树的一些基本概念
#算法/二叉树 #算法/树 #算法/数据结构 #2023/04/18
目录
- 1. 二叉树、满二叉树、完全二叉树
- 2. 堆、大顶堆、小顶堆
- 3. 疑问:数据结构中的
堆栈与 内存中的堆栈的区别? - 4. 查找二叉树(二叉搜索树)
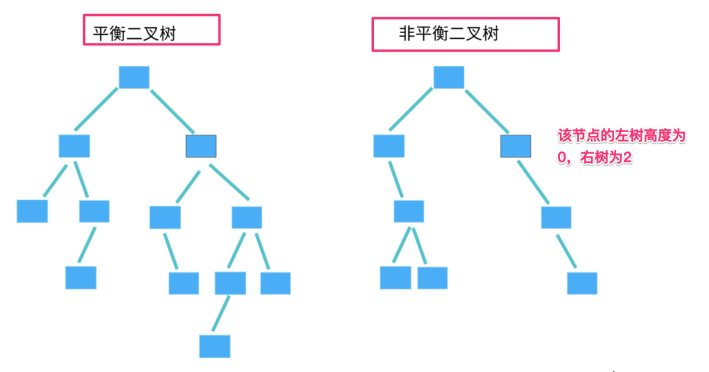
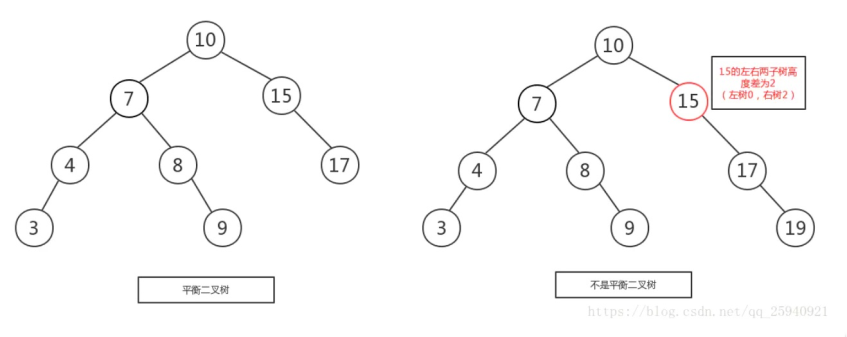
- 5. 平衡二叉查找树
- 6. 二叉树的存储方式
- 7. 数据结构设计 - 实现一个
二叉搜索树
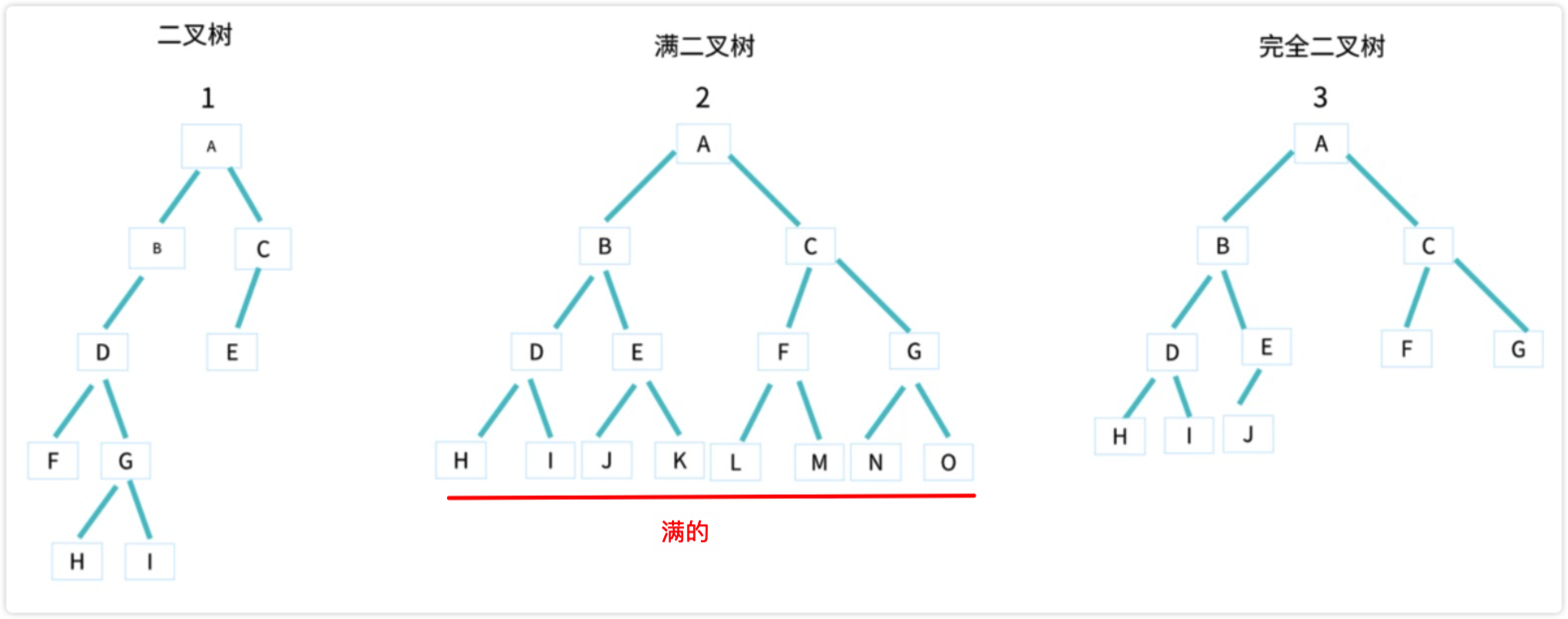
1. 二叉树、满二叉树、完全二叉树
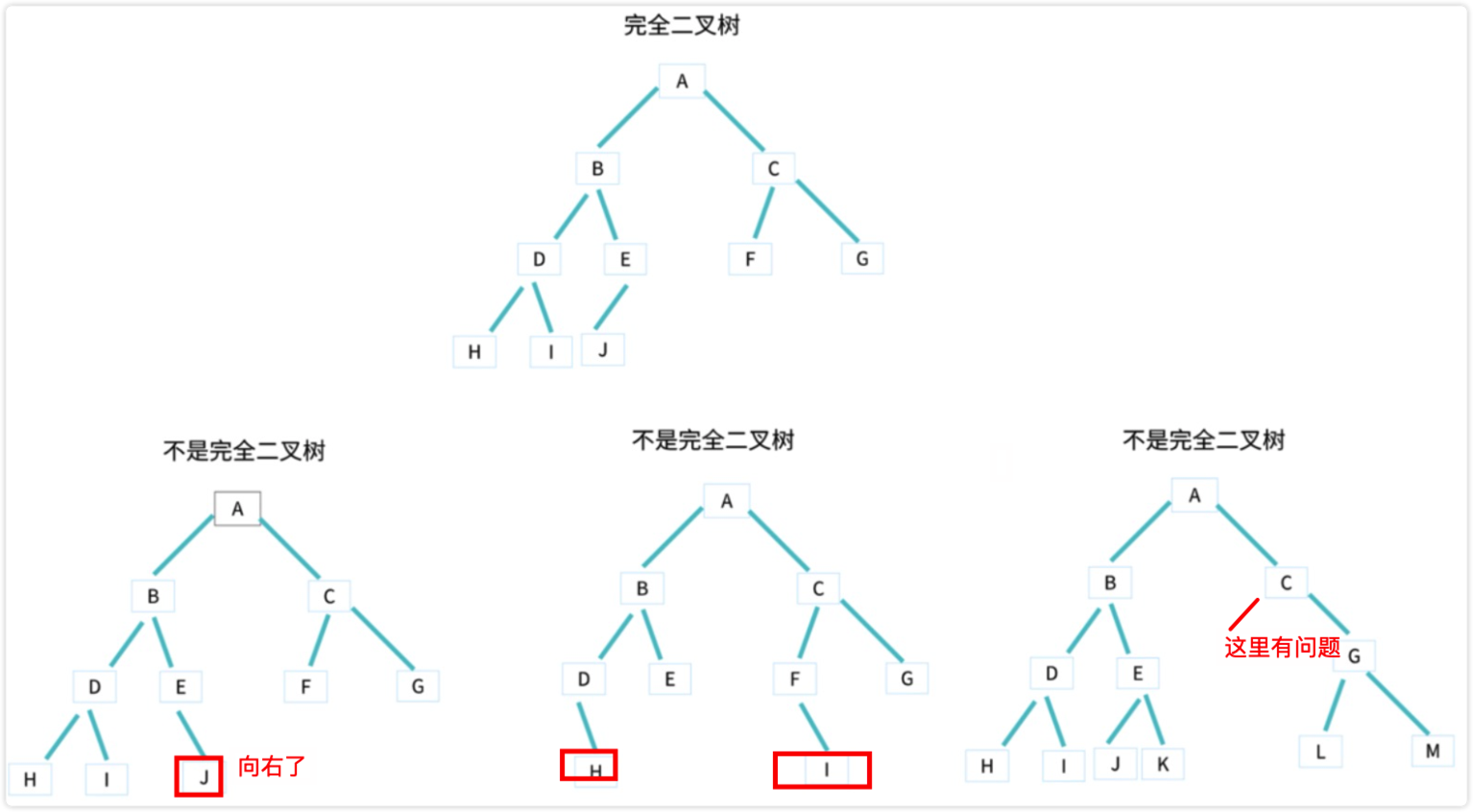
这里着重说下完全二叉树:
- 叶子节点都在
最底下两层 - 最后一层叶子节都靠
左排列 - 并且
除了最后一层,其他层的节点个数都要达到最大
2. 堆、大顶堆、小顶堆
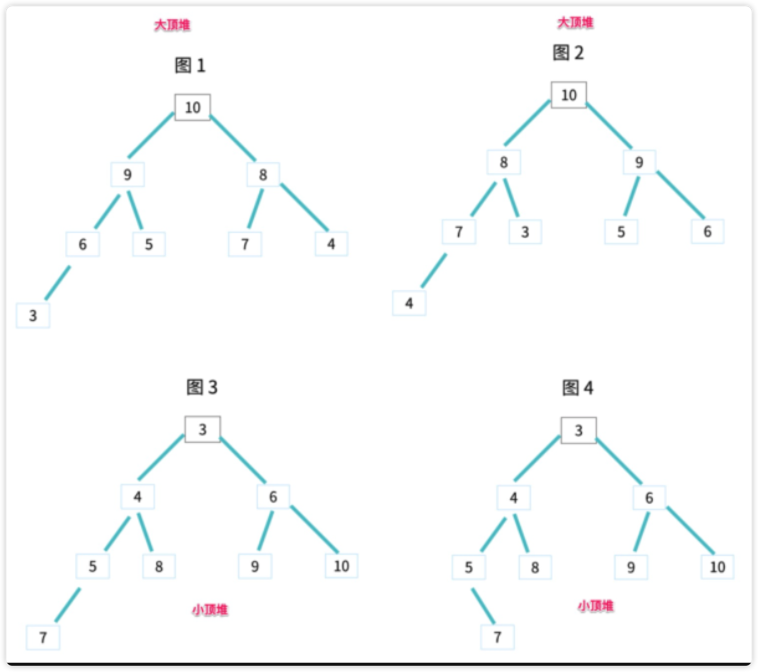
2.1. 堆的基本概念
堆是一个完全二叉树。堆中每个节点的值都大于等于(或者小于等于)其左右子节点的值- 大的再上面,
大顶堆 - 小的再上面,
小顶堆
- 大的再上面,
2.2. 堆的价值
2.2.1. 大顶堆的价值
- 优先队列
- 高效排序
- 高效的动态中位数
2.2.2. 小顶堆的价值
主要价值和应用:
- 优先队列:小顶堆也常用于实现优先队列,支持快速获取和删除最小元素。
- 图算法:在图算法中,小顶堆用于实现 Dijkstra 最短路径算法和 Prim 最小生成树算法,以快速找到权重最小的边或路径。
- 合并有序列表:小顶堆可以高效地合并多个有序列表,例如用于外部排序或归并排序
2.2.2.1. 堆的总体价值
- 高效的插入和删除操作:堆支持
O(log n)的插入和删除操作,使其在需要频繁调整元素顺序的场景中非常高效。 - 内存利用率高:堆是一种基于数组实现的数据结构,内存利用率高,不需要额外的指针或链接。
- 广泛应用:堆在各种算法和系统中有广泛应用,包括调度系统、内存管理、图算法、实时数据处理等。
总之,堆结构因其高效的插入、删除和查找操作,在许多需要维护动态有序集合的场景中具有重要价值。
2.3. 实现一个小顶堆
