调研:Schema 协议设计(amis、schema 设计、事件流、Vdom 等)
#lowcode
目录
- 总结
- 1. Schema 结构设计对比
- 2. AMIS JSON、Vue3 VNode、React JSX VDom 详细对比
- 3. Amis 基本概念&名词解释
- 4. Amis 的事件&动作设计&事件流设计
- 5. Amis 行为
- 6. Amis:class、主题、css变量
- 7. 结论
总结
- vue vdom 结构
- React vdom 结构
- amis
1. Schema 结构设计对比
1.1. 先看看 vue dom 的结构
type VNodeTypes =
| string
| VNode
| Component
| typeof Text
| typeof Static
| typeof Comment
| typeof Fragment
| typeof Teleport
| typeof Suspense;
const vdom = {
type: "div",
props: {
id: "foo",
},
children: [
{
type: "p",
children: "p tag",
},
{
type: "h1",
children: "H1 tag",
},
{
type: "div",
children: [
{
type: "span",
children: "div > span > tag",
},
],
},
],
};
很重要的一个类型:
type=action
1.2. 再看看一段 React Vdom 示例
1.2.1. JSX
import React from 'react';
function Welcome({ name }) {
return <h1>Hello, {name}</h1>;
}
function App() {
return (
<div className="app">
<Welcome name="Alice" />
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<ul>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
</ul>
<button onClick={() => alert('Clicked!')}>Click me</button>
</div>
);
}
1.2.2. 对应 JSON 树结构
{
"type": "div",
"props": {
"className": "app"
},
"children": [
{
"type": "Welcome",
"props": {
"name": "Alice"
}
},
{
"type": "p",
"props": {},
"children": [
"This is a paragraph."
]
},
{
"type": "ul",
"props": {},
"children": [
{
"type": "li",
"props": {},
"children": [
"Item 1"
]
},
{
"type": "li",
"props": {},
"children": [
"Item 2"
]
}
]
},
{
"type": "button",
"props": {
"onClick": {
"__function": "() => alert('Clicked!')"
}
},
"children": [
"Click me"
]
}
]
}
1.3. Amis JSON Schema 结构设计
1.3.1. 示例
{
"type": "page",
"body": {
"type": "form",
"api": "/amis/api/mock2/form/saveForm",
"body": [
{
"type": "input-text",
"name": "name",
"label": "姓名:"
}
]
}
}
是
body不是上面 vdom 的children
1.3.2. schema.ts 结构设计
import {PageSchema} from './renderers/Page';
import {FlexSchema} from './renderers/Flex';
import {TplSchema} from './renderers/Tpl';
// 省略 ....,有多少个amis组件,这里就应该多少个 import schema
// 每加个类型,这补充一下。
export type SchemaType =
| 'form'
| 'alert'
| 'app';
export type SchemaObject =
| PageSchema
| FlexSchema
| TplSchema
// 省略 ....,有多少个amis组件,这里就应该多少个 SchemaObject ;
export type SchemaCollection =
| SchemaObject
| SchemaTpl
| Array<SchemaObject | SchemaTpl>;
export interface SchemaApiObject {
method?: 'get' | 'post' | 'put' | 'delete' | 'patch' | 'jsonp' | 'js';
url: SchemaUrlPath;
