常见编程题
#前端面试 #R1
目录
- 1. 实现字符串的翻转的 5 种方法
- 2. 实现一个 Object.create(null):两种方式
- 3. 实现
classNames库的能力 - 5. 自己实现
Array.prototype.splice - 6. 实现
1,2,3,5,7,8,9=>1~3,5,7~9 - 7. 要求设计
LazyMan类,实现以下功能 - 8.
[abc[bcd[def]]]转成对象 - 9. howOld(tree,name)实现
- 10. 罗马数字转化整数
- 11. 整数转成罗马数字
- 12. 实现 retry 并指定尝试次数
- 13. 柯里化参数固定场景
add(1)(2)(3) - 14. 参数不固定的柯里化场景
- 15. 封装一个支持请求超时和重试机制的请求函数
1. 实现字符串的翻转的 5 种方法
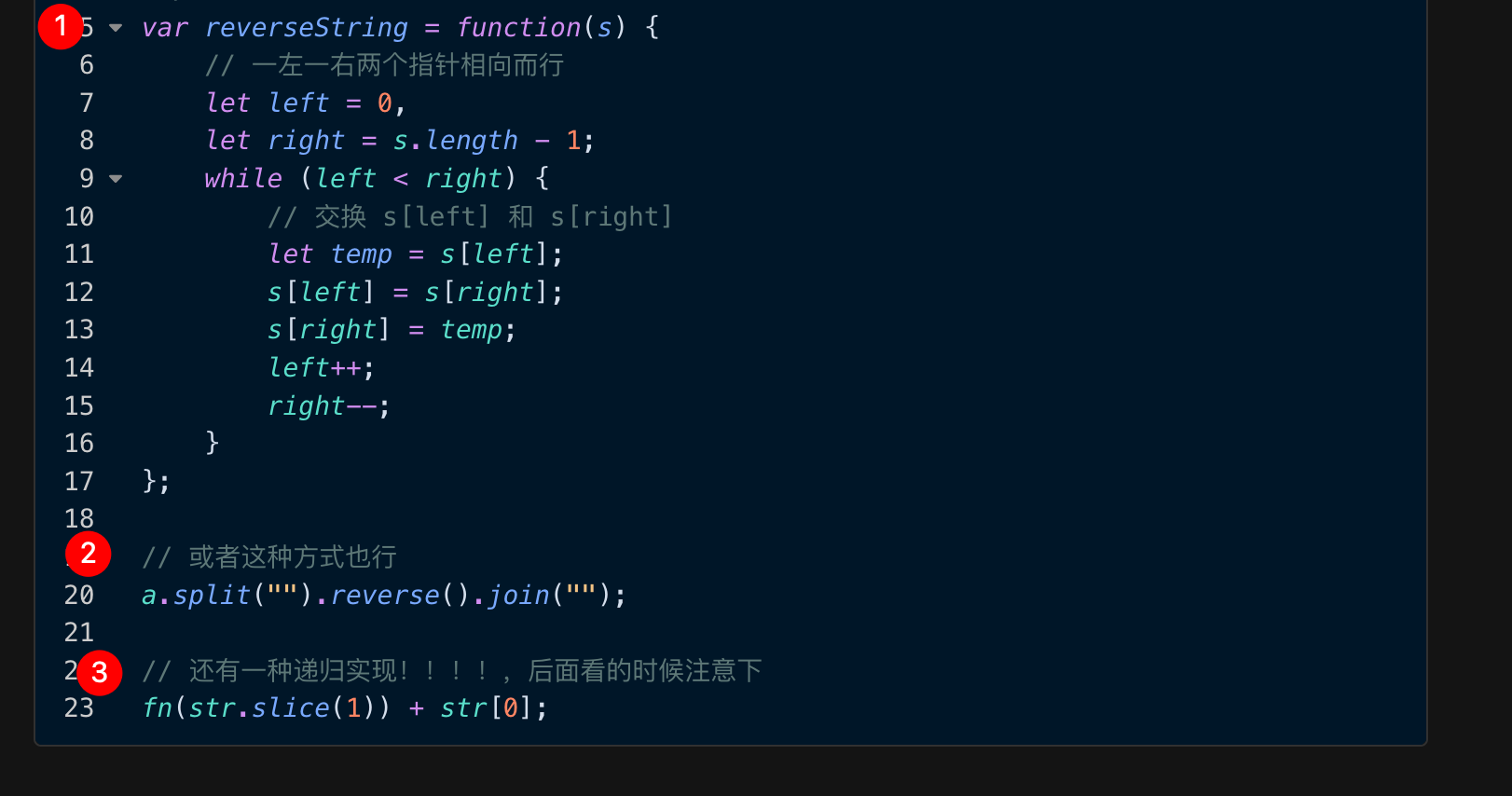
==④== [...'abc'].reverse().join("")
==⑤== 递归实现反转字符串
let str = "1234";
function fn(str) {
// base case
if (str === "") {
return str;
}
return fn(str.slice(1)) + str[0];
}
console.log(fn(str));
2. 实现一个 Object.create(null):两种方式
Object.myCreate = function (proto) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = proto;
return new F();
};
Object.myCreate = function (proto) {
return Object.setPrototypeOf({}, proto);
};