使用数组来存储,代码如下:
- 关键是
this.head = []来存储
function swap(array, a, b) {
[array[a], array[b]] = [array[b], array[a]];
}
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
// 使用数组来存储
this.heap = [];
}
// 左孩子的索引
getLeftIndex(index) {
return (2 * index) + 1;
}
// 右孩子的索引
getRightIndex(index) {
return (2 * index) + 2;
}
// 父节点的索引
getParentIndex(index) {
if (index === 0) {
return 0;
}
return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
}
// 返回个数
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() <= 0;
}
clear() {
this.heap = [];
}
// ::::小顶堆,最小的肯定在最上面
findMinimum() {
return this.isEmpty() ? null : this.heap[0];
}
// 插入一个值,插入的元素添加到堆底的最后,然后让其上浮到正确位置(如果大顶的话)
insert(value) {
if (value != null) {
const index = this.heap.length;
// 先放在最后一位
this.heap.push(value);
// 父节点向上移动,直到父节点小于插入的值
this.siftUp(index);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 下沉,堆化,递归
siftDown(index) {
// 插入的元素的位置
let element = index;
const left = this.getLeftIndex(index);
const right = this.getRightIndex(index);
const size = this.size();
if (left < size // base 判断
&& this.heap[element] > this.heap[left]
// 如果该元素大于它的左子节点,则下沉
) {
element = left;
}
if (right < size // base判断
&& this.heap[element] > this.heap[left]
// 如果该元素大于它的右子节点,则下沉
) {
element = right;
}
// 如果element 最后 和传入的index不一样了,说明需要交换数据,然后继续下沉递归
if (index !== element) {
swap(this.heap, index, element);
this.siftDown(element);
}
}
// 向上移动,直到父节点的值小于插入的值
siftUp(index) {
let parent = this.getParentIndex(index);
while (
index > 0 // base 判断
&& this.heap[parent] > this.heap[index]) // 父节点的元素大于子元素的时候,才需要移动
{
swap(this.heap, parent, index);
index = parent;
parent = this.getParentIndex(index);
}
}
// delete min 堆顶元素(最小值)和 堆底元素 对调
// 1、删除删除堆顶元素
// 2、让堆底元素沉到正确位置
deleteMin() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
if (this.size() === 1) {
return this.heap.shift();
}
const removedValue = this.heap[0]; // 堆顶元素
const lastElement = this.heap.pop(); // 移除堆底元素
this.heap[0] = lastElement; // 将 堆顶元素 赋值为 堆底元素
// 从堆顶开始下沉
this.siftDown(0);
return removedValue;
}