data?: {
[propName: string]: any;
};
convertKeyToPath?: boolean;
responseData?: {
[propName: string]: any;
};
attachDataToQuery?: boolean;
dataType?: 'json' | 'form-data' | 'form';
responseType?: 'blob';
headers?: {
[propName: string]: string | number;
};
/**
* 设置发送条件
*/
sendOn?: SchemaExpression;
replaceData?: boolean;
autoRefresh?: boolean;
trackExpression?: string;
cache?: number;
forceAppendDataToQuery?: boolean;
qsOptions?: {
arrayFormat?: 'indices' | 'brackets' | 'repeat' | 'comma';
indices?: boolean;
allowDots?: boolean;
};
silent?: boolean;
downloadFileName?: string;
}
export type SchemaApi = string | SchemaApiObject;
- 每个类型(
type) 的组件都有一个详细 Schema 结构来描述- 详细的
Schema来描述,因为这个后面会直接影响到编辑态的展示
- 详细的
1.3.3. 比如 type = action 时
export interface Action extends Button {
actionType?:
| 'submit'
| 'copy'
| 'reload'
| 'ajax'
| 'saveAs'
| 'dialog'
| 'drawer'
| 'jump'
| 'link'
| 'url'
| 'email'
| 'close'
| 'confirm'
| 'add'
| 'remove'
| 'delete'
| 'edit'
| 'cancel'
| 'next'
| 'prev'
| 'reset'
| 'validate'
| 'reset-and-submit'
| 'clear'
| 'clear-and-submit'
| 'toast'
| 'goto-step'
| 'goto-image'
| 'expand'
| 'collapse'
| 'step-submit'
| 'selectAll'
| 'changeTabKey'
| 'click'
| 'stopAutoRefresh'
| 'preview'
| 'zoom';
api?: SchemaApi;
asyncApi?: SchemaApi;
payload?: any;
dialog?: SchemaNode;
to?: string;
target?: string;
link?: string;
url?: string;
cc?: string;
bcc?: string;
subject?: string;
body?: string;
mergeData?: boolean;
reload?: string;
messages?: {
success?: string;
failed?: string;
};
feedback?: any;
required?: Array<string>;
[propName: string]: any;
}
1.3.4. 通用字段
- type
- data 表示数据,另外有数据链的概念
- classname
- style
- hidden / hiddenOn:表达式
- visible / visibleOn:表达式
- SchemaArray:即
body: [schem1,schema2], - classname
"className": {
"text-muted": "${status == 1}",
"text-success": "${status == 2}",
"text-${status}": true
}
- api
{
"type": "crud",
"api": {
"url": "/amis/api/mock2/sample",
"method": "post",
"graphql": "{ pages(page: $page, perPage: $perPage) { id, engine } }",
"data": {
"page": "${page}",
"perPage": "${perPage}"
}
},
"columns": [
{
"name": "id",
"label": "ID"
},
{
"name": "engine",
"label": "Rendering engine"
}
]
}
Definitions建立当前页面公共的配置项,在其他组件中可以通过$ref来引用当前配置项中的内容
- 下面
aa可以服用 - 下面
option枚举项可以复用
{
"definitions": {
"options":[],
"aa": {
"type": "input-text",
"name": "jack",
"value": "ref value",
"labelRemark": "通过<code>\\$ref</code>引入的组件"