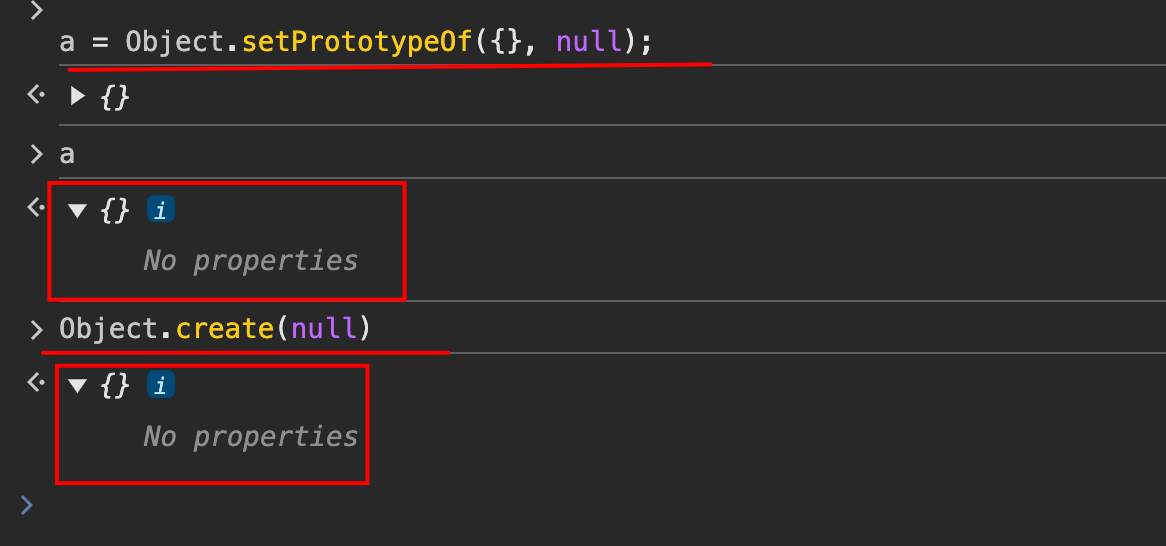
// 如下图:
Object.create(null)
// 等价于
Object.setPrototypeOf({}, null);
**
3. 实现 classNames 库的能力
function classNames(...args) {中的args转成了==数组==
function classNames(...args) {
let arr = [];
for (let item of args) {
// 必须if/else if ,一个经验是尽量这么写,别分开,不然可能会重复命中
if (typeof item === "string" || typeof item === "number") {
arr.push(item);
} else if (Array.isArray(item)) {
// 彻底打平,然后把它放到args参数里面去
item.flat(Infinity).forEach((it) => {
args.push(it);
})
}
// 这里需要过滤掉 null
else if (typeof item === "object" && item !== null) {
Object.entries(item).forEach(([k, v]) => {
if(v){
arr.push(k)
}
})
}
}
return arr;
}
console.log(
// :::: BigInt 可以表示任意大的整数。1n是一种表达方式, 1n == 1 相等
classNames(
null, undefined, Symbol(), 1n, true, false
) || ''
)
console.log(
classNames('BFE', 'dev', 100)
)
const obj = new Map()
obj.cool = '!'
