React Class 类生命周期如何对应 Hooks
目录
- 1. 总结
- 2. 先说Class组件的生命周期
- 3. React 16 废弃了那些生命周期函数
- 4. getDerivedStateFromError vs componentDidCatch 以及 Hooks 中的错误处理
- 5. Class 和 Hooks 对应的生命周期
1. 总结
- Class 组件 ==<=>== Hooks 等效实现
// Class 组件 Hooks 等效实现
// ------------------------------------------
// constructor -> useState, useRef
// getDerivedStateFromProps -> useEffect 配合 useState
// shouldComponentUpdate -> React.memo
// render -> 函数本身
// componentDidMount -> useEffect([])
// componentDidUpdate -> useEffect([deps])
// componentWillUnmount -> useEffect 返回的清理函数
// componentDidCatch -> 需要使用 Class 组件
// getSnapshotBeforeUpdate -> 没有直接等效实现
- getDerivedStateFromError 与 componentDidCatch 区别
- getDerivedStateFromError 在
渲染阶段调用,是==同步==的 - 用于==降级 UI,容错==
- componentDidCatch 在
提交阶段调用,可以执行副作用 getDerivedStateFromError必须返回一个状态对象getDerivedStateFromError支持服务端渲染,而componentDidCatch不支持
- getDerivedStateFromError 在
- Class组件的生命周期,分==五个阶段==
- 初始化 + 挂载阶段 + 组件更新 + 卸载 + 错误处理
- React 为什么要废弃
componentwillMount、componentWillReceiveProps、componentWillUpdate`- 在
fiber中,==render 可被打断==,**可能在 wilMount 中获取到的元素状态很可能与实际需要的不同 - ==一句话就是,Render 阶段可能会被打断,那么 willxxx 就可以执行多次==
- 在
2. 先说Class组件的生命周期
分四个阶段:组件挂载阶段 + 组件更新 + 卸载 + 错误处理阶段 ,如下图:
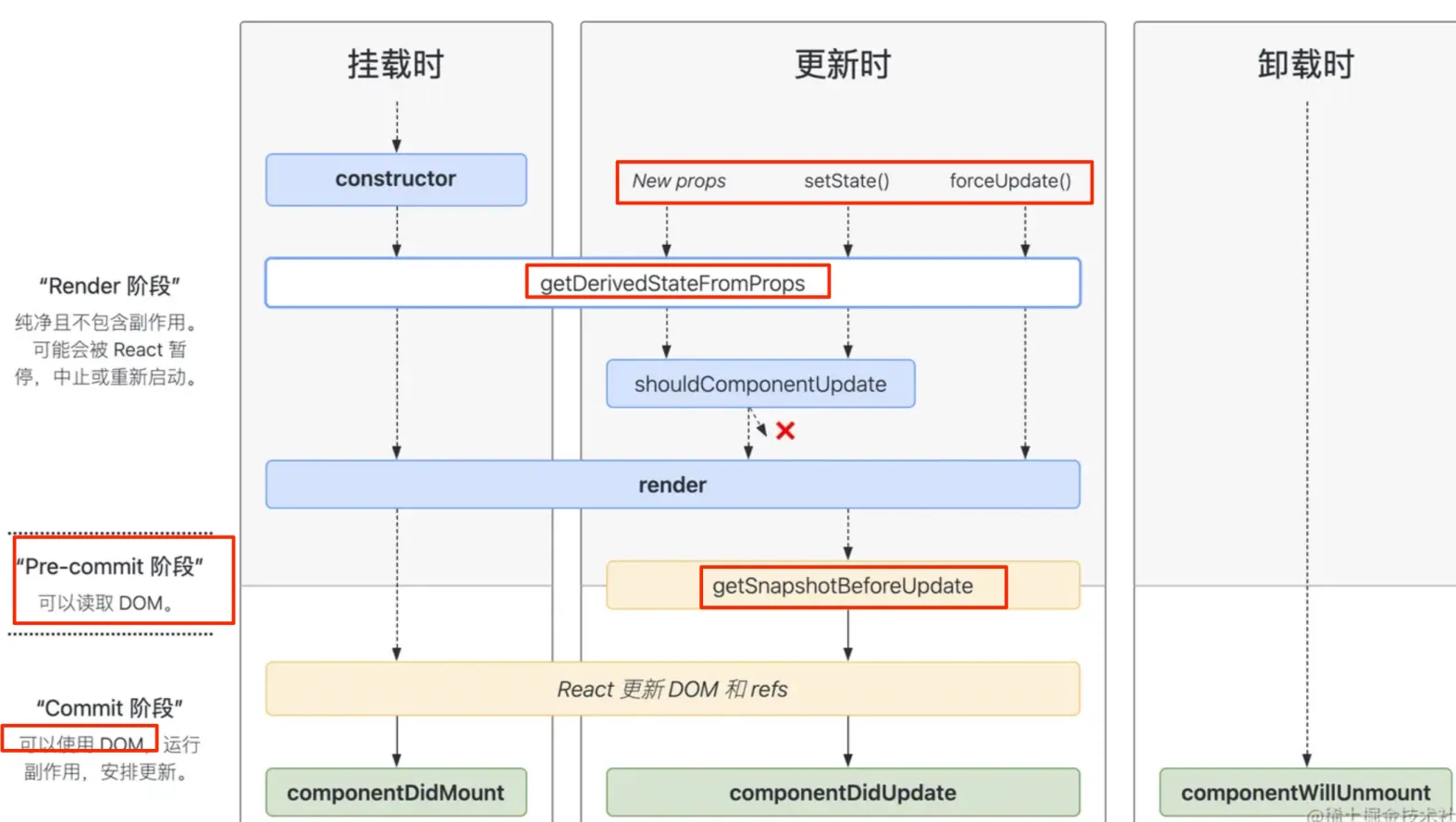
2.1. 第一阶段:组件挂载阶段
挂载阶段组件被创建,然后组件实例插入到 DOM 中,完成组件的第一次渲染,在此阶段会依次调用以下这些方法
constructor:初始化组件的state,给事件处理方法绑定thisgetDerivedStateFromProps,静态方法,它存在只有一个目的:让组件在 props 变化时更新 state。- 该方法返回一个对象用于更新
state,如果返回null则不更新任何内容
- 该方法返回一个对象用于更新
render:根据状态state和属性props渲染组件。- 这个函数只做一件事,就是返回需要渲染的内容,不要在这里面做其他事情
componentDidMount:代表组件挂载完成, 在这里可以DOM操作、网络请求、事件订阅等- 其实
不推荐直接在componentDidMount直接调用setState,因为我们又调用了一次setState,就会在未来再进行一次render,造成不必要的性能浪费,大多数情况可以设置初始值来搞定
- 其实
2.1.1. 代码详细示例
下面是详细使用示例:
- constructor
- static getDerivedStateFromProps
- render
- componentDidMount
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
// 1. constructor
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0
};
// 用途:
// - 初始化 state
// - 绑定事件处理器
// - 不应该在这里调用 setState
// - 不应该产生副作用
}
// 2. static getDerivedStateFromProps
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
// 参数:
// - props: 新的属性
// - state: 当前状态
// 返回值:返回一个对象来更新 state,或者返回 null 表示不更新
// 用途:
// - 根据 props 更新 state
// - 是静态方法,不能访问 this
// - 应该是纯函数,不应该产生副作用
if (props.count !== state.prevCount) {
return {
count: props.count,
prevCount: props.count
};
}
return null;
}
// 3. render
render() {
// 用途:
// - 返回要渲染的内容
// - 必须是纯函数
// - 不能调用 setState
// - 不能直接与浏览器交互
return <div>{this.state.count}</div>;
}
// 4. componentDidMount
componentDidMount() {
// 用途:
// - 发起网络请求
// - 添加订阅
// - 操作 DOM
// - 设置定时器
fetch('api/data')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => this.setState({ data }));
}
}
2.2. 第二阶段:组件更新阶段
getDerivedStateFromProps,如上shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)是否应该渲染组件性能优化的点