}
},
"type": "page",
"title": "引用",
"body": [
{
"type": "form",
"api": "api/xxx",
"actions": [],
"body": [
{
"$ref": "aa"
}
]
}
]
}
2. AMIS JSON、Vue3 VNode、React JSX VDom 详细对比
2.1. 基础结构对比
| 特性 | AMIS JSON | Vue3 VNode | React JSX VDom |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基本格式 | 纯 JSON 对象 | JavaScript 对象 | JavaScript 对象 |
| 节点类型 | type 字段指定 | type 属性 | type 属性 |
| 属性定义 | props 对象 | props 对象 | props 对象 |
| 子节点 | body/items 数组 | children 数组 | children 属性 |
2.2. 属性处理
| 特性 | AMIS JSON | Vue3 VNode | React JSX VDom |
|---|---|---|---|
| 样式处理 | className/style 对象 | class/style 对象 | className/style 对象 |
| 事件绑定 | onEvent | on + 大写事件名 | on + 大写事件名 |
| 自定义属性 | 直接在对象中定义 | attrs 对象 | data-* 属性 |
2.3. 组件特性
| 特性 | AMIS JSON | Vue3 VNode | React JSX VDom |
|---|---|---|---|
| 组件复用 | “$ref” 引用 | 组件实例 | React.memo/PureComponent |
| 状态管理 | data 字段 | reactive/ref | useState/useReducer |
| 生命周期 | 通过 api 配置 | setup/生命周期钩子 | useEffect 等 hooks |
2.4. 渲染流程
| 阶段 | AMIS JSON | Vue3 VNode | React JSX VDom | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 解析 | JSON 解析器 | 模板编译 | JSX 转换 | |
| 更新 | 数据驱动 | 响应式系统 | 虚拟 DOM diff | |
| 渲染 | 渲染引擎 | render 函数 | render 方法 | |
2.5. 数据绑定示例
{
"type": "text",
"value": "${username}",
"visibleOn": "this.show"
}
{
type: 'div',
props: {
innerHTML: state.username,
'v-show': show
}
}
{
type: 'div',
props: {
children: username,
style: {
display: show ? 'block' : 'none'
}
}
}
2.6. 条件渲染
| AMIS JSON | Vue3 VNode | React JSX VDom |
|---|---|---|
| visibleOn/hiddenOn | v-if/v-show | 条件表达式 |
{
"type": "div",
"visibleOn": "this.show"
}
{
type: 'div',
props: {
'v-if': show
}
}
show && {
type: 'div',
props: {}
}
2.7. 列表渲染
{
"type": "repeat",
"items": {
"type": "tpl",
"tpl": "${item}"
},
"source": "${items}"
}
{
type: 'Fragment',
children: items.map(item => ({
type: 'div',
key: item.id,
props: {
innerHTML: item.text
}
}))
}
{
type: 'Fragment',
props: {
children: items.map(item => ({
type: 'div',
key: item.id,
props: {
children: item.text
}
}))
}
}
3. Amis 基本概念&名词解释
- 完全通过
JSON 树配置出页面、应用- 有一个组件就叫做
APP,有个字段pages来承载所有页面
- 有一个组件就叫做
- 数据与数据域
- 首先会先尝试在当前组件的数据域中寻找变量,当成功找到变量时,通过数据映射完成渲染,停止寻找过程;
- 当在当前数据域中没有找到变量时,则向上寻找,在父组件的数据域中,重复步骤
1和2; - 一直寻找,直到顶级节点,也就是
page节点,寻找过程结束。 - 但是如果 url 中有参数,还会继续向上查找这层,所以很多时候配置中可以直接
${id}取地址栏参数。
- 数据域数据更新
- 通常顶层数据域数据更新,孩子中具备数据域的组件都会更新,但更新代价大,性能差
- 可配置
trackExpressiontrackExpression配置成"none"也就是说不追踪任何数据。trackExpression配置成"${xxxVariable}"这样xxxVariable 变化了更新当前组件的数据链。
