Node.js 中异常捕获和容错的常见处理方式
#nodejs
目录
- 1. try-catch 捕获同步异常
- 2. Promise 异常处理
- 3. 全局未捕获异常处理:
process.on('uncaughtException', (error) => {} - 4. Express 错误处理中间件
- 5. 数据库操作错误处理
- 6. 事件触发器错误处理 →
events - 7. 定时器错误处理
- 8. 错误监控和报警
- 9. 写一个koa中间件,用于捕获相关的异常
- 10. 总结
1. try-catch 捕获同步异常
// 基本的同步异常捕获
function syncOperation() {
try {
const result = JSON.parse('{"invalid": json}');
return result;
} catch (error) {
console.error('同步错误:', {
name: error.name,
message: error.message,
stack: error.stack
});
// 可以返回默认值或重新抛出错误
return { error: true };
}
}
2. Promise 异常处理
// Promise 链式调用异常处理
async function asyncOperation() {
try {
const result = await fetch('https://api.example.com/data')
.then(response => response.json())
.catch(error => {
console.error('Fetch 错误:', error);
return null;
});
if (!result) {
throw new Error('获取数据失败');
}
return result;
} catch (error) {
console.error('异步操作错误:', error);
return null;
}
}
// Promise.all 错误处理
async function multipleAsyncOperations() {
try {
const promises = [
fetch('https://api1.example.com'),
fetch('https://api2.example.com'),
fetch('https://api3.example.com')
];
const results = await Promise.all(
promises.map(p => p.catch(error => {
console.error('单个请求失败:', error);
return null;
}))
);
return results.filter(result => result !== null);
} catch (error) {
console.error('批量请求错误:', error);
return [];
}
}
3. 全局未捕获异常处理:process.on('uncaughtException', (error) => {}
// 未捕获的异常处理
process.on('uncaughtException', (error) => {
console.error('未捕获的异常:', {
error: error,
time: new Date().toISOString(),
pid: process.pid
});
// 记录错误日志
logError(error);
// 优雅退出(建议在处理完关键操作后退出)
process.exit(1);
});
// 未处理的 Promise 拒绝
process.on('unhandledRejection', (reason, promise) => {
console.error('未处理的 Promise 拒绝:', {
reason: reason,
time: new Date().toISOString(),
pid: process.pid
});
// 记录错误日志
logError(reason);
});
// 自定义错误日志记录函数
function logError(error) {
// 这里可以实现错误日志记录逻辑
// 比如写入文件或发送到日志服务
}
4. Express 错误处理中间件
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
// 自定义错误类
class AppError extends Error {
constructor(statusCode, message) {
super(message);
this.statusCode = statusCode;
this.status = `${statusCode}`.startsWith('4') ? 'fail' : 'error';
this.isOperational = true;
Error.captureStackTrace(this, this.constructor);
}
}
// 异步函数错误捕获包装器
const catchAsync = fn => {
return (req, res, next) => {
fn(req, res, next).catch(next);
};
};
// 路由处理
app.get('/api/data', catchAsync(async (req, res) => {
const data = await fetchData();
if (!data) {
throw new AppError(404, '数据不存在');
}
res.json(data);
}));
// 404 错误处理
app.use((req, res, next) => {
next(new AppError(404, '找不到请求的资源'));
});
// 全局错误处理中间件
app.use((error, req, res, next) => {
error.statusCode = error.statusCode || 500;
error.status = error.status || 'error';
// 开发环境错误响应
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
res.status(error.statusCode).json({
status: error.status,
error: error,
message: error.message,