render,如上getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState)- 在
render之后,componentDidUpdate之前调用 - 最近一次渲染输出(提交到 DOM 节点)之前调用。即
React更新DOM或Refs之前调用 - 返回值作为第三个参数传给
componentDidUpdate
- 在
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot){},更新后立即被调用,通常做以下操作- 当组件更新后,对
DOM 进行操作; - 参数
- snapshot: getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 的返回值
- prevProps: 更新前的属性
- prevState: 更新前的状态
- 如果你对更新前后的
props进行了比较,也可以选择在此处进行网络请求;- (例如,当
props未发生变化时,则不会执行网络请求)
- (例如,当
- 当组件更新后,对
2.2.1. 代码详细示例
- static getDerivedStateFromProps
- shouldComponentUpdate
- render
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
- componentDidUpdate
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
// 1. static getDerivedStateFromProps
// 同上,每次更新也会调用
// 2. shouldComponentUpdate
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
// 参数:
// - nextProps: 新的属性
// - nextState: 新的状态
// 返回值:true 表示需要更新,false 表示不更新
// 用途:
// - 性能优化
// - 控制组件是否需要重新渲染
return this.props.value !== nextProps.value;
}
// 3. render
// 同上
// 4. getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
// 参数:
// - prevProps: 更新前的属性
// - prevState: 更新前的状态
// 返回值:传递给 componentDidUpdate 的第三个参数
// 用途:
// - 在 DOM 更新之前获取一些信息
// - 例如:滚动位置
const list = this.listRef.current;
return list.scrollHeight - list.scrollTop;
}
// 5. componentDidUpdate
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
// 参数:
// - prevProps: 更新前的属性
// - prevState: 更新前的状态
// - snapshot: getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 的返回值
// 用途:
// - 对 DOM 进行操作
// - 网络请求
// - 注意:调用 setState 需要有条件,否则会无限循环
if (this.props.userID !== prevProps.userID) {
this.fetchData(this.props.userID);
}
}
}
2.3. 第三阶段:组件卸载阶段
- componentWillUnmount
- 清除
timer,取消网络请求或清除 - 取消在
componentDidMount()中创建的订阅等;
- 清除
2.3.1. 代码详细示例
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
// componentWillUnmount
componentWillUnmount() {
// 用途:
// - 清理工作
// - 取消网络请求
// - 清除订阅
// - 清除定时器
this.subscription.unsubscribe();
clearInterval(this.timer);
}
}
2.4. 第四阶段:错误处理阶段
- getDerivedStateFromError,后代组件抛出错误后被调用,发生在渲染阶段
- 返回值:返回一个对象来更新 state
- 用途:
- 在渲染错误页面之前更新 state ,==用于容错==
- 不应该产生副作用
componentDidCatch(error, info)- 参数:
- error: 错误对象
- errorInfo: 包含
componentStack信息的对象
- 用途:
- 错误日志记录
- 可以产生副作用
- 参数:
2.4.1. 代码详细示例
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
// static getDerivedStateFromError
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
// 参数:
// - error: 错误对象
// 返回值:返回一个对象来更新 state
// 用途:
// - 在渲染错误页面之前更新 state
// - 不应该产生副作用
return { hasError: true };
}
// componentDidCatch
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
// 参数:
// - error: 错误对象
// - errorInfo: 包含 componentStack 信息的对象
// 用途:
// - 错误日志记录
// - 可以产生副作用
logErrorToService(error, errorInfo);
}
}
2.5. 完整的生命周期示例
class CompleteLifecycleComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0,
data: null,
error: null