- 模板,内部采用 lodash template 实现
{
"data": {
"text": "World!"
},
"type": "page",
"body": "<h1>Hello</h1> <span>${text}</span>"
}
- 数据映射
- 链式取值
- 支持
& - 目前有以下三种
namespacewindow即全局变量ls即 localStorage, 如果值是 json 对象,可以直接当对象用比如:${ls:xxxxxlocalStrorageKey.xxxx}ss即 sessionStorage,同上。cookie即 cookies,同上
- 过滤器&管道
- 定义管道:
amisLib.registerFilter
- 定义管道:
- 表达式,记得使用
loadsh和moment
{
"type": "tpl",
"tpl": "当前作用域中变量 show 是 1 的时候才可以看得到我哦~",
"visibleOn": "${show === 1}"
}
- 联动
visibleOndisabledOn- 接口联动一般只适用于初始化接口,例如:
form组件中的initApi;select组件中的source选项源接口url,data只能用于主动联动;"source": "/amis/api/mock2/options/level2?a=${a}",a 变化就会发请求
service组件中的api和schemaApi;crud组件中的api;- crud 默认是跟地址栏联动,如果要做请关闭同步地址栏 syncLocation: false
- 等等…
3.1. 主动触发
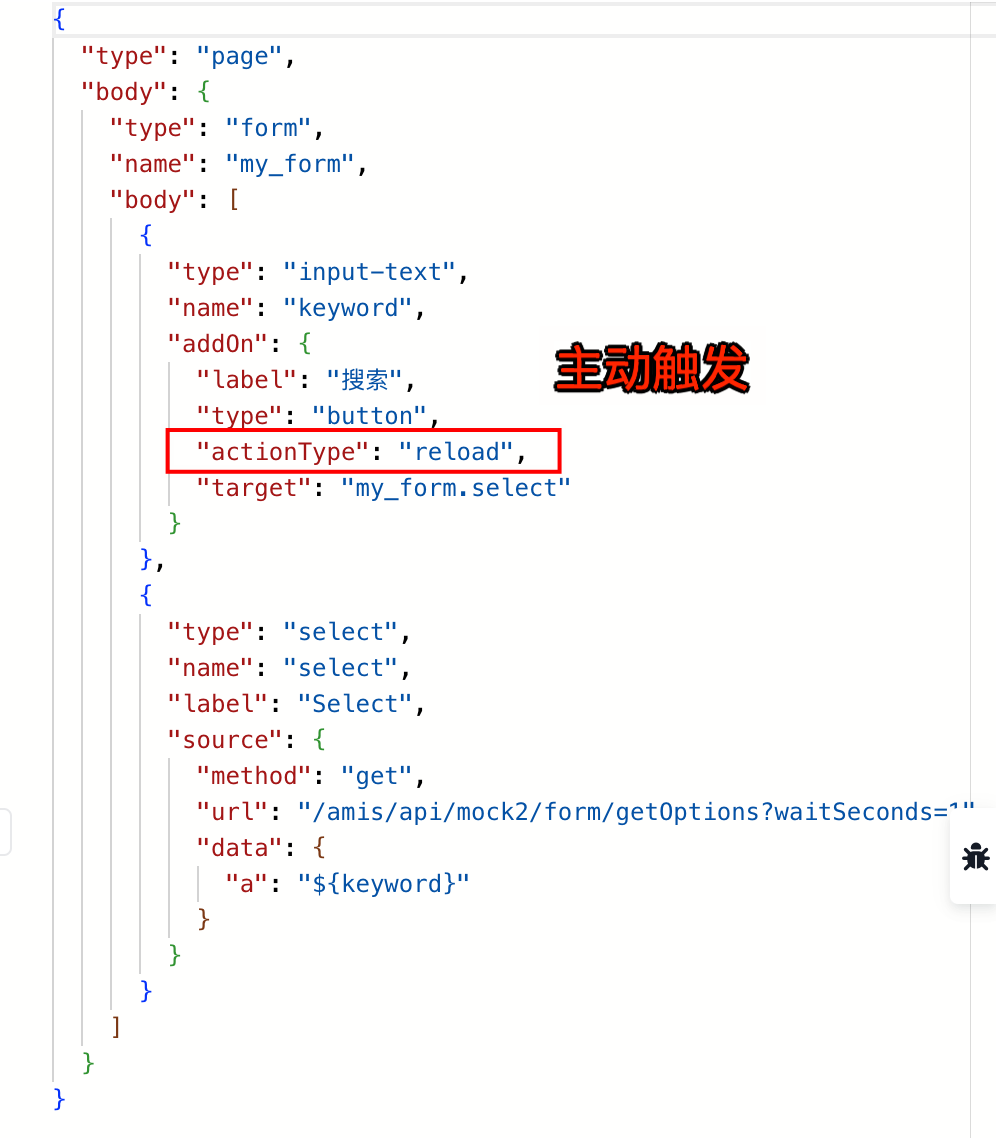
3.2. 发送指定数据
target属性支持通过配置参数来发送指定数据,例如:"target" :"xxx?a=${a}&b=${b}",这样就会把当前数据域中的a变量和b变量发送给目标组件 xxx
3.3. 刷新目标组件
{
"type": "action",
"actionType": "reload",
"label": "刷新目标组件",
"target": "target1,target2"
}
3.4. 发送动态目标
- 刷新目标支持表达式,比如目标的
name可以配置成form-${ xxx ? '1' : '2'}
4. Amis 的事件&动作设计&事件流设计
- 解决复杂的 UI 交互场景,支持渲染器事件监听和响应设计,无需关心组件层级关系
4.1. 属性表
| 属性名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| actionType | string | - | 动作名称 |
| args | object | - | 动作属性{key:value},支持数据映射 |
| data | object | - | 追加数据{key:value},支持数据映射,如果是触发其他组件的动作,则该数据会传递给目标组件,> 2.3.2 及以上版本 |
| dataMergeMode | string | ‘merge’ | 当配置了 data 的时候,可以控制数据追加方式,支持合并(merge)和覆盖(override)两种模式,> 2.3.2 及以上版本 |
| preventDefault | boolean|表达式|ConditionBuilder | false | 阻止事件默认行为,> 1.10.0 及以上版本支持表达式,> 2.9.0 及以上版本支持ConditionBuilder |
| stopPropagation | boolean|表达式|ConditionBuilder | false | 停止后续动作执行,> 1.10.0 及以上版本支持表达式,> 2.9.0 及以上版本支持ConditionBuilder |
| expression | boolean|表达式|ConditionBuilder | - | 执行条件,不设置表示默认执行,> 1.10.0 及以上版本支持表达式,> 2.9.0 及以上版本支持ConditionBuilder |
| outputVar | string | - | 输出数据变量名 |
| ignoreError | boolean | false | 当动作执行出错后,是否忽略错误继续执行。3.3.1 及以上版本支持 |
4.2. onEvent
onEvent-click-actions:[]
{
"type": "button",
"label": "尝试点击、鼠标移入/移出",
"level": "primary",
"onEvent": {
"click": { // 监听点击事件
"actions": [ // 执行的动作列表
{
"actionType": "toast", // 执行toast提示动作
"args": { // 动作参数
"msgType": "info",
"msg": "派发点击事件"
}
}
]
},
"mouseenter": {{ // 监听鼠标移入事件
"actions": [
{
"actionType": "toast",
"args": {
"msgType": "info",
"msg": "派发鼠标移入事件"
}
}
]
},
"mouseleave": {{ // 监听鼠标移出事件
"actions": [
