React Hooks 的原理
#react
目录
1. 数据结构
- Hooks 的状态存储在
Fiber 节点的memoizedState属性中 - React 使用
链表结构来存储 Hooks 状态: - 每个 Hook 节点包含:
- 当前状态:
state - 更新队列:
queue,存储多次更新行为 - 依赖项(对于 useEffect 等)
- next:指向下一个 Hook 的指针
- 当前状态:
1.1. 示例
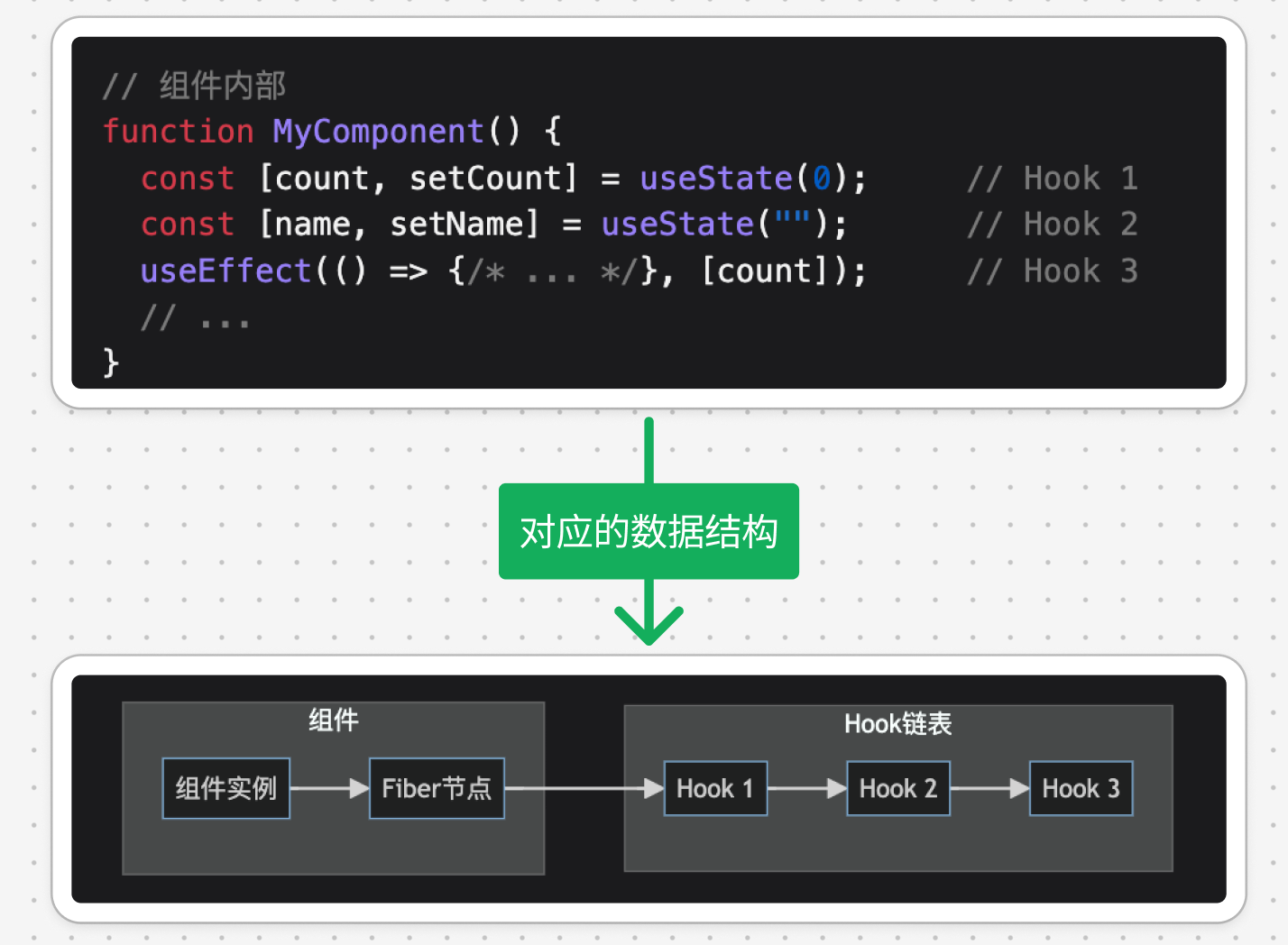
- Hooks 状态存储在 Fiber 节点上
- 通过 Fiber 实现时间切片和优先级调度
- 支持并发模式下的状态管理
2. Hooks 规则
- 只在顶层调用 Hooks
- 不能在循环、条件或嵌套函数中调用
- 确保 Hooks 的调用顺序保持一致
- 只在 React 函数组件中调用 Hooks
- 不能在普通 JavaScript 函数中调用
- 不能在类组件中调用
3. useState 的源码分析
3.1. 入口
所有的 Hooks 在 React.js 中被引入,挂载在 React 对象中,如下:
// React.js
import {
useCallback,
useContext,
useEffect,
useImperativeHandle,
useDebugValue,
useLayoutEffect,
useMemo,
useReducer,
useRef,
useState,
} from './ReactHooks';
3.2. Hook 对象的结构
// ReactFiberHooks.js
export type Hook = {
memoizedState: any,
baseState: any,
baseUpdate: Update<any, any> | null,
queue: UpdateQueue<any, any> | null,
next: Hook | null,
};
3.3. 一个示例
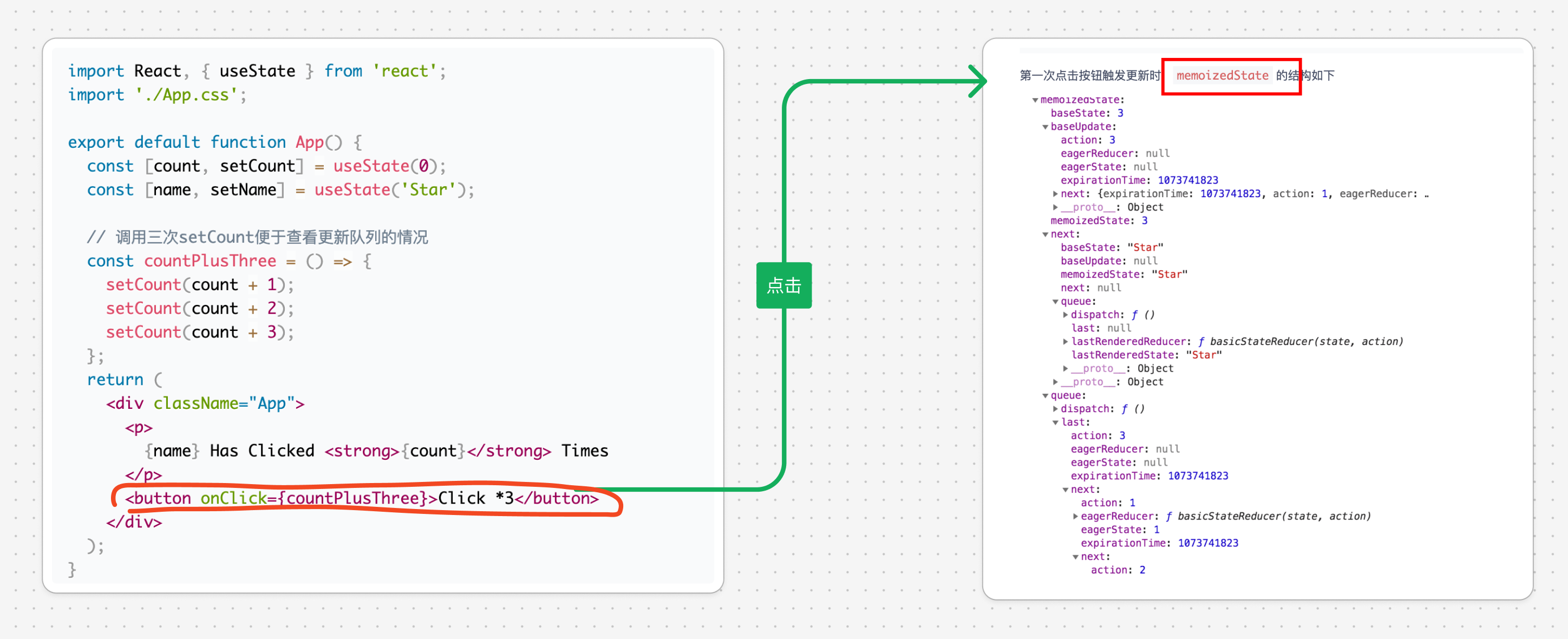
4. 简化版的 useState 实现
4.1. 先给出一个架子
function useState(initialValue) {
let state = initialValue;
const setState = (newValue) => {
state = newValue;
// 这里可以触发组件重新渲染
};
return [state, setState];
}
React useState 的核心原理:
- 通过
闭包保存状态 - 使用
游标确保 hooks 的调用顺序 - 触发重新渲染来更新视图
- 维护状态的一致性
// 保存状态的数组
let states = [];
// 当前处理的 hook 索引
let cursor = 0;
// 简单的 useState 实现
function useState(initialState) {
// 获取当前 hook 的索引
const currentCursor = cursor;
// 初始化状态
states[currentCursor] = states[currentCursor] || initialState;
// 更新函数
