React render 方法的原理和触发时机
#react
目录
1. 总结
- React 的 render 过程
- 执行 render 方法,获取虚拟 DOM
- 对比虚拟 DOM(Diffing)
- 更新真实 DOM
- Render 的触发时机
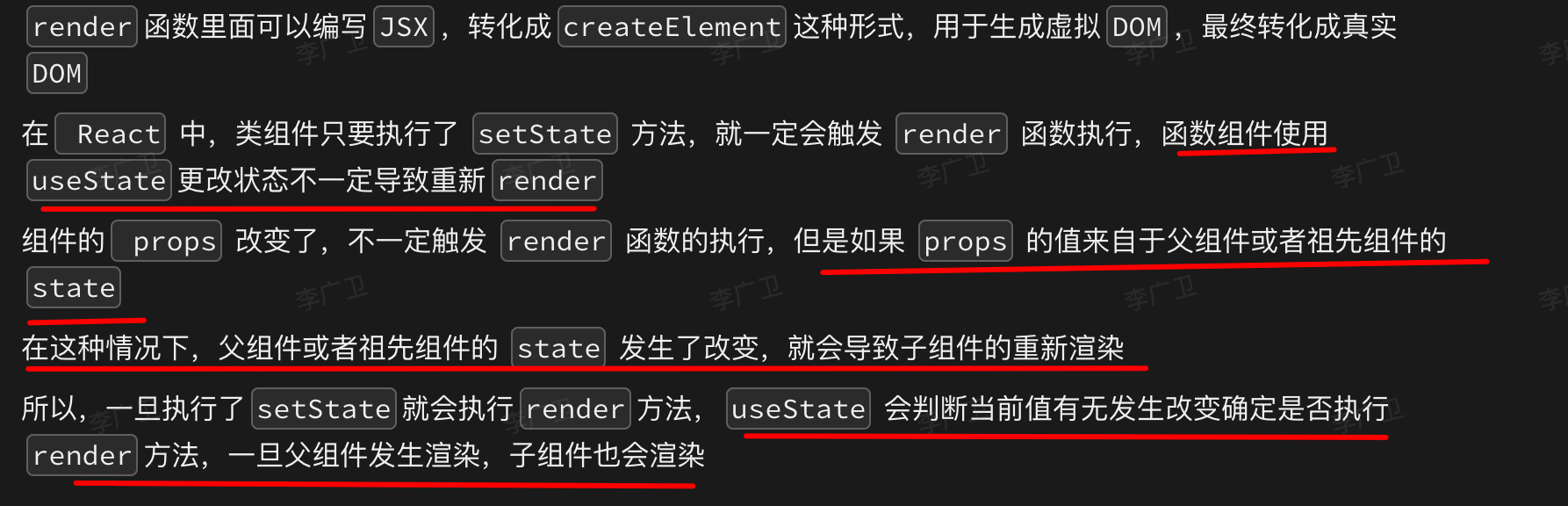
- 首次挂载时
- props 变化
- state 变化
- 父组件重新渲染
- 性能优化方法
- React.memo
- PureComponent
- shouldComponentUpdate
- 避免==内联==对象或函数 → 提出来
- 使用 useMemo 缓存结果
- 使用 useCallback 缓存函数
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {- 返回
null表示不需要更新状态 - 这个方法在==每次渲染前都会调用==,包括首次渲染
- 返回
2. Render 方法的基本原理
React 的 render 方法主要负责将组件转换为虚拟 DOM(Virtual DOM):
// 类组件中的 render
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>{this.props.title}</h1>
<p>{this.props.content}</p>
</div>
);
}
}
// 函数组件
function MyFunctionalComponent(props) {
// 整个函数体相当于 render 方法
return (
<div>
<h1>{props.title}</h1>
<p>{props.content}</p>
</div>
);
}
3. Render 的执行过程
- 执行 render 方法,获取虚拟 DOM
- 对比虚拟 DOM(Diffing)
- 更新真实 DOM
// 简化的 render 过程
const render = (Component, props) => {
// 1. 执行 render 方法,获取虚拟 DOM
const vdom = Component(props);
// 2. 对比虚拟 DOM(Diffing)
const patches = diff(previousVDOM, vdom);
// 3. 更新真实 DOM
patch(realDOM, patches);
}
4. Render 的触发时机
4.1. 首次渲染
// 组件首次挂载时
ReactDOM.render(
<App />,
document.getElementById('root')
);
4.2. Props 改变
function Parent() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<Child count={count} /> // props 改变会触发 Child 重新渲染
);
}
4.3. State 改变
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>
Increment
</button>
</div>
);
}
4.4. 父组件重新渲染
function Parent() {
const [update, setUpdate] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<Child /> {/* Parent 重新渲染会导致 Child 也重新渲染 */}
<button onClick={() => setUpdate(update + 1)}>
Update Parent
</button>
</div>
);
}
4.5. 性能优化方法
4.5.1. React.memo 用于函数组件
const MemoizedComponent = React.memo(function MyComponent(props) {
return (
<div>{props.value}</div>
);
});
4.5.2. PureComponent 用于类组件
class MyPureComponent extends React.PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<div>{this.props.value}</div>
);
}
}
4.5.3. shouldComponentUpdate 用于自定义更新逻辑
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
return this.props.value !== nextProps.value;
}
render() {
return (
<div>{this.props.value}</div>
);
}
}
5. 常见的渲染优化问题
5.1. 避免在渲染中创建新对象或函数
// 不好的写法
function BadComponent() {
return (
<button onClick={() => console.log('clicked')}> // 每次渲染都创建新函数
Click me
</button>
);
}
// 好的写法
function GoodComponent() {
const handleClick = useCallback(() => {
console.log('clicked');
}, []);
return (
<button onClick={handleClick}>
Click me
</button>
);
}
5.2. 使用 useMemo 缓存计算结果
function ExpensiveComponent({ data }) {
const processedData = useMemo(() => {
return data.map(item => expensiveCalculation(item));
}, [data]);
return <div>{processedData}</div>;
}
6. 渲染阶段的生命周期
对于类组件,render 相关的生命周期方法执行顺序:
class LifecycleComponent extends React.Component {
// 1. 在 render 之前
注意点:
1. getDerivedStateFromProps 是静态方法,无法访问 this
2. 应该谨慎使用,大多数情况下可以用其他方式替代
3. 返回 null 表示不需要更新状态
4. 这个方法在每次渲染前都会调用,包括首次渲染
5. 适合用于状态需要根据 props 变化而变化的场景
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
// 当 props.email 改变时更新 state
if (props.email !== state.prevEmail) {
return {
email: props.email,
prevEmail: props.email
};
}
return null; // 返回 null 表示不需要更新状态
}
// 2. 判断是否需要更新
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
return true;
}
// 3. render 方法
render() {
return <div>Content</div>;
}
// 4. render 后,更新前
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
return null;
}
// 5. 更新后
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
}
}
7. 总结
- Render 方法是 React 组件的核心,负责生成虚拟 DOM。
- 触发时机包括:
- 首次渲染、props 变化、state 变化、父组件重渲染。
- React 提供了多种优化方法来避免不必要的渲染。
- 合理使用这些优化方法可以显著提升应用性能。
- 理解渲染原理和触发时机对于编写高性能的 React 应用至关重要。