{
"actionType": "toast",
"args": {
"msgType": "info",
"msg": "派发鼠标移出事件"
}
}
]
}
}
}
4.3. 获取上下文
执行动作时,可以通过${event.data}获取事件对象的数据、通过${__rendererData}获取组件当前数据域
{
"type": "input-text",
"name": "age",
"label": "年龄:",
"onEvent": {
"change": {
"actions": [
{
"actionType": "toast",
"args": {
"msg": "${__rendererData|json}"
}
}
]
}
}
}
4.4. 事件类型
事件包含渲染器事件和广播事件。
- 渲染器事件,由具体的渲染器组件提供,每个渲染器组件暴露的事件可以查看具体的组件文档的事件表;
- 广播事件,即
自定义事件,可以自定义派发的事件名称eventName,其他渲染器可以监听该自定义事件并配置响应动作。- 动作包含
通用动作、组件动作、广播动作、自定义动作,可以通过配置actionType来指定具体执行什么动作。
- 动作包含
4.5. 请求 ajax
"expression": "${event.data.responseResult.responseStatus === 0}"仅在这个条件才显示 toast- 当配置
silent: true时,请求完成后不会弹出提示信息 - 点击按钮,校验表单:
- 通过
"${event.data.validateResult.payload.name}"来校验
- 通过
{
"type": "page",
"data": {
"name": "lll"
},
"body": [
{
"type": "button",
"id": "b_001",
"label": "发送 Ajax 请求",
"level": "primary",
"confirmText": "确认要发出这个请求?",
"onEvent": {
"click": {
"actions": [
{
"actionType": "ajax",
"api": {
"url": "/amis/api/mock2/form/saveForm?name=${name}",
"method": "post",
"responseData": {
"resId": "${id}"
},
"messages": {
"success": "成功了!欧耶",
"failed": "失败了呢。。"
},
// `silent: true`
},
"data": {
"age": 18
}
},
{
"actionType": "toast",
"expression": "${event.data.responseResult.responseStatus === 0}",
"args": {
"msg": "${event.data.responseResult|json}"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
动作属性
| 属性名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| api | API | - | 接口配置 |
| options | object | - | 其他配置 |
| messages | {success: string, failed: string} | - | 请求成功/失败后的提示信息 |
其他属性
| 属性名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| outputVar | string | - | 请求响应结果缓存在${event.data.responseResult}或${event.data.{outputVar}} |
4.6. 弹窗
- 通过配置
actionType: 'dialog'实现 Dialog 弹窗 - 通过配置
actionType: 'closeDialog'实现关闭当前弹窗; - 附加配置
componentId可以实现关闭指定弹窗。
button->onEnvent->click->actions->actionType
{
"type": "page",
"body": [
{
"type": "button",
"className": "ml-2",
"label": "打开弹窗(模态)",
"level": "primary",
"onEvent": {
"click": {
"actions": [
{
"actionType": "dialog",
"dialog": {
"type": "dialog",
"title": "模态弹窗",
"id": "dialog_001",
"data": {
"myage": "22"
},
"body": [
{
"type": "tpl",
"tpl": "<p>对,你打开了模态弹窗</p>",
"inline": false
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
| 属性名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| dialog | string/DialogObject | - | 指定弹框内容,格式可参考Dialog |