};
this.listRef = React.createRef();
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
if (props.count !== state.prevCount) {
return {
count: props.count,
prevCount: props.count
};
}
return null;
}
componentDidMount() {
// 初始化数据获取
this.fetchData();
// 设置定时器
this.timer = setInterval(this.tick, 1000);
// 添加事件监听
window.addEventListener('resize', this.handleResize);
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
// 性能优化
return (
this.props.count !== nextProps.count ||
this.state.data !== nextState.data
);
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
if (prevState.data !== this.state.data) {
const list = this.listRef.current;
return list.scrollHeight - list.scrollTop;
}
return null;
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
// 处理数据变化
if (this.props.dataId !== prevProps.dataId) {
this.fetchData();
}
// 使用 snapshot
if (snapshot !== null) {
const list = this.listRef.current;
list.scrollTop = list.scrollHeight - snapshot;
}
}
componentWillUnmount() {
// 清理工作
clearInterval(this.timer);
window.removeEventListener('resize', this.handleResize);
this.cancelPendingRequests();
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
return { error: error };
}
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
// 错误日志记录
logErrorToService(error, errorInfo);
}
// 自定义方法
fetchData = async () => {
try {
const response = await fetch(`api/data/${this.props.dataId}`);
const data = await response.json();
this.setState({ data });
} catch (error) {
this.setState({ error });
}
};
handleResize = () => {
// 处理窗口大小变化
};
tick = () => {
this.setState(state => ({ count: state.count + 1 }));
};
render() {
if (this.state.error) {
return <ErrorDisplay error={this.state.error} />;
}
return (
<div ref={this.listRef}>
<h1>Count: {this.state.count}</h1>
<DataDisplay data={this.state.data} />
</div>
);
}
}
2.6. 注意点与总结
- 不是所有方法都需要使用:
- 大多数情况下只需要
constructor、render和componentDidMount - 其他方法用于特定场景的优化或处理
- 大多数情况下只需要
- 避免常见错误:
- 不要在
constructor和render中调用setState - 在
componentDidUpdate中调用setState需要条件判断 - 清理工作要在
componentWillUnmount中完成
- 不要在
- 性能考虑:
- 使用
shouldComponentUpdate优化性能 - 避免在
render中进行复杂计算 - 注意内存泄漏问题
- 使用
- 最佳实践:
- 保持生命周期方法简洁
- 遵循单一职责原则
- 适当使用错误边界
- 正确处理异步操作
- 最后,还是多使用 Hooks 吧
3. React 16 废弃了那些生命周期函数
componentWillMount:- 完全可以使用
componentDidMount和constructor来代替
- 完全可以使用
componentWillReceiveProps- 来回比较数据状态不可预测行
- 增加组件重回次数
- 使用静态方法代替:
getDerivedStateFromProps,不使用this,纯函数,不会写出副作用代码
componentWillUpdate:- 在
fiber中,==render 可被打断==,可能在wilMount中获取到的元素状态很可能与实际需要的不同 - 会触发多次
- 比如,在这个生命周期中,
调用setState会造成死循环,导致程序崩溃。
- 比如,在这个生命周期中,
- 在
React 为什么要废弃 componentwillMount、componentWillReceiveProps、componentWillUpdate 这三个生命周期钩子?,它们有哪些问题呢? React 又是如何解决的呢?
==一句话就是,Render 阶段可能会被打断,那么 willxxx 就可以执行多次==
4. getDerivedStateFromError vs componentDidCatch 以及 Hooks 中的错误处理
关于错误处理,更多 23. React 中错误捕获的方式
