值
# return -self.heap[0] if self.heap else None
if self.heap:
return -self.heap[0]
else:
return None
def size(self):
return len(self.heap)
# 使用示例
max_heap = MaxHeap()
max_heap.push(3)
max_heap.push(1)
max_heap.push(4)
max_heap.push(2)
print(max_heap.pop()) # 输出: 4
print(max_heap.pop()) # 输出: 3
print(max_heap.peek()) # 输出: 2
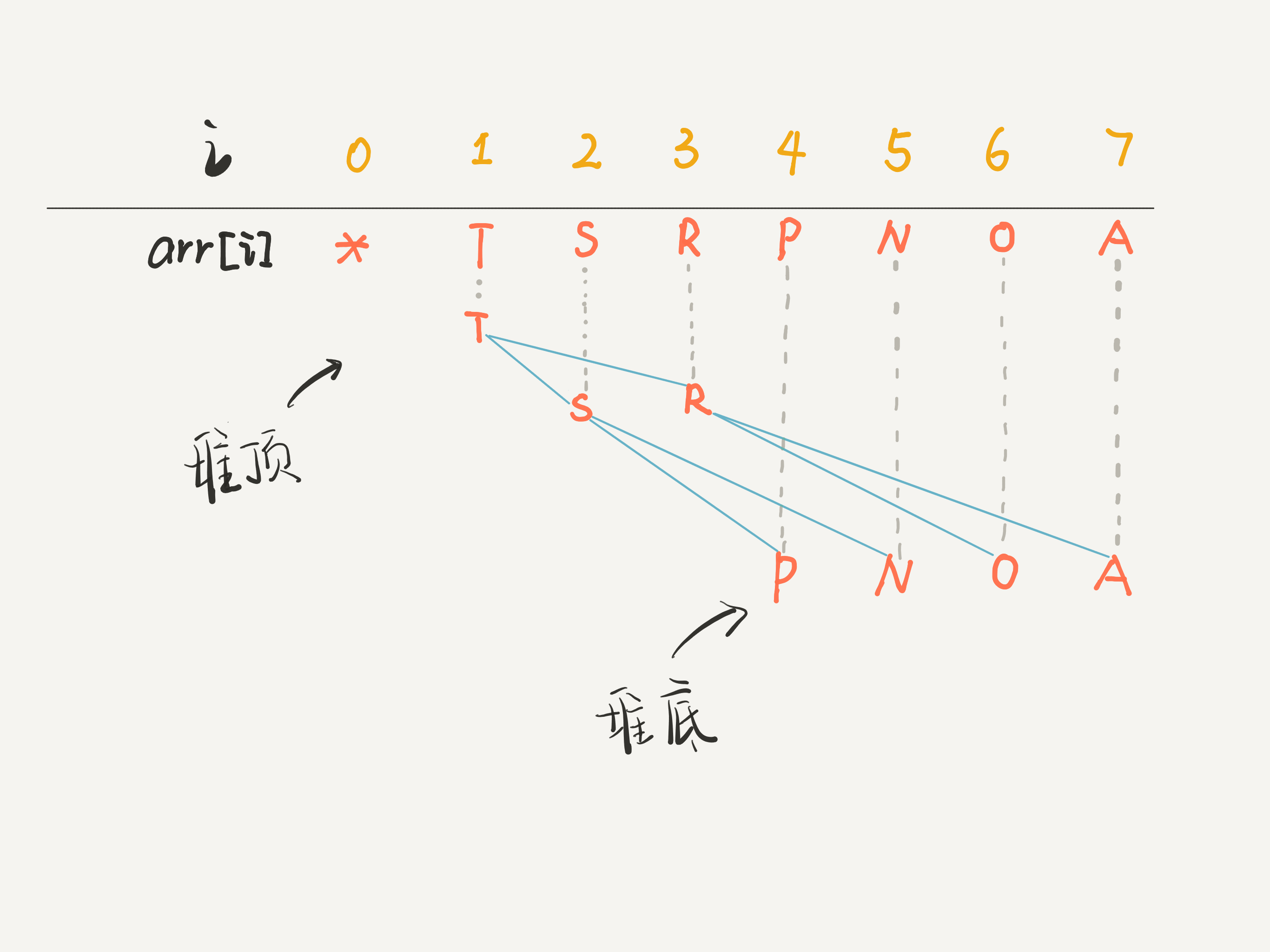
7. 实现一个小顶堆:JavaScript 描述
使用数组来存储,因为二叉堆是个完全二叉树,如下tu:
[!danger] 注意下面代码的高亮部分
function swap(array, a, b) {
[array[a], array[b]] = [array[b], array[a]];
}
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
// 使用数组来存储
this.heap = [];
}
// 获取左孩子的索引
getLeftIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 1;
}
// 获取右孩子的索引
getRightIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 2;
}
// 父节点的索引
getParentIndex(index) {
if (index === 0) {
return 0;
}
return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
}
// 返回个数
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() <= 0;
}
clear() {
this.heap = [];
}
// ::::小顶堆,最小的肯定在最上面
findMinimum() {
return this.isEmpty() ? null : this.heap[0];
}
// 插入一个值,插入的元素添加到堆底的最后,然后让其上浮到正确位置(如果大顶的话)
insert(value) {
if (value != null) {
const index = this.heap.length;
// 先放在最后一位
this.heap.push(value);
// 向上移动,直到父节点小于插入的值
this.shiftUp(index);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* @description 下沉,堆化,递归
* @param {number} index, 插入的元素的位置, 这个位置是指 数组的索引
*/
shiftDown(index) {
// 插入的元素的位置
let pos = index;
const left = this.getLeftIndex(index);
const right = this.getRightIndex(index);
const size = this.size();
if (
left < size && // 如果左子节点小于数组的长度,说明有左子节点
this.heap[pos] > this.heap[left] // 如果该元素大于它的左子节点,则下沉,即 pos = left
) {
pos = left;
}
if (
right < size && // 如果右子节点小于数组的长度,说明有右子节点