| waitForAction | boolean | - | 是否等待弹窗响应,开启后将等待弹窗操作 |
| outputVar | string | - | 输出数据变量名, 输出数据格式为 {confirmed: boolean; value: any[]},当 waitForAction 开启时才有用 |
4.7. 抽屉
类似于弹窗
4.8. 动作属性(args)
| 属性名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| msgType | string | "info" | 消息类型 info|success|error|warning |
| msg | string | - | 消息内容 |
| position | string | top-center(移动端为center) | 提示显示位置 top-right|top-center|top-left|bottom-center|bottom-left|bottom-right|center |
| closeButton | boolean | false | 是否展示关闭按钮 |
| showIcon | boolean | true | 是否展示图标 |
| timeout | number | 5000(error类型为6000,移动端为3000) | 持续时间 |
4.9. 链接跳转
通过配置actionType: 'url'或actionType: 'link'实现链接跳转
| 属性名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | string | - | 按钮点击后,会打开指定页面。可用 ${xxx} 取值 |
| blank | boolean | false | 如果为 true 将在新 tab 页面打开 |
| params | object | - | 页面参数{key:value},支持数据映射,> 1.10.0 及以上版本 |
4.10. 浏览器
- 通过配置
actionType: 'goBack'实现页面回退。 - 通过配置
actionType: 'goPage'实现浏览器页面的前进/后退。只有当历史记录中存在目标页面时才会生效。 - 通过配置
actionType: 'refresh'实现浏览器刷新。
4.11. 打印
"actionType": "print",
4.12. 一个异步串行场景
vue中的做法是,
setEventData可以 通过它来设置setGlocalsetPageDate等等来修改 vue pinia的数据
{
"onEvent": {
"click": {
"actions": [
{
"actionType": "wait",
"args": {
"time": 3000
}
},
{
"actionType": "setEventData",
"args": {
"key": "title",
"value": "页面标题:${window:document[title]}"
}
},
{
"actionType": "toast",
"args": {
"msg": "${title}"
}
}
]
}
}
}
4.13. 自定义 JS
- 通过配置
actionType: 'custom'实现自定义 JS- JS 中可以访问以下对象和方法:
- context,渲染器上下文
- doAction() 动作执行方法,用于调用任何
actionType指定的动作 - event,事件对象,可以调用 setData()、stopPropagation()、preventDefault() 分别实现事件上下文设置、动作干预、事件干预,可以通过 event.data 获取事件上下文
自定义函数签名: script:(context,doAction,event)=>{}
{
"type": "page",
"body": [
{
"type": "button",
"label": "发送一个 http 请求",
"level": "primary",
"onEvent": {
"click": {
"actions": [
{
"actionType": "custom",
"script": "doAction({actionType: 'ajax', args: {api: '/amis/api/mock2/form/saveForm'}});\n //event.stopPropagation();"
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
看看源码部分
// 外部可以直接调用doAction来完成动作调用
// 可以通过上下文直接编排动作调用,通过event来进行动作干预
let result = await (scriptFunc as any)?.call(
proxy,
renderer,
(action: ListenerAction) => runActions(action, renderer, event),
event,
action
);
调用的方式
{
"actions": [
{
"componentId": "u:52cd013e120f",
"actionType": "disabled"
},
{
// promise的方式