4.1. getDerivedStateFromError vs componentDidCatch
这两个生命周期方法都用于错误处理,但有重要区别:
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
state = { hasError: false };
// 用于渲染降级 UI
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
// 返回新的 state
return { hasError: true };
}
// 用于错误日志记录
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
// 可以将错误日志发送到服务器
logErrorToService(error, errorInfo);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
return <h1>Something went wrong.</h1>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
主要区别:
- getDerivedStateFromError 在
渲染阶段调用,是==同步==的- 用于==降级 UI,容错==
- componentDidCatch 在
提交阶段调用,可以执行副作用 getDerivedStateFromError必须返回一个状态对象getDerivedStateFromError支持服务端渲染,而componentDidCatch不支持
使用示例如下:
// 创建错误边界组件
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
state = {
hasError: false,
error: null,
errorInfo: null
};
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
// 基础错误状态
return {
hasError: true,
error
};
}
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
// 记录详细错误信息
this.setState({
errorInfo
});
// 发送到错误追踪服务
logErrorToService(error, errorInfo);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
return (
<div className="error-ui">
<h2>Something went wrong</h2>
{process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development' && (
<details>
<summary>Error Details</summary>
<pre>{this.state.error?.toString()}</pre>
<pre>{this.state.errorInfo?.componentStack}</pre>
</details>
)}
<button onClick={() => this.setState({ hasError: false })}>
Try again
</button>
</div>
);
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
4.2. 在现代 React(Hooks)中的使用
虽然目前 Hooks 不能直接实现错误边界,但有几种推荐的解决方案:
4.2.1. 使用第三方库 react-error-boundary
import { ErrorBoundary } from 'react-error-boundary';
function ErrorFallback({error, resetErrorBoundary}) {
return (
<div role="alert">
<p>Something went wrong:</p>
<pre>{error.message}</pre>
<button onClick={resetErrorBoundary}>Try again</button>
</div>
);
}
function MyApp() {
return (
<ErrorBoundary
FallbackComponent={ErrorFallback}
onReset={() => {
// 重置应用状态
}}
onError={(error, errorInfo) => {
// 记录错误
logError(error, errorInfo);
}}
>
<MyComponent />
</ErrorBoundary>
);
}
4.2.2. 自定义 Hook 配合错误边界
function useErrorHandler() {
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
if (error) {
throw error; // 抛出错误给最近的错误边界
}
}, [error]);
return setError;
}
function MyComponent() {
const handleError = useErrorHandler();
const handleClick = async () => {
try {
await riskyOperation();
} catch (error) {
handleError(error);
}
};
return <button onClick={handleClick}>Risky Operation</button>;
}
4.3. 最佳实践和注意事项
4.3.1. 错误边界的粒度控制
function App() {
return (
<ErrorBoundary>
<Header />
<ErrorBoundary>
{/* 关键功能单独错误处理 */}
<MainContent />
</ErrorBoundary>
<ErrorBoundary>
{/* 非关键功能单独错误处理 */}
<Sidebar />
</ErrorBoundary>
<Footer />
</ErrorBoundary>
);
}