this.heap[pos] > this.heap[right] // 如果该元素大于它的右子节点,则下沉
) {
pos = right;
}
// 如果 pos 最后 和传入的index不一样了,说明需要交换数据,然后继续下沉递归
if (index !== pos) {
swap(this.heap, index, pos);
this.shiftDown(pos);
}
}
/**
* @description 上浮,堆化,递归:向上移动,直到父节点的值小于插入的值
* @param {number} index, 插入的元素的位置, 这个位置是指 数组的索引
*/
shiftUp(index) {
let parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index);
while (
index > 0 && // index必须大于0,因为根节点的父节点是自己
this.heap[parentIndex] > this.heap[index] // 父节点的元素大于子元素的时候,才需要移动
) {
swap(this.heap, parentIndex, index);
// 交换后,继续向上移动
index = parentIndex;
parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index);
// 以下是错误的写法 需要注意,因为这是在 while 循环中,所以不需要递归,被递归影响了
// 这是 while 循环,不是递归
// 这是 while 循环,不是递归
// // 交换后,继续向上移动,传入的index变成了父节点的索引
// this.getParentIndex(parentIndex);
}
}
// delete min 堆顶元素(最小值)和 堆底元素 对调
// 1、删除删除堆顶元素
// 2、让堆底元素替换到堆顶
// 3、然后从堆顶开始下沉
deleteMin() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
if (this.size() === 1) {
return this.heap.shift();
}
const removedValue = this.heap[0]; // 堆顶元素
const lastElement = this.heap.pop(); // 移除堆底元素
this.heap[0] = lastElement; // 将 堆顶元素 赋值为 堆底元素
// 从堆顶开始下沉
this.shiftDown(0);
return removedValue;
}
getAsArray() {
return this.heap;
}
}
let arr = [5, 3, 7, 9, 0, 0, -1, -2, 7, -8];
let heapObj = new MinHeap();
arr.forEach((item) => {
heapObj.insert(item);
});
console.log(heapObj);
console.log("************************");
console.log(heapObj.findMinimum());
堆的使用场景
- 优先队列:堆通常作为实现优先队列的首选数据结构,其入队和出队操作的时间复杂度均为 O(logn) ,而建堆操作为 O(n) ,这些操作都非常高效。
- 堆排序:给定一组数据,我们可以用它们建立一个堆,然后不断地执行元素出堆操作,从而得到有序数据。然而,我们通常会使用一种更优雅的方式实现堆排序,详见“堆排序”章节。
- 获取最大的 k 个元素:这是一个经典的算法问题,同时也是一种典型应用,例如选择热度前 10 的新闻作为微博热搜,选取销量前 10 的商品等。