stack: error.stack
});
}
// 生产环境错误响应
else {
// 操作型错误:发送给客户端
if (error.isOperational) {
res.status(error.statusCode).json({
status: error.status,
message: error.message
});
}
// 程序型错误:不暴露详细信息
else {
console.error('ERROR 💥', error);
res.status(500).json({
status: 'error',
message: '服务器内部错误'
});
}
}
});
5. 数据库操作错误处理
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// MongoDB 连接错误处理
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/myapp', {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
})
.then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功'))
.catch(error => {
console.error('数据库连接失败:', error);
process.exit(1);
});
// 数据库操作错误处理
async function databaseOperation() {
const session = await mongoose.startSession();
try {
session.startTransaction();
// 执行数据库操作
await Model.create([{ data: 'example' }], { session });
await session.commitTransaction();
} catch (error) {
await session.abortTransaction();
throw error;
} finally {
session.endSession();
}
}
6. 事件触发器错误处理 → events
const EventEmitter = require('events');
class MyEmitter extends EventEmitter {
execute() {
try {
this.emit('start');
// 某些操作
if (error) {
this.emit('error', new Error('操作失败'));
}
this.emit('end');
} catch (error) {
this.emit('error', error);
}
}
}
const myEmitter = new MyEmitter();
// 错误事件监听
myEmitter.on('error', (error) => {
console.error('事件错误:', error);
});
// 其他事件监听
myEmitter.on('start', () => console.log('开始执行'));
myEmitter.on('end', () => console.log('执行完成'));
7. 定时器错误处理
class SafeInterval {
constructor(callback, interval) {
this.callback = callback;
this.interval = interval;
this.timer = null;
}
start() {
this.timer = setInterval(() => {
try {
this.callback();
} catch (error) {
console.error('定时器执行错误:', error);
this.stop(); // 发生错误时停止定时器
}
}, this.interval);
}
stop() {
if (this.timer) {
clearInterval(this.timer);
this.timer = null;
}
}
}
// 使用示例
const safeTimer = new SafeInterval(() => {
// 定时执行的操作
}, 1000);
safeTimer.start();
8. 错误监控和报警
class ErrorMonitor {
constructor() {
this.errors = new Map();
this.threshold = 10; // 错误阈值
this.timeWindow = 60000; // 时间窗口(1分钟)
}
recordError(error) {
const errorKey = error.message;
const now = Date.now();
if (!this.errors.has(errorKey)) {
this.errors.set(errorKey, []);
}
const errorList = this.errors.get(errorKey);
errorList.push(now);
// 清理超出时间窗口的错误记录
const validErrors = errorList.filter(time =>
now - time < this.timeWindow
);
this.errors.set(errorKey, validErrors);
// 检查是否需要报警
if (validErrors.length >= this.threshold) {
this.sendAlert(error, validErrors.length);
}
}
sendAlert(error, count) {
console.error(`警告: 错误 "${error.message}" 在最近1分钟内出现了 ${count} 次`);
// 这里可以添加发送邮件或其他通知的逻辑
}
}
// 使用示例
const errorMonitor = new ErrorMonitor();
process.on('uncaughtException', error => {
errorMonitor.recordError(error);
});
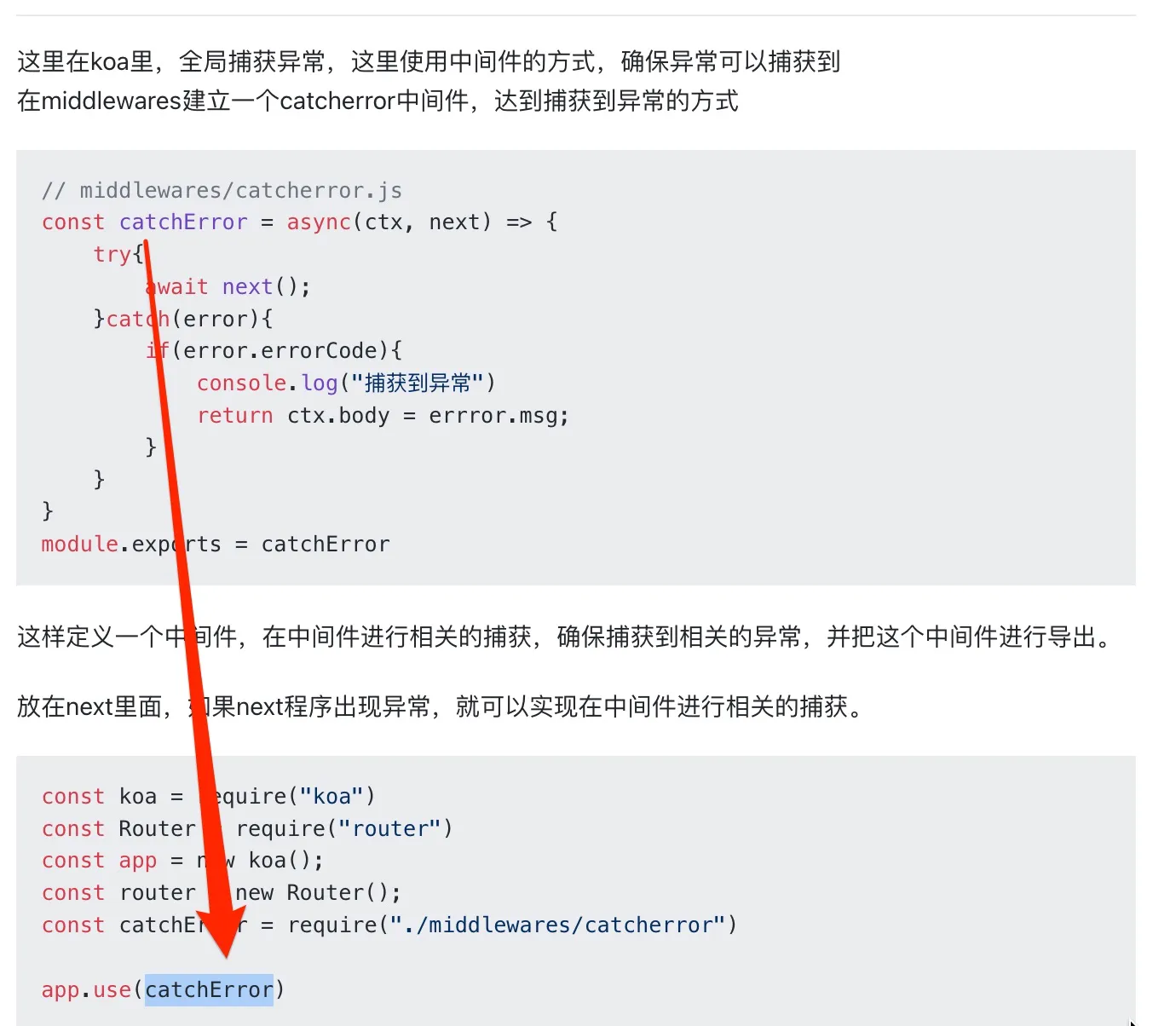
9. 写一个koa中间件,用于捕获相关的异常
10. 总结
- 合理区分开发环境和生产环境的错误处理
- 确保错误被正确记录和监控
- 实现优雅的错误恢复机制
- 避免敏感信息泄露
- 保持应用的稳定性