// 'BFE dev is cool'
console.log(
classNames({BFE: [], dev: true, is: 3}, obj)
)
console.log(
classNames(['BFE', [{dev: true}, ['is', [obj]]]])
)
5. 自己实现Array.prototype.splice
Array.prototype.splice =
Array.prototype.splice ||
function (start, deleteCount, ...addList) {
//// 处理开始 startIndex
if (start < 0) {
if (Math.abs(start) > this.length) {
start = 0;
} else {
start += this.length;
}
}
// 处理删除的的个数,如果没传,直接等于长度 - start
if (typeof deleteCount === "undefined") {
deleteCount = this.length - start;
}
// 处理,移除的
const removeList = this.slice(start, start + deleteCount);
const right = this.slice(start + deleteCount);
//// 重新修改this -> 原数组 ,即加入addlist数组片段 + right剩余的数组片段
// 关键是这里,没有发现所谓的left,因为left还在this里呢,也就是本身没变
let addIndex = start;
addList.concat(right).forEach((item) => {
this[addIndex] = item;
addIndex++;
});
this.length = addIndex;
return removeList;
};
6. 实现1,2,3,5,7,8,9 => 1~3,5,7~9
同 3. 合并连续的数字:1,2,3,5,7,8,9 => 1~3,5,7~9
7. 要求设计 LazyMan 类,实现以下功能
LazyMan('Tony');
// Hi I am Tony
LazyMan('Tony').sleep(10).eat('lunch');
// Hi I am Tony
// 等待了10秒...
// I am eating lunch
LazyMan('Tony').eat('lunch').sleep(10).eat('dinner');
// Hi I am Tony
// I am eating lunch
// 等待了10秒...
// I am eating diner
LazyMan('Tony').eat('lunch').eat('dinner').sleepFirst(5).sleep(10).eat('junk food');
// Hi I am Tony
// 等待了5秒...
// I am eating lunch
// I am eating dinner
// 等待了10秒...
// I am eating junk food
- 关键点:tasklist 任务队列,注意优先级
next实际执行下一个任务
class LazyManClass {
constructor(name) {
this.taskList = [];
this.name = name;
console.log(`Hi I am ${this.name}`);
setTimeout(() => {
this.next();
}, 0);
}
eat (name) {
var that = this;
// 这里包装了一下,放在一个函数里面
var fn = (function (n) {
return function () {
console.log(`I am eating ${n}`)
that.next();
}
})(name);
this.taskList.push(fn);
return this;
}
sleepFirst (time) {
var that = this;
var fn = (function (t) {
return function () {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`等待了${t}秒...`)
that.next();
}, t * 1000);
}
})(time);
// 优先级较高
this.taskList.unshift(fn);
return this;
}
sleep (time) {
var that = this
var fn = (function (t) {
return function () {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`等待了${t}秒...`)
that.next();
}, t * 1000);
}
})(time);
this.taskList.push(fn);
return this;
}
next () {
var fn = this.taskList.shift();
fn && fn();
}
}
function LazyMan(name) {
return new LazyManClass(name);
}
LazyMan('Tony').eat('lunch').eat('dinner').sleepFirst(5).sleep(4).eat('junk food');
8. [abc[bcd[def]]] 转成对象
- 注意点
- 正则 :
/[\[\]]/- 需要
[]包裹起来
- 需要
- for 倒着遍历
- 正则 :
题目
/**
* 字符串仅由小写字母和 [] 组成,且字符串不会包含多余的空格。
* 示例一: 'abc' --> {value: 'abc'}
* 示例二:'[abc[bcd[def]]]' -->
* {value: 'abc', children: {value: 'bcd', children: {value: 'def'}}}
*/
for 倒着遍历
const str = "[abc[bcd[def]]]";
let values = str.split(/[\[\]]/).filter((item) => !!item);
// 从后往前遍历构建对象
let result = null;
for (let i = values.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (result === null) {
// 第一次遍历,创建最内层对象
result = { value: values[i] };
} else {
// 后续遍历,将之前的结果作为 children
result = {
value: values[i],
children: result,
};
}
}
console.log(result);
reduce 的方案
let str = "[abc[bcd[def]]]";
// 先转成数组,再递归处理
let arr = str.split(/[\[\]]/).filter((item) => {
return !!item;
});
let res = {};
arr.reduce((prev, curent, index, array) => {
prev.value = curent;
// 除了最后一个,都返回 prev.children
if (array.length - 1 !== index) {
prev.children = {};
return prev.children;
}
}, res);
console.log(JSON.stringify(res));
9. howOld(tree,name)实现
var tree = {
age: 100,
name: "a",
child: [
{
age: 88,
name: "b",
},
{
age: 66,
name: "c",
child: [
{
age: 0,
name: "d",
child: [
{
age: -1,
name: "e",
},
],
},
],
},
],
};
function howOld(tree, name) {
let res = null;
function dfs(root, name) {
// base case
if (root.name === name) {
res = root.age;
return;
}
// 如果是数组,则遍历子节点
if (Array.isArray(root.child)) {