const setState = (newState) => {
// 支持函数式更新
states[currentCursor] =
typeof newState === "function"
? newState(states[currentCursor])
: newState;
// 触发重新渲染
render();
};
// 移动游标到下一个位置
cursor++;
return [states[currentCursor], setState];
}
// 示例组件
function Component() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const [text, setText] = useState("hello");
return {
render: () => {
console.log("State:", { count, text });
},
click: () => setCount(count + 1),
type: (newText) => setText(newText),
};
}
// 模拟 React 的渲染过程
function render() {
// 重置游标
cursor = 0;
// 渲染组件
const component = Component();
component.render();
return component;
}
// 测试代码
console.log("Initial render:");
const component = render();
console.log("\nAfter clicking:");
component.click();
console.log("\nAfter typing:");
component.type("world");
在实际的 React 实现中,还包含了更多的特性和优化,比如:
- Fiber 架构的集成
- 批量更新的处理
- 优先级调度
- 内存优化
- 开发环境的调试支持
5. 极简 React Hooks 实现
// 存储 hooks 状态
let hooks = [];
let currentHook = 0;
// 模拟 React 的工作原理
function createReactLike() {
// 重置 hooks 游标
const render = (Component) => {
currentHook = 0;
const app = Component();
app.render();
return app;
}
// useState 实现
const useState = (initialValue) => {
const hookId = currentHook;
hooks[hookId] = hooks[hookId] || initialValue;
const setState = (newValue) => {
hooks[hookId] = typeof newValue === 'function'
? newValue(hooks[hookId])
: newValue;
reRender(); // 触发重新渲染
};
currentHook++;
return [hooks[hookId], setState];