4.3.2. 错误恢复策略
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
state = { hasError: false };
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
return { hasError: true };
}
resetError = () => {
this.setState({ hasError: false });
// 可能需要清除缓存或重新获取数据
this.props.onReset?.();
};
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
return (
<div>
<h2>Something went wrong</h2>
<button onClick={this.resetError}>
Reset and try again
</button>
</div>
);
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
4.4. 需要注意的是
- 错误边界无法捕获以下错误:
- 事件处理器中的错误
- 异步代码错误
- 服务端渲染错误
- 错误边界组件自身的错误
- 在开发环境中,错误会冒泡到窗口,这是为了确保错误更容易被发现
- 在生产环境中,错误会被限制在错误边界内
- 建议在应用的不同层级设置错误边界,以实现更细粒度的错误处理
5. Class 和 Hooks 对应的生命周期
5.1. 初始化阶段
5.1.1. Class 组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0
};
}
}
5.1.2. Hooks 方式
function MyComponent(props) {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
// 如果需要复杂的初始状态计算
const [state, setState] = useState(() => {
const initialState = someExpensiveComputation(props);
return initialState;
});
}
5.2. 挂载阶段
5.2.1. Class 组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
componentDidMount() {
console.log('组件已挂载');
// 执行副作用,如 API 调用
this.fetchData();
// 添加事件监听
window.addEventListener('resize', this.handleResize);
}
}
5.2.2. Hooks 方式:空依赖数组表示仅在挂载时执行
function MyComponent() {
useEffect(() => {
console.log('组件已挂载');
// 执行副作用
fetchData();
// 添加事件监听
window.addEventListener('resize', handleResize);
// 清理函数(相当于 componentWillUnmount)
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('resize', handleResize);
};
}, []); // 空依赖数组表示仅在挂载时执行
}
5.3. 更新阶段
5.3.1. Class 组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
if (this.props.userID !== prevProps.userID) {
this.fetchData(this.props.userID);
}
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
return this.props.value !== nextProps.value;
}
}
5.3.2. Hooks 方式
function MyComponent({ userID }) {
// 替代 componentDidUpdate
useEffect(() => {
fetchData(userID);
}, [userID]); // 仅在 userID 改变时执行
// 替代 shouldComponentUpdate
const MemoizedComponent = React.memo(MyComponent, (prevProps, nextProps) => {
return prevProps.value === nextProps.value;
});
}
5.4. 卸载阶段
5.4.1. Class 组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
componentWillUnmount() {
// 清理工作
window.removeEventListener('resize', this.handleResize);
this.clearIntervals();
}
}
5.4.2. Hooks 方式
function MyComponent() {
useEffect(() => {
// 设置
const interval = setInterval(() => {
// 一些操作
}, 1000);
// 返回清理函数
return () => {
clearInterval(interval);
};
}, []);
}
5.5. 错误处理
5.5.1. Class 组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
logErrorToService(error, errorInfo);
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
return { hasError: true };
}
}
5.5.2. Hooks 方式
// 错误边界目前还需要使用 Class 组件
// 但可以创建自定义 Hook 处理组件内的错误
function useErrorHandler(error) {