root.child.forEach((item) => {
dfs(item, name);
});
}
}
dfs(tree, name);
return res;
}
console.log(howOld(tree, "e"));
console.log(howOld(tree, "c"));
10. 罗马数字转化整数
let map = {
I: 1,
V: 5,
X: 10,
L: 50,
C: 100,
D: 500,
M: 1000,
};
var romanToInt = function (s) {
let arr = s.split("");
let res = [];
arr.forEach((item) => {
res.push(map[item]);
});
let val = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
let a = res[i];
let b = res[i + 1];
if (b && b > a) {
val += b - a;
i++;
} else {
val += a;
}
}
console.log(val);
return val;
};
11. 整数转成罗马数字
let intToRoman = function (num) {
let values = [1000, 900, 500, 400, 100, 90, 50, 40, 10, 9, 5, 4, 1],
strs = ["M", "CM", "D", "CD", "C", "XC", "L", "XL", "X", "IX", "V", "IV", "I"],
result = '';
for (let i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
while (num >= values[i]) {
num -= values[i];
result += strs[i];
}
}
return result;
};
12. 实现 retry 并指定尝试次数
while(times--)
Promise.retry = function (fn, times = 3) {
return new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => {
while (times--) {
try {
let ret = await fn();
resolve(ret);
// 成功了就直接break了
break;
} catch (error) {
if (!times) reject(error);
}
}
});
};
13. 柯里化参数固定场景 add(1)(2)(3)
/**
* 柯里化
* 参数固定场景
* add(1)(2)(3)
* add(4)(5)(6)
* */
const curry = (fn, ...args1) => {
if (args1.length >= fn.length) {
return fn(...args1)
}
// 两个return
return (...args2) => {
return curry(fn, ...args1, ...args2);
}
}
function add1(x, y, z) {
return x + y + z;
}
const add = curry(add1);
console.log(add(1, 2, 3));
console.log(add(1)(2)(3));
console.log(add(1, 2)(3));
console.log(add(1)(2, 3));
14. 参数不固定的柯里化场景
/**
* 柯里化
* 参数不固定场景
* add(1)(2)(3,4).sumof()
* */
const add = (...args) => {
let vars = [];
// 写一个函数,形成闭包
const curried = (...arg2) => {
// ::::这里 vars,记住了
vars = [...vars, ...arg2];
return curried
}
curried.sumof = () => {
//todo 做你想做的事情
return vars;
}
return curried(...args)
}
console.log(add(1)(2)(3, 4).sumof())
console.log(add(1)(2)(3, 4)(7, 8).sumof())
15. 封装一个支持请求超时和重试机制的请求函数
/**
* 延迟函数
* @param {number} ms 延迟时间(毫秒)
* @returns {Promise<void>}
*/
const delay = (ms) => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
/**
* 带有超时和重试机制的请求函数
* @param {Function} fetchFn - 实际的请求函数
* @param {Object} options - 配置选项
* @param {number} options.timeout - 超时时间(毫秒)
* @param {number} options.retries - 重试次数
* @param {number} options.retryDelay - 重试间隔(毫秒)
* @param {Function} options.retryCondition - 重试条件函数
* @param {AbortSignal} options.signal - 取消信号
* @returns {Promise}
*/
async function fetchWithRetry(fetchFn, {
timeout = 5000,
retries = 3,
retryDelay = 1000,
retryCondition = (error) => true, // 默认所有错误都重试
signal = null
} = {}) {
let lastError;
// 创建超时 Promise
const timeoutPromise = (ms) => new Promise((_, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error(`Request timeout after ${ms}ms`));
}, ms);
});
// 重试循环
for (let i = 0; i <= retries; i++) {
try {
// 如果已经被取消,直接抛出错误
if (signal?.aborted) {
throw new Error('Request aborted');
}
// 创建实际的请求 Promise
const fetchPromise = fetchFn();
// 使用 Promise.race 实现超时控制
const result = await Promise.race([
fetchPromise,
timeoutPromise(timeout)
]);
return result; // 如果成功,直接返回结果
} catch (error) {
lastError = error;
// 如果是最后一次重试,或者不满足重试条件,直接抛出错误
if (i === retries || !retryCondition(error)) {
throw error;
}
// 如果需要重试,等待指定时间
console.log(`Retry attempt ${i + 1} of ${retries} after ${retryDelay}ms`);
await delay(retryDelay);
}
}
throw lastError;
}
// 使用示例:
async function example4() {
try {
const result = await fetchWithRetry(
() => axios.get('https://api.example.com/data'),
{
timeout: 3000,
retries: 3,
retryCondition: (error) => {
// axios 特定的错误处理
return axios.isAxiosError(error) &&
(!error.response || error.response.status >= 500);
}
}
);
console.log(result.data);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Final error:', error);
}
}