"script": "return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {event.setData({...event.data, pId: '01027359'});resolve();}, 3000)})",
// callback的方式 thunk function
"script": "return (callback) => { setTimeout(() => {event.setData({...event.data, pId: '01027359' });callback();}, 3000) };",
"actionType": "custom"
},
{
"componentId": "u:e47e2c8e6be8",
"args": {
"value": "${pId}"
},
"actionType": "setValue"
},
{
"componentId": "u:52cd013e120f",
"actionType": "enabled"
}
]
}
4.13.1. 事件流数据覆盖
有时在执行自定义 JS 的时候,希望该过程中产生的数据可以分享给后面的动作使用,此时可以通过event.setData()来实现事件上下文的设置,这样后面动作都可以通过事件上下文来获取共享的数据。
注意:直接调用event.setData()将修改事件的原有上下文,如果不希望覆盖可以通过event.setData({...event.data, ...{xxx: xxx}})来进行数据的合并。
4.14. 触发指定组件动作
通过配置componentId或componentName来触发指定组件的动作(不配置将调用当前组件自己的动作),组件动作配置通过args传入(> 1.9.0 及以上版本),动作参数请查看对应的组件的动作表,更多示例请查看组件事件动作示例。
4.14.1. 示例
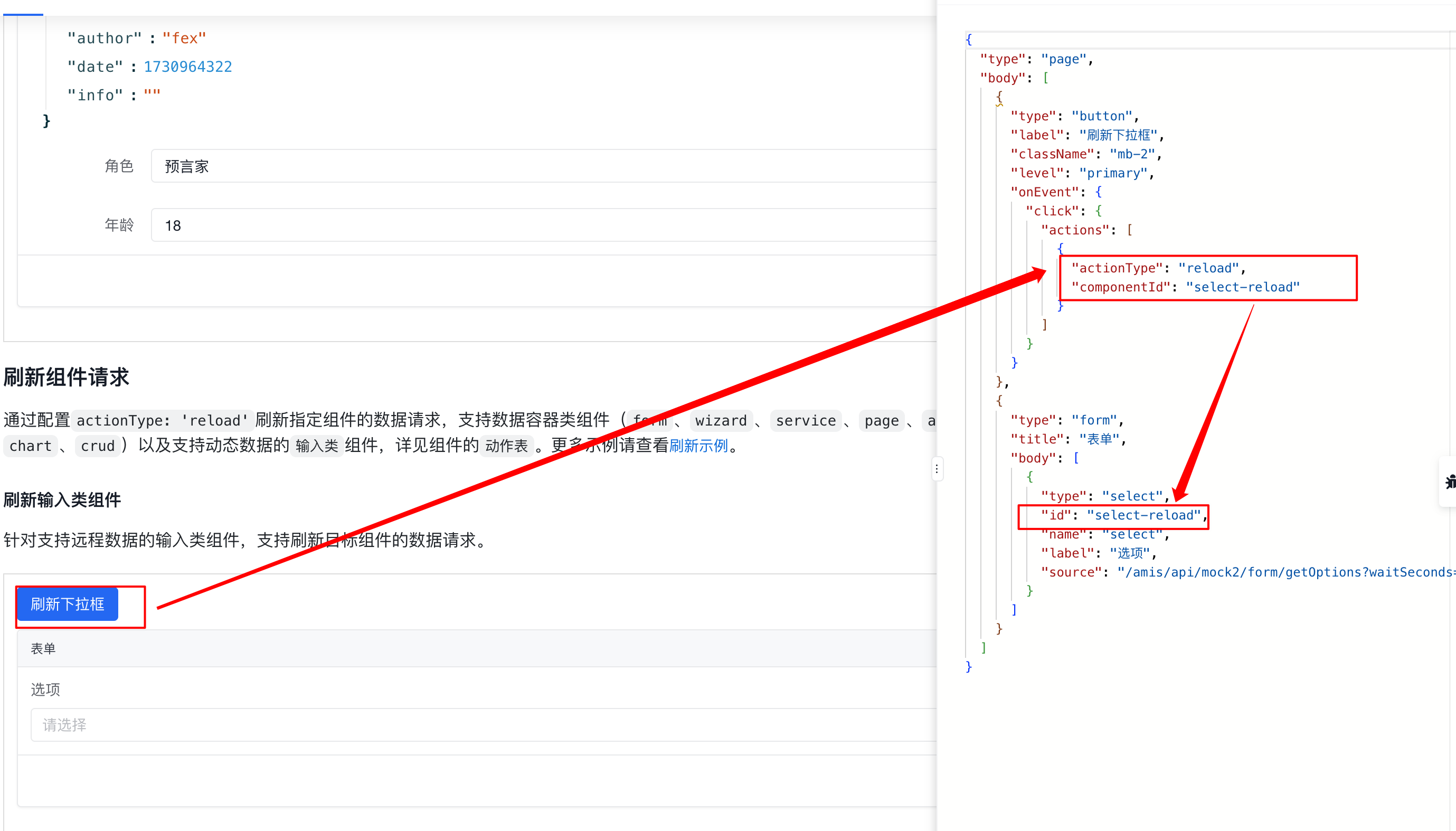
4.14.2. 修改 组件状态
通过配置actionType: 'show'或'hidden'或'enabled'或'disabled'或'static'或'nonstatic'实现对指定组件的显示、隐藏、启用、禁用,仅支持实现了对应状态控制功能的数据输入类组件。
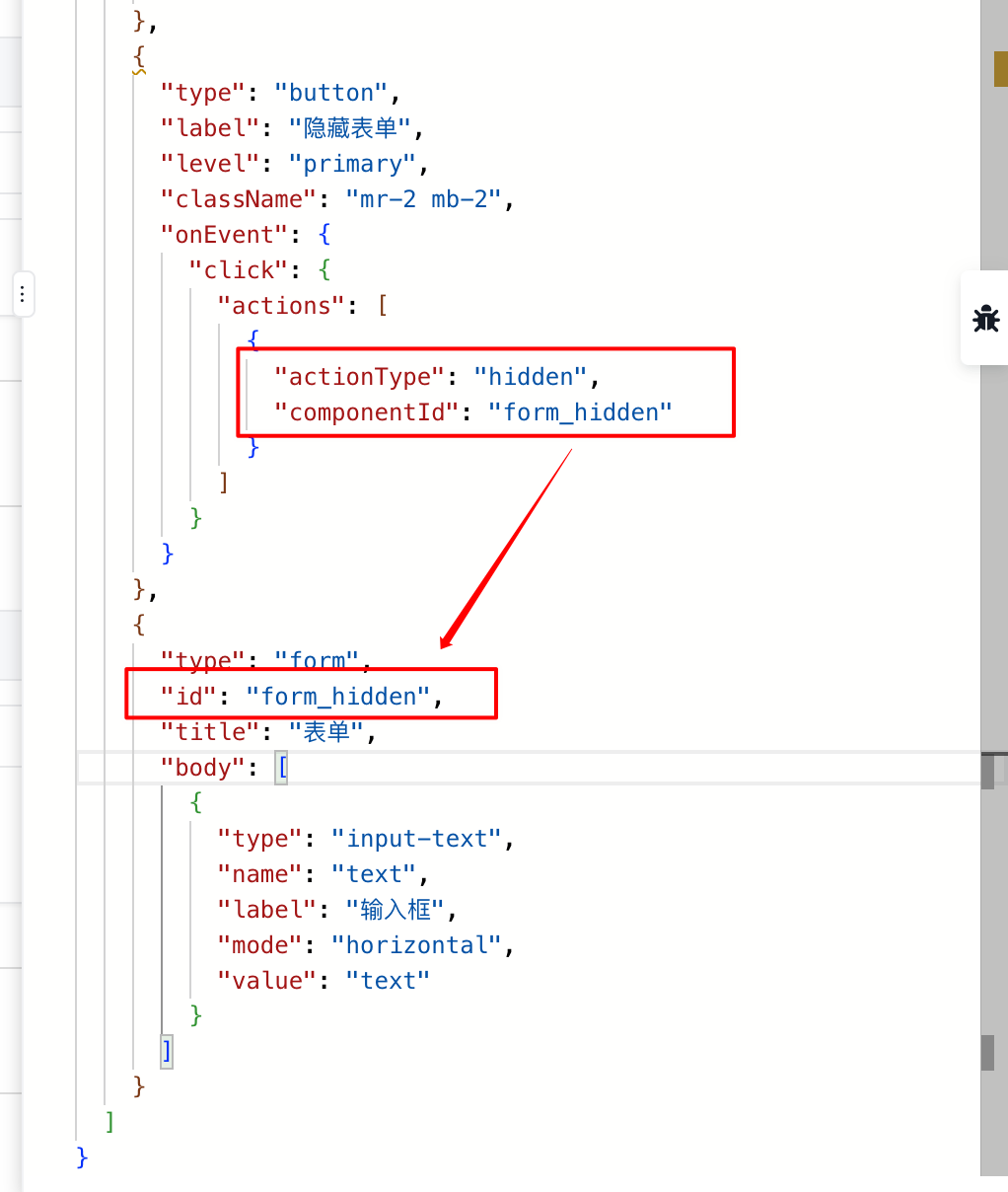
4.14.3. 刷新 CRUD 列表
{
"actions": [
{
"componentId": "crud_id-1",
"actionType": "reload",
"data": { // 还可以穿参数,取决于 crud 的实现
"author": "${author}"
}
}
]
}
4.14.4. 切换到具体 Tab
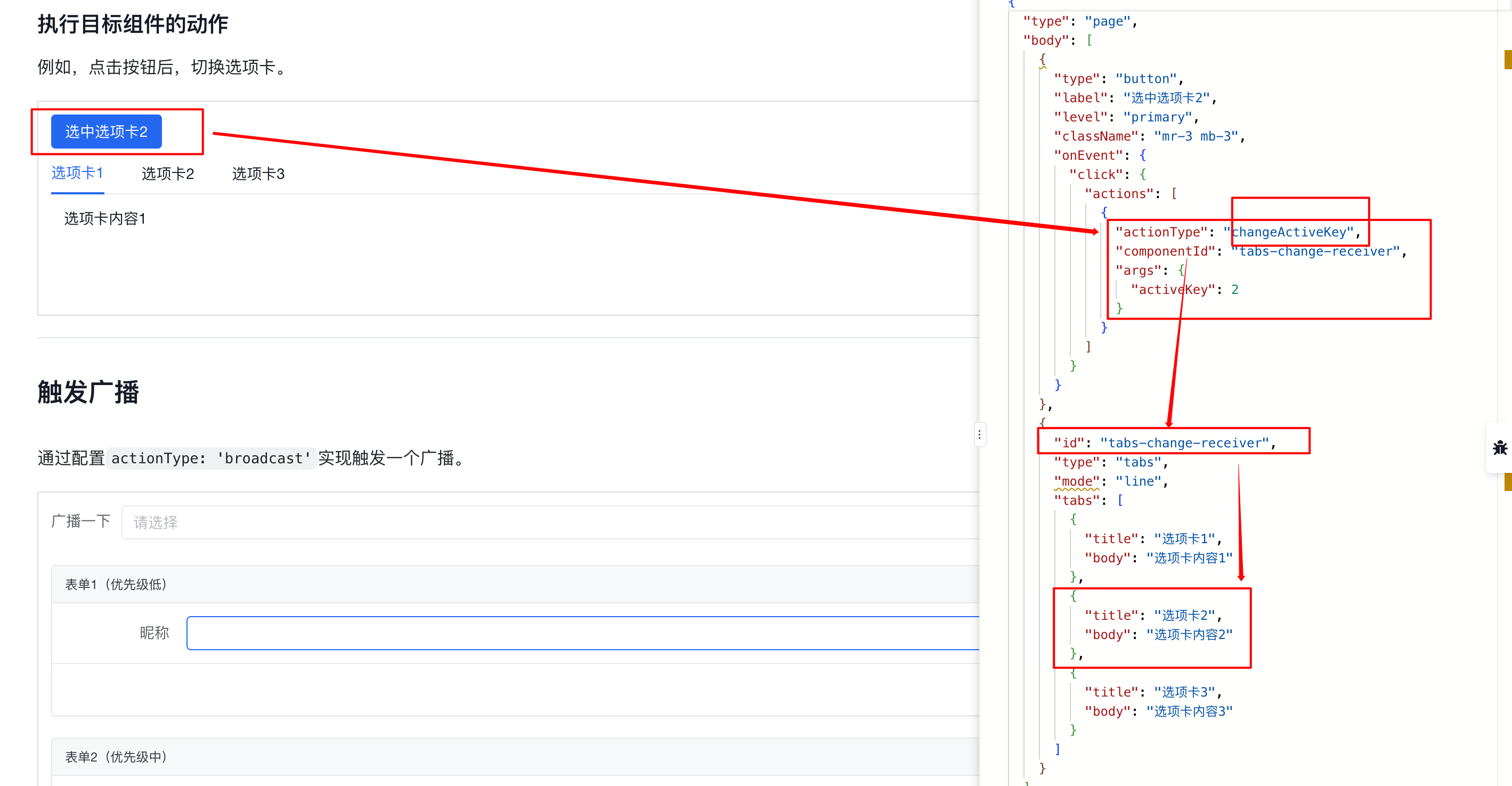
4.15. 注册自定义动作:RendererAction 中注册
除了以上内置动作,你还可以注册自己的动作。
- 通过对
RendererAction的run方法的实现可以定制自己的动作逻辑,最后通过registerAction注册到 amis 事件动作中。
import {
ListenerAction,
ListenerContext,
registerAction,
RendererAction
} from 'amis-core';
import {RendererEvent} from 'amis-core';
// 动作定义
interface IMyAction extends ListenerAction {
actionType: 'my-action';
args: {
param1: string, // 动作参数1
param2: string // 动作参数2
};
}
/**
* 我的动作实现
*/
export class MyAction implements RendererAction {
run(action: IMyAction, renderer: ListenerContext, event: RendererEvent<any>) {
const props = renderer.props;
const {param1, param2} = action.args;
// 你的动作逻辑
// ...
}
}
// 注册自定义动作
registerAction('my-action', new MyAction());
4.16. 触发广播
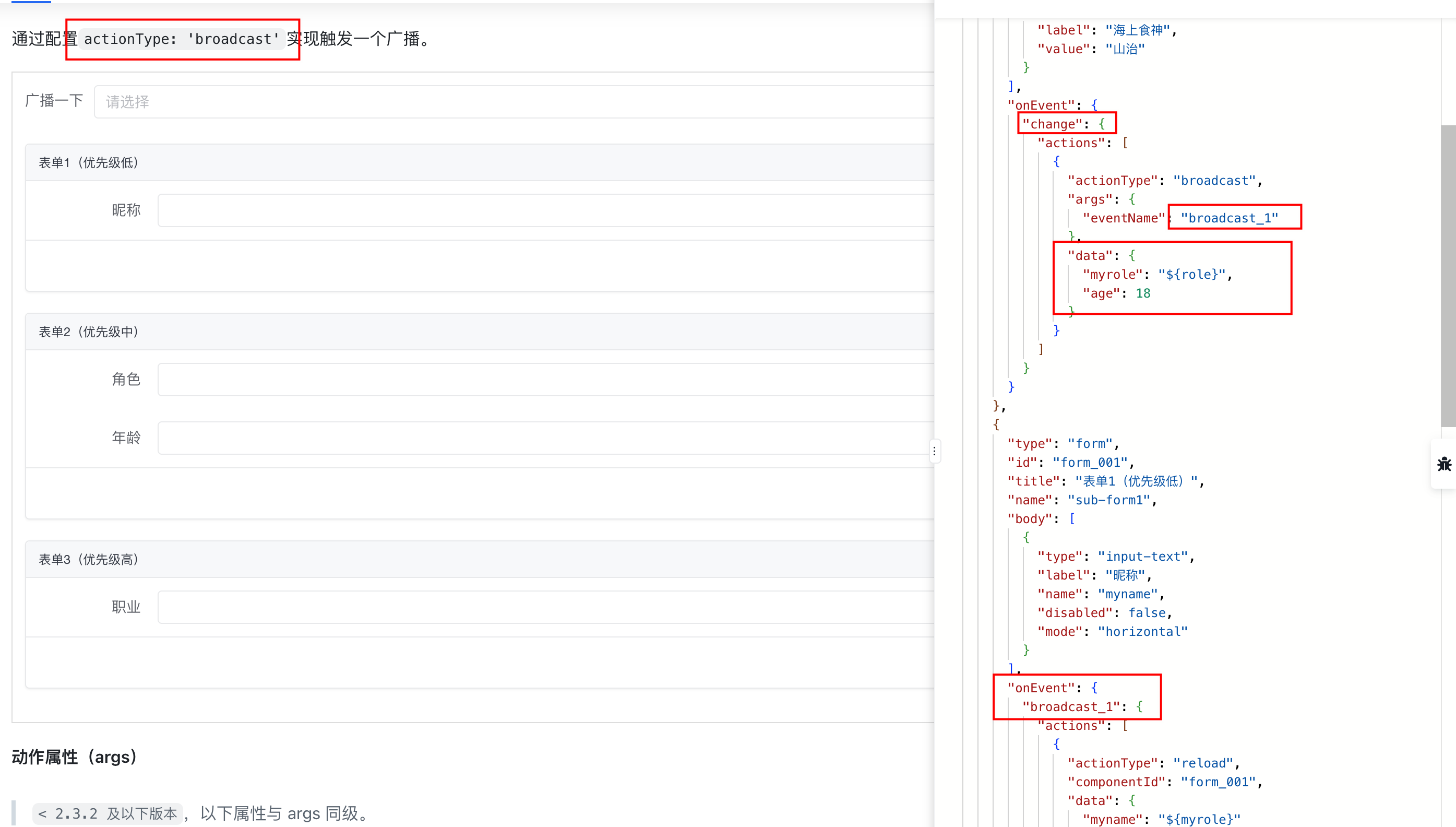
4.17. 编排事件&动作
events 和 actions 需要作区分
4.17.1. 条件与循环
- 通过配置
expression: 表达式或ConditionBuilder组合条件来实现条件逻辑 - 通过配置
actionType: 'loop'实现循环逻辑
{
"actions": [
{
"componentId": "crud_reload",
"actionType": "reload",
"data": {
"author": "${author}"
}
},
// 仅在 expression 表达式为真时,才会触发 toast
{
"actionType": "toast",
"args": {
"msgType": "success",
"msg": "expression表达式 ok~"
},
"expression": "expression === \"okk\""
},
// 循环发送两次请求,且每次携带了循环的数据