const [hasError, setHasError] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
if (error) {
setHasError(true);
logErrorToService(error);
}
}, [error]);
return hasError;
}
5.6. 获取派生状态
5.6.1. Class 组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
if (props.currentRow !== state.lastRow) {
return {
isScrollingDown: props.currentRow > state.lastRow,
lastRow: props.currentRow
};
}
return null;
}
}
5.6.2. Hooks 方式
function MyComponent(props) {
const [isScrollingDown, setIsScrollingDown] = useState(false);
const [lastRow, setLastRow] = useState(0);
// 使用 useEffect 模拟 getDerivedStateFromProps
useEffect(() => {
if (props.currentRow !== lastRow) {
setIsScrollingDown(props.currentRow > lastRow);
setLastRow(props.currentRow);
}
}, [props.currentRow, lastRow]);
}
5.7. 性能优化
5.7.1. Class 组件
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
return this.props.value !== nextProps.value;
}
}
5.7.2. Hooks 方式
function MyComponent({ value }) {
// 使用 useMemo 缓存计算结果
const expensiveValue = useMemo(() => {
return computeExpensiveValue(value);
}, [value]);
// 使用 useCallback 缓存函数
const handleClick = useCallback(() => {
doSomething(value);
}, [value]);
}
// 使用 React.memo 进行组件级别的优化
const MemoizedComponent = React.memo(MyComponent);
5.8. 自定义生命周期 Hook
// 组合多个生命周期的自定义 Hook
function useLifecycle(props) {
// 模拟 componentDidMount
useEffect(() => {
console.log('组件已挂载');
return () => console.log('组件将卸载');
}, []);
// 模拟 componentDidUpdate
const prevPropsRef = useRef();
useEffect(() => {
if (prevPropsRef.current) {
// 比较 props 变化
const prevProps = prevPropsRef.current;
// 执行更新后的操作
}
prevPropsRef.current = props;
});
// 返回需要的值或方法
return {
// ...
};
}
5.9. Hooks 完整的生命周期示例
function CompleteLifecycleComponent({ data }) {
// 1. 构造函数阶段
const [state, setState] = useState(() => {
// 初始化状态
return { data: processData(data) };
});
// 2. 挂载阶段
useEffect(() => {
console.log('组件已挂载');
// 执行副作用
const subscription = subscribeToData();
// 3. 卸载阶段
return () => {
console.log('组件将卸载');
subscription.unsubscribe();
};
}, []);
// 4. 更新阶段
useEffect(() => {
console.log('数据已更新');
updateUIWithData(data);
}, [data]);
// 5. 错误处理
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
if (error) {
logError(error);
}
}, [error]);
// 6. 性能优化
const memoizedValue = useMemo(() => {
return expensiveComputation(state.data);
}, [state.data]);
if (error) {
return <ErrorDisplay error={error} />;
}
return (
<div>{/* 渲染内容 */}</div>
);
}
5.10. 生命周期方法对照表
// Class 组件 Hooks 等效实现
// ------------------------------------------
// constructor -> useState, useRef
// getDerivedStateFromProps -> useEffect 配合 useState
// shouldComponentUpdate -> React.memo
// render -> 函数本身
// componentDidMount -> useEffect([])
// componentDidUpdate -> useEffect([deps])
// componentWillUnmount -> useEffect 返回的清理函数
// componentDidCatch -> 需要使用 Class 组件
// getSnapshotBeforeUpdate -> 没有直接等效实现