getAsArray() {
return this.heap;
}
}
let arr = [5, 3, 7, 9, 0, 0, -1, -2, 7, -8];
let heapObj = new MinHeap();
arr.forEach((item) => {
heapObj.insert(item)
})
console.log(heapObj);
console.log('************************')
console.log(heapObj.findMinimum());
// MinHeap { heap: [
// -8, -2, 0, 3, -1,
// 7, 0, 9, 7, 5
// ] }
// ************************
// -8
3. 疑问:数据结构中的堆栈 与 内存中的堆栈 的区别?
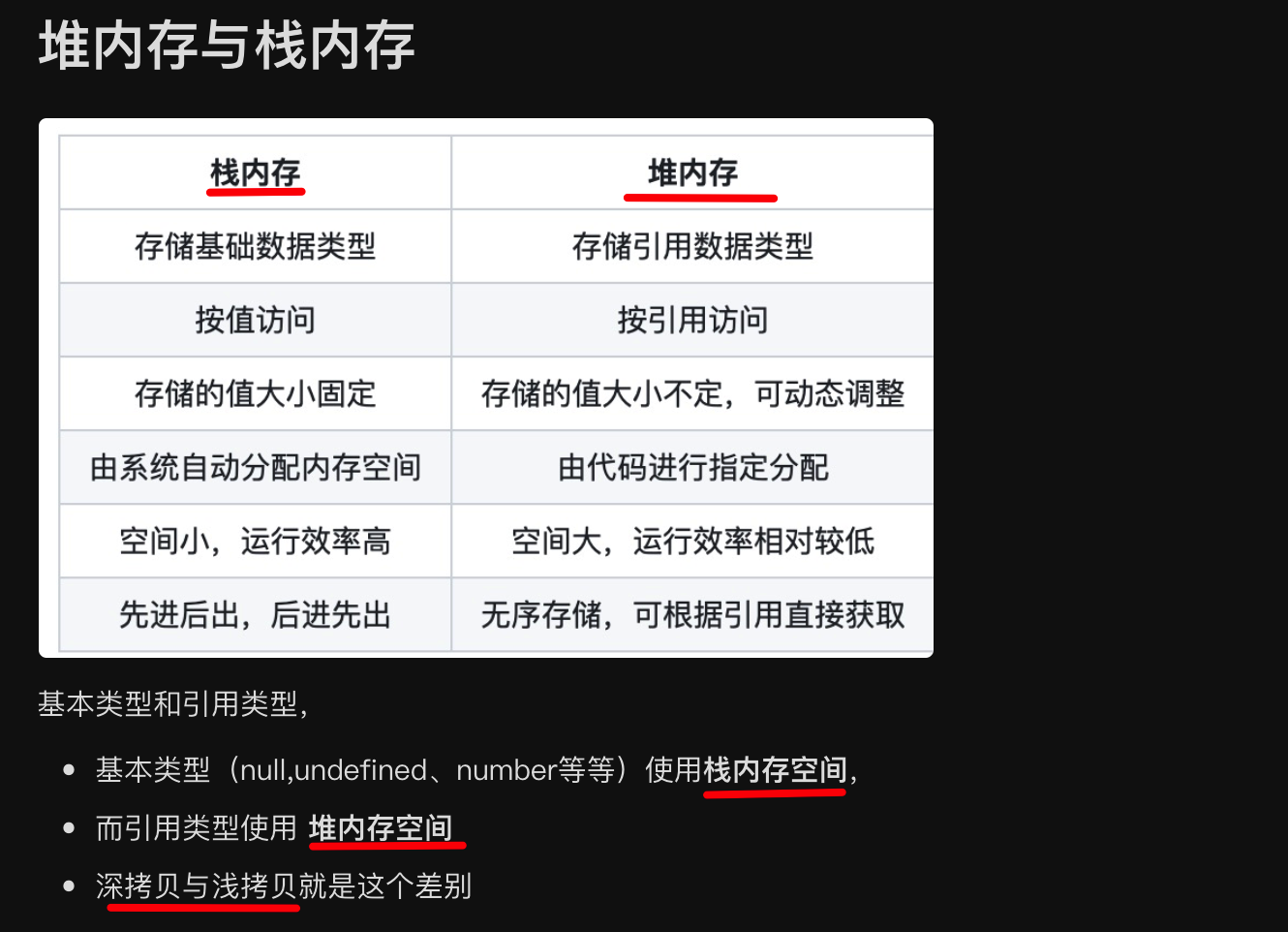

堆内存(Heap Memory)和栈内存(Stack Memory)是计算机内存管理中两种不同的内存分配区域。它们在用途、管理方式、生命周期和性能上有显著区别。以下是它们的主要区别:
3.1. 用途
- 堆内存
- 用于动态分配内存,通常由程序运行时分配和释放。
- 适用于需要在运行时决定大小和生命周期的对象和数据结构,例如动态数组、链表等。
- 栈内存
- 用于静态分配内存,主要用于函数调用、局部变量和函数参数。
- 适用于生命周期明确且较短的变量,例如局部变量和函数参数。
3.2. 管理方式
- 堆内存:
- 内存管理较复杂,容易导致内存泄漏和碎片化问题。
- 由程序员显式分配(如
malloc在 C/C++ 中,new在 C++/Java 中)和释放(如free在 C/C++ 中,垃圾回收在 Java 中)。
- 栈内存:
- 内存管理简单,不会出现内存泄漏问题,但栈空间有限,不能用于大对象或长生命周期对象。
- 由编译器自动管理,内存分配和释放在函数调用和返回时自动进行。
3.3. 生命周期
- 堆内存:
- 对象的生命周期由程序员控制,可以在程序运行过程中动态分配和释放。
- 对象在不再使用后需要显式释放,否则会导致内存泄漏。
- 栈内存
- 对象的生命周期由函数调用栈决定,当函数返回时,栈上的所有局部变量自动销毁。
- 生命周期短暂且明确,不需要显式释放。