{
"actionType": "loop",
"args": {
"loopName": "${loopName}"
},
"children": [
{
"actionType": "ajax",
"args": {
"api": "/amis/api/mock2/form/saveForm?name=${name}&age=${age}"
}
}
]
}
]
}
- 嵌套循环,
- 注意配置
children
- 注意配置
- 通过配置
actionType: 'loop'和actionType: 'break'实现循环跳出。 - 通过配置
actionType: 'loop'和actionType: 'continue'实现循环跳过。 - 通过配置
actionType: 'switch'实现排他逻辑。 - 通过配置
actionType: 'parallel'实现并行执逻辑。- children
子动作 - 比如同时发送两个 ajax 请求,并显示请求返回
- children
所以本质是一棵树,里面有
children等属性,但要注意的是,action 上下文数据是有连贯性的
4.18. 动作间的事件传递
1、事件触发开始,整个数据流包含事件本身产生的事件数据和动作产生的动作数据,事件源头产生的数据在 AMIS 事件动作机制底层已经自动加入渲染器数据域,可以通过xxx直接获取
比如
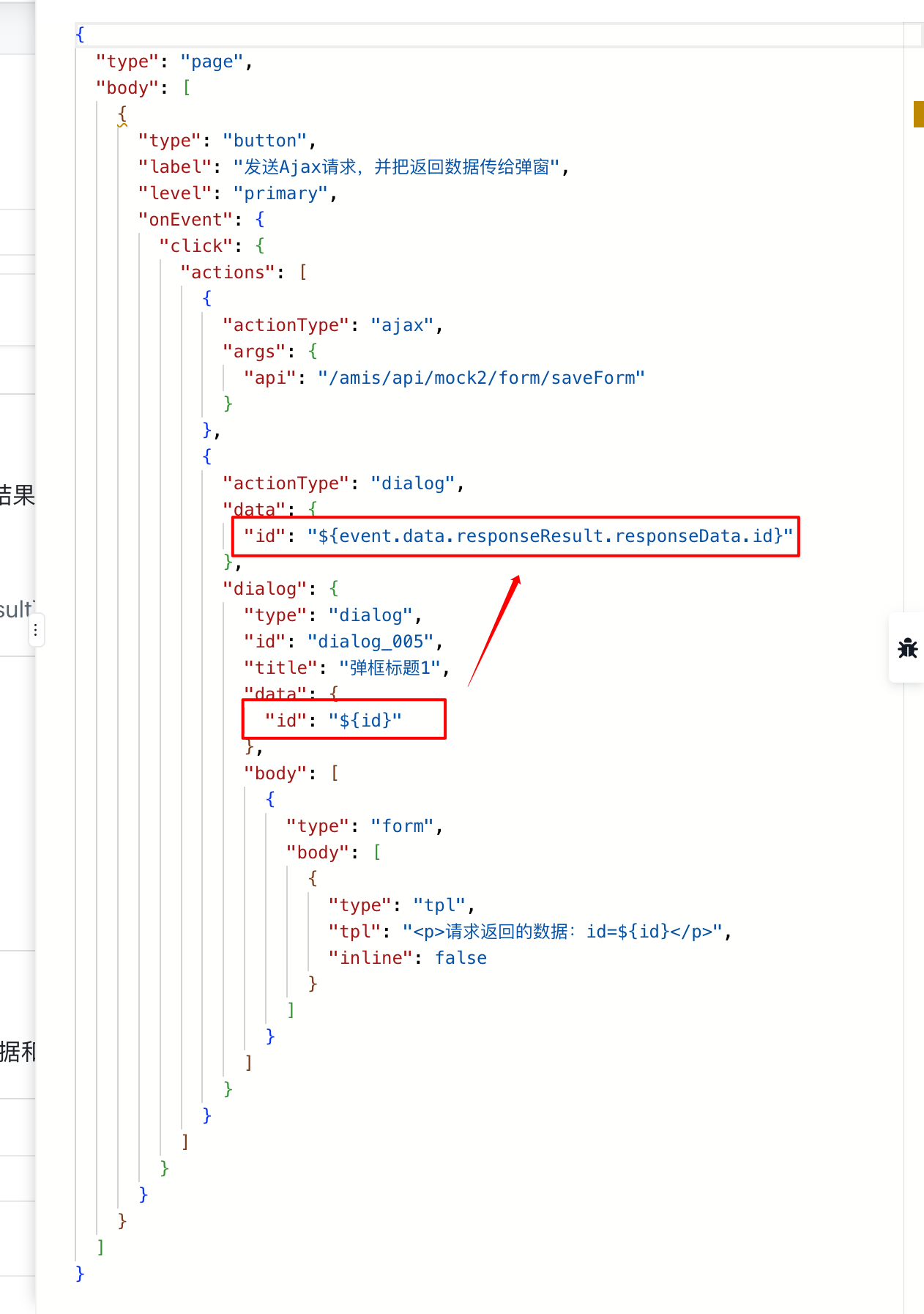
events → click →
actions:[] (可编排)
2、部分动作产生的数据如何流动需要交互设计者进行介入,对于数据流动可以通过数据映射,将上一个动作产生的数据作为动作参数写入下一个动作
3、可以通过表达式函数GETRENDERERDATA(id, path)和GETRENDERERPROP(id, path)分别获取指定组件的数据和属性
| 参数名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| id | 组件 ID,即组件的 id 属性的值 |
| path | 数据路径,即数据变量的路径 |
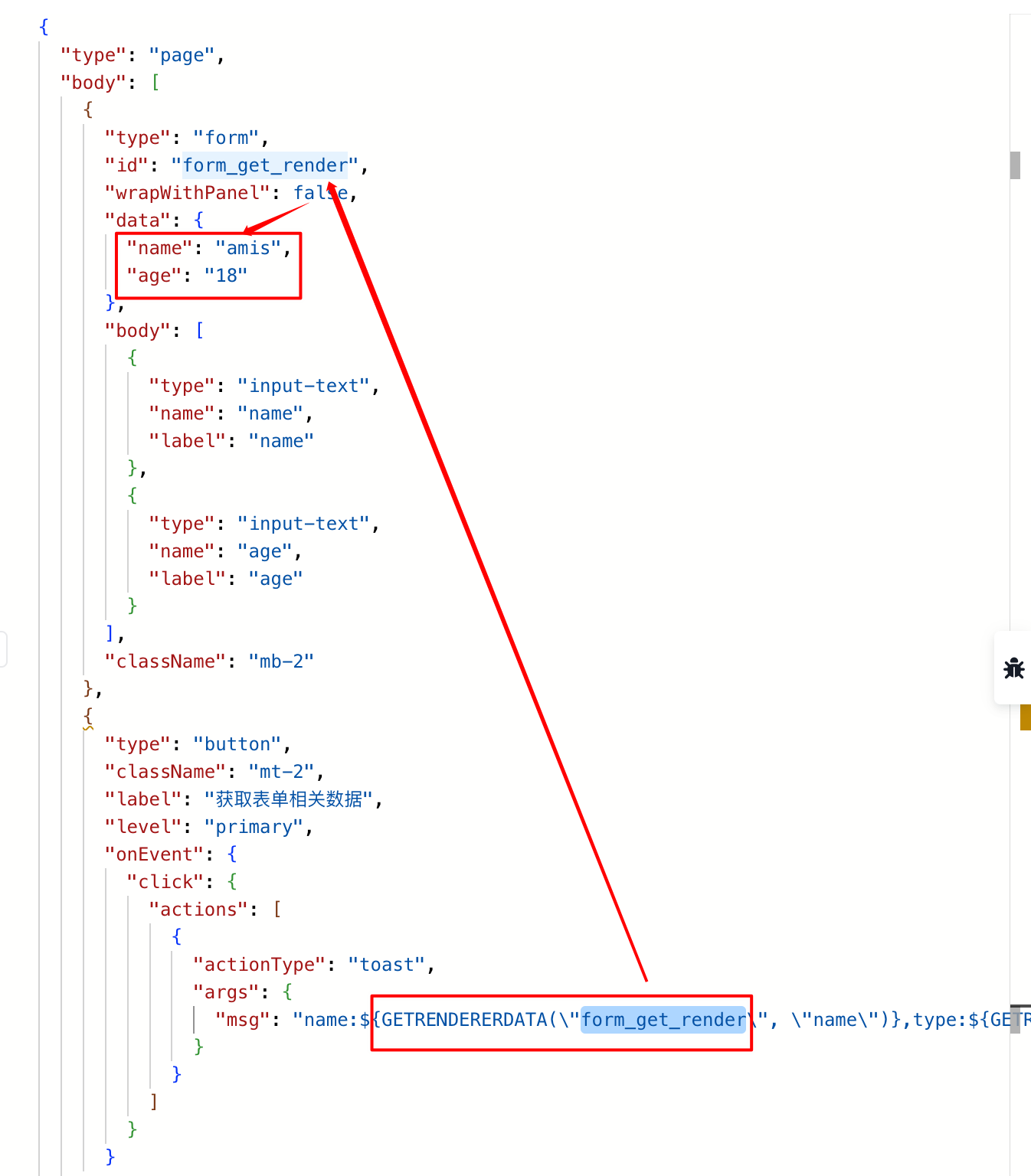
同样的,vue 是可以直接拿到全局数据的,从这种模板里面
4.19. 干预动作执行
事件动作干预是指执行完当前动作后,干预所监听事件默认处理逻辑和后续其他动作的执行。
- 通过
preventDefault、stopPropagation分别阻止监听事件默认行为和停止下一个动作执行。
4.19.1. 阻止默认行为
{
"actions": [
{
"actionType": "toast",
"args": {
"msg": "不关闭"
},
"preventDefault": "command === \"Do not close\""
}
]
}
通过表达式
{
"confirm": {
"actions": [
{
"actionType": "preventDefault",
"expression": "${command === 'Do not close'}"
}
]
}
}
4.19.2. 停止后续动作执行
通过onEvent可以对监听的事件配置一组动作,这些动作是顺序执行的,有时间设计者希望执行某个/些动作后就停止继续执行后面的动作,这时候可以通过stopPropagation来停止执行后面配置的所有动作。
编辑代码
{
"actions": [
{
"actionType": "toast",
"args": {
"msgType": "info",
"msg": "动作1"
}
},
{
"actionType": "toast",
"args": {
"msgType": "info",
"msg": "动作2"
},
"stopPropagation": true
},
{
"actionType": "toast",
"args": {
"msgType": "info",
"msg": "动作3",
"position": "top-right"
}
}
]
}
或者通过表达式
{
"actionType": "stopPropagation",
"expression": "${command === 'Do not close'}"
}
4.19.3. 忽略动作报错继续执行
可以通过
ignoreError: true来忽略动作报错继续执行后面的动作
5. Amis 行为
页面的交互操作,例如:提交表单、显示一个弹框、跳转页面、复制一段文字到粘贴板等等操作,都可以视作页面的一种行为。
在 amis 中,大部分 行为 是跟 行为按钮组件 进行绑定的,也就是说,当你想要配置一个行为,大部分情况下你应该遵循下面的步骤:
- 添加一个 行为按钮组件;
- 配置当前 行为类型(actionType);
- 根据当前行为类型,配置你想要的 属性。
更多见 Action 按钮组件
6. Amis:class、主题、css变量
- amis 中有大量的
功能类 class可以使用 - 即主题,css 变量等
7. 结论
- amis 使用 vue 实现的可能性分析 ?
- 可以参考啊
- 理论上没什么问题的
- 本质是:
- 再基于 Vue 包一层 DSL 而已,JSON Schema 的协议可以参考 Amis 的结构
- 但 Amis 的功能点较多,先实现==最小 MVP==
- ==amis 的事件流的设计很符合业务要求==