}
// useEffect 实现
const useEffect = (callback, deps) => {
const hookId = currentHook;
const oldDeps = hooks[hookId];
// 检查依赖是否变化
const hasChanged = !oldDeps ||
!deps ||
deps.some((dep, i) => !Object.is(dep, oldDeps[i]));
if (hasChanged) {
// 执行清理函数
if (hooks[hookId]?.cleanup) {
hooks[hookId].cleanup();
}
// 执行 effect 并保存清理函数
hooks[hookId] = {
deps,
cleanup: callback()
};
}
currentHook++;
}
return {
useState,
useEffect,
render
}
}
// 创建 React 实例
const React = createReactLike();
let reRender;
// 示例组件
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
const [text, setText] = React.useState('hello');
React.useEffect(() => {
console.log(`Count changed to: ${count}`);
// 返回清理函数
return () => console.log(`Cleaning up count: ${count}`);
}, [count]);
React.useEffect(() => {
console.log(`Text changed to: ${text}`);
// 返回清理函数
return () => console.log(`Cleaning up text: ${text}`);
}, [text]);
return {
render: () => {
console.log('Render:', { count, text });
},
increment: () => setCount(c => c + 1),
decrement: () => setCount(c => c - 1),
updateText: (newText) => setText(newText)
};
}
// 初始渲染
console.log('=== Initial Render ===');
const component = React.render(Counter);
// 保存重新渲染函数
reRender = () => React.render(Counter);
// 测试状态更新
console.log('\n=== After Increment ===');
component.increment();
console.log('\n=== After Text Update ===');
component.updateText('world');
console.log('\n=== After Decrement ===');
component.decrement();