3.4. 性能
- 堆内存:
- 动态分配和释放内存的开销较大,因为需要查找合适的内存块,并处理碎片化问题。
- 常见于需要灵活管理内存的大型复杂应用中。
- 栈内存:
- 更适合小型、短生命周期的数据,具有更高的访问速度。
- 内存分配和释放速度快,仅通过移动栈指针即可完成。
3.5. 总结
- 堆内存:适用于动态分配的对象,生命周期由程序员控制,管理复杂但灵活。
- 栈内存:适用于局部变量和函数调用,生命周期短暂且由编译器自动管理,性能高但空间有限。
理解堆和栈的区别对于高效编写和调试代码至关重要,尤其是涉及到内存管理和性能优化时。
4. 查找二叉树(二叉搜索树)
- 一种特殊的二叉树,
较小的值保存在左节点中,较大的值保存在右节点中根节点的左子树都比根节点的值小,右子树的值都比根节点的值大。二叉查找树是一种有序的树,所以支持快速查找、快速插入、删除一个数据
5. 平衡二叉查找树
二叉树中任意一个节点的左右子树的高度相差不能大于 1
6. 二叉树的存储方式
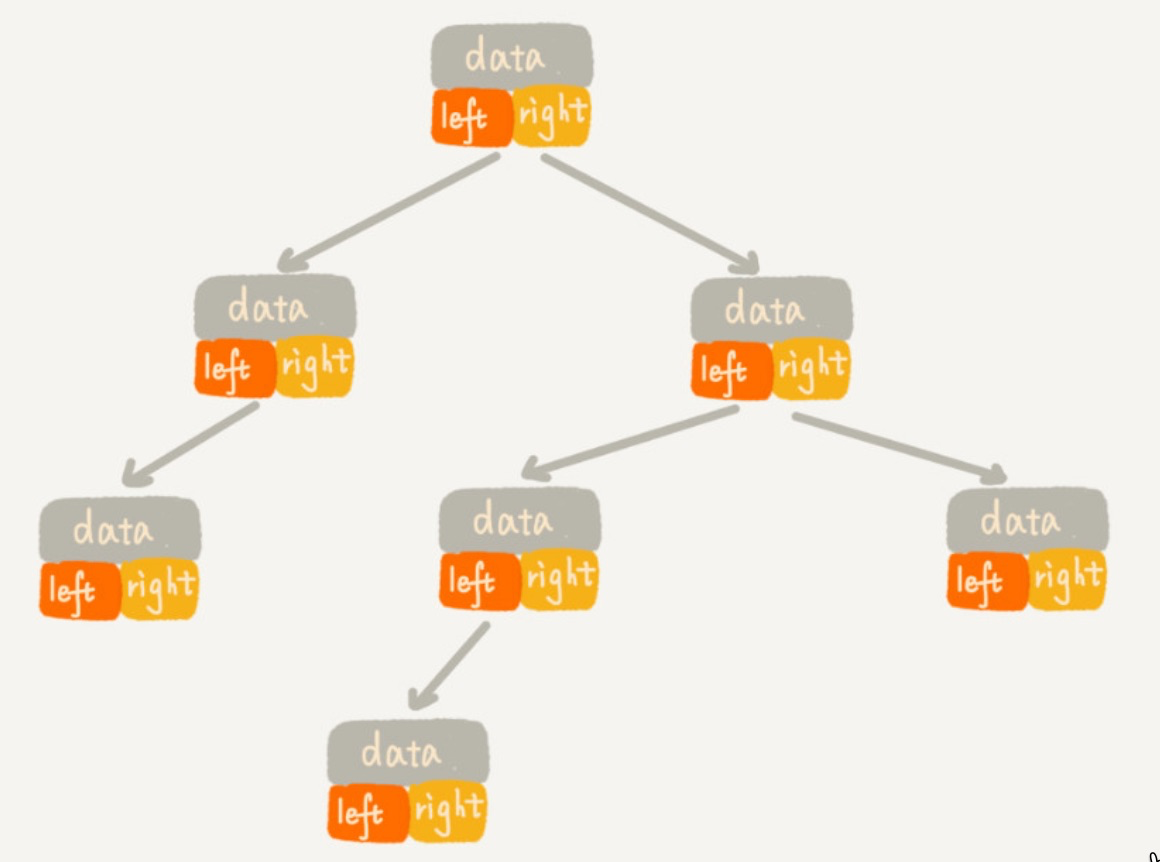
6.1. 链式存储 - 对象
6.2. 顺序存储 - 数组
完全二叉树用数组来存储是最省内存的方式
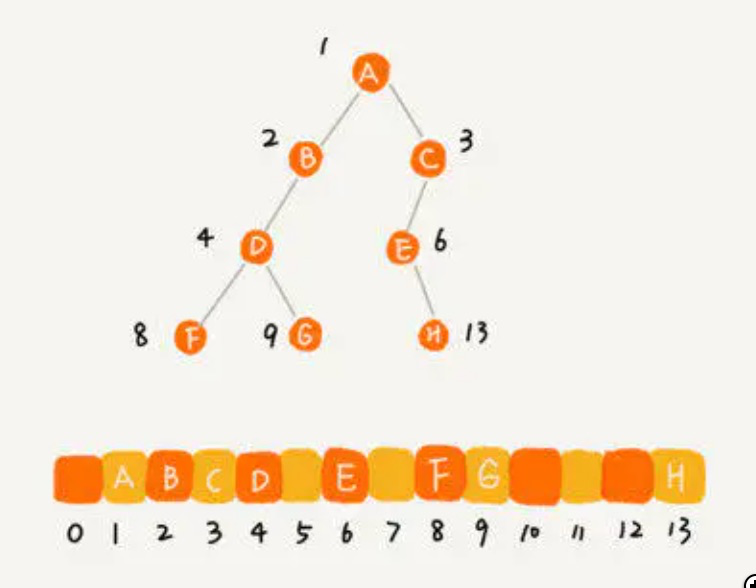
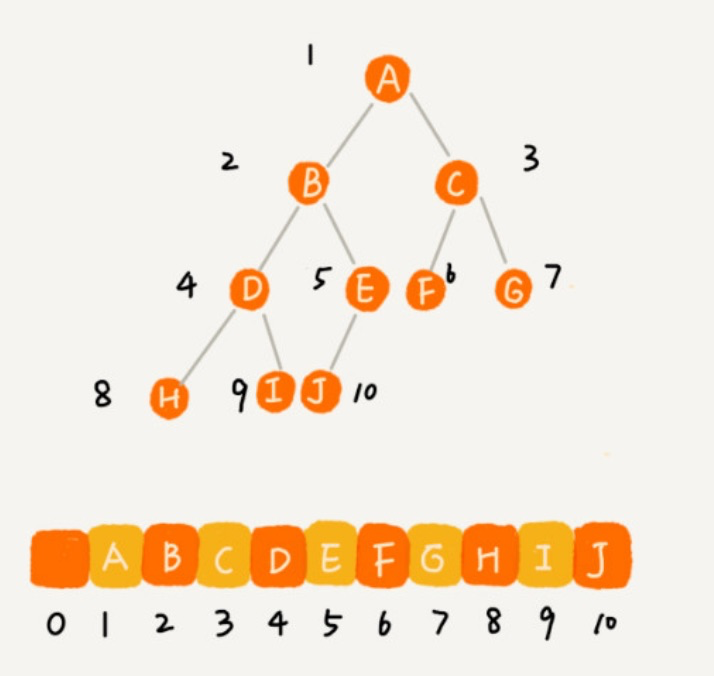 非完全二叉树则会浪费空间,如下图:
非完全二叉树则会浪费空间,如下图:
7. 数据结构设计 - 实现一个二叉搜索树
7.1. 插入节点
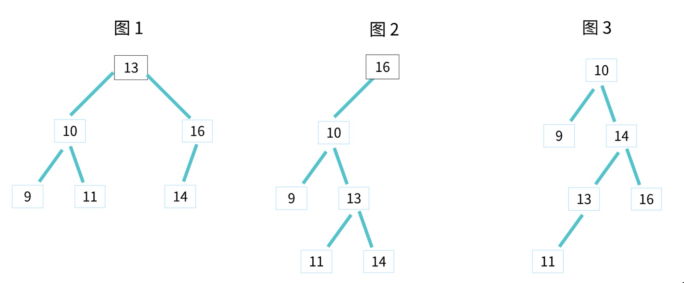
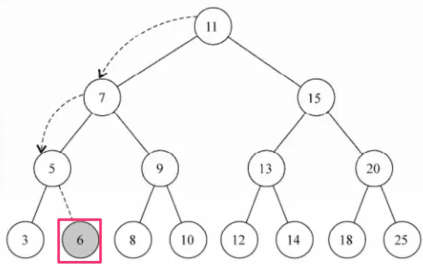
看下面一张图,在下图的树中插入健值为 6 的节点,过程如下:
7.2. 移除节点
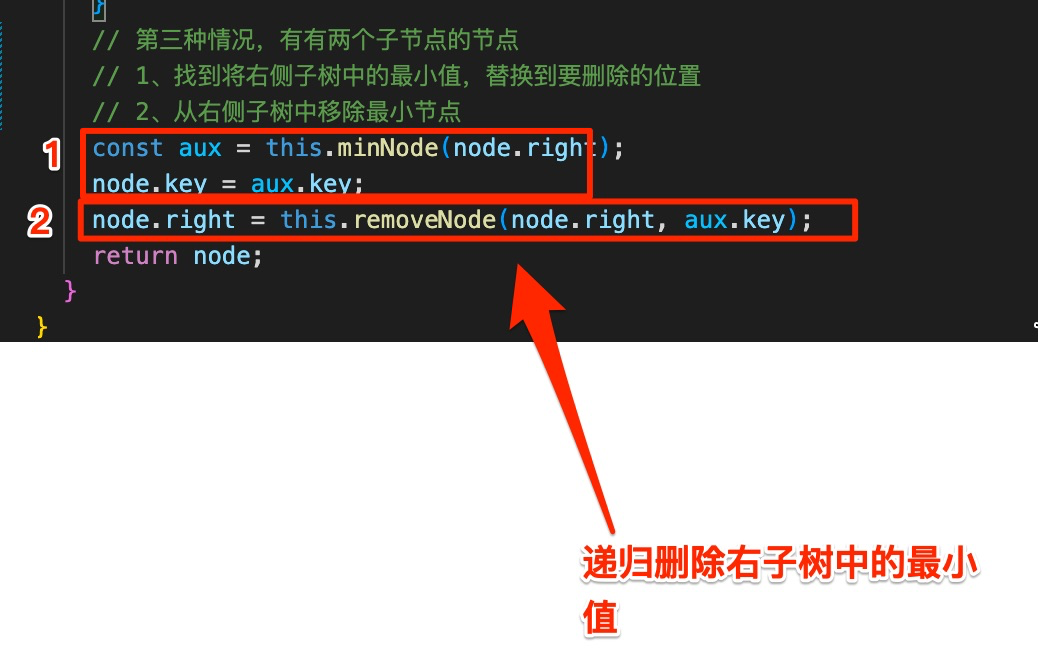
关键看下删除有两个子节点的节点:
1、【该节点与右子树中最小值位置置换】找到将右侧子树中的最小值,替换到要删除的位置
2、 然后 递归 从 从右侧子树中移除最小节点
如下图:

7.3. 代码部分
// node节点类
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.key = key;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
toString() {
return `${this.key}`;
}
}
export default class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
// 向树中插入一个新的键。
insert(key) {
// special case: first key
if (this.root == null) {
this.root = new Node(key);
} else {
// 从root开始遍历查找合适的位置插入
this.insertNode(this.root, key);
}
}
// 遍历树,将插入节点的键值与遍历到的节点键值比较,如果前者大于后者,继续递归遍历右子节点,
// 反之,继续遍历左子节点,直到找到一个空的节点,在该位置插入。
insertNode(node, key) {
// 如果插入节点的键值小于当前节点的键值,则需要插入左边
if (key < node.key) {
// 左节点没有值,则直接插入
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, key);
}
// 否则需要插入右边
} else {
if (node.right == null) {
node.right = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, key);
}
}
}
getRoot() {
return this.root;
}
inOrderTraverse(callback) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
inOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
callback(node.key);
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
preOrderTraverse(callback) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
preOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
callback(node.key);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
postOrderTraverse(callback) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback);
}
postOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
this.postOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
callback(node.key);
}
}
search(key) {
return this.searchNode(this.root, key);
}
// 搜索特定值的处理与插入值的处理类似。遍历树,
// 将要搜索的值与遍历到的节点比较,如果前者大于后者,
// 则递归遍历右侧子节点,反之,则递归遍历左侧子节点。
searchNode(node, key) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
// 如果要查找的值小于该节点,继续递归遍历其左侧节点
if (key < node.key) {
return this.searchNode(node.left, key);
}
// 如果要查找的值大于该节点,继续递归遍历其右侧节点
if (key > node.key) {
return this.searchNode(node.right, key);
}
return true;
}
min() {
return this.minNode(this.root);
}
// 在二叉搜索树里,不管是整个树还是其子树,最小值一定在树最左侧的最底层。
// 因此给定一颗树或其子树,只需要一直向左节点遍历到底就行了。
minNode(node) {
let current = node;
while (current != null && current.left != null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current;
}
max() {
return this.maxNode(this.root);
}
// 搜索最大值与搜索最小值类似,只是沿着树的右侧遍历。
maxNode(node) {
let current = node;
while (current != null && current.right != null) {
current = current.right;
}
return current;
}
// 移除节点,首先要在树中查找到要移除的节点,再判断该节点是否有子节点、有一个子节点或者有两个子节点,最后分别处理。
remove(key) {
// 同样从root开始遍历查找
this.root = this.removeNode(this.root, key);
}
removeNode(node, key) {
// 如果 node 不存在,直接返回
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
// 找到要删除的node
node = this.searchNode(node, key)
// 第一种情况,该节点没有子节点
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
node = null;
return node;
}
// 第二种情况,该节点只有一个子节点的节点
if (node.left == null) {
// 将右子节点替换自己
node = node.right;
return node;
}
if (node.right == null) {
// 将左子节点替换自己
node = node.left;
return node;
}
// 第三种情况,有有两个子节点的节点
// 1、找到将右侧子树中的最小值,替换到要删除的位置
// 2、从右侧子树中移除最小节点
const aux = this.minNode(node.right);
node.key = aux.key;
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, aux.key);
